 W
WHMS Active was a 28-gun Coventry-class sixth-rate sailing frigate of the Royal Navy, launched in 1758. She was one of the captors of the Spanish ship Hermione. After Hermione surrendered, her captors found that she carried a large cargo of gold and silver that would lead to the greatest single amount of prize money awarded to the crew of a British warship.
 W
WAimable was an Alcmène-class 26-gun frigate of the French Navy.
 W
WHMS Ambuscade was a 32-gun fifth-rate frigate of the Royal Navy, built in the Grove Street shipyard of Adams & Barnard at Depford in 1773. The French captured her in 1798 but the British recaptured her in 1803. She was broken up in 1810.
 W
WAréthuse was a French frigate, launched in 1757 during the Seven Years' War. She was captured by the Royal Navy in 1759 and became the fifth-rate HMS Arethusa. She remained in Royal Navy service for twenty years until she was wrecked after being badly damaged in battle.
 W
WArtémise was a 32-gun Magicienne-class frigate of the French Navy.
 W
WThe Artémise was a 60-gun frigate of the French Navy, designed by Jean-Baptiste Hubert.
 W
WAstrée was a 44-gun Pallas-class frigate of the French Navy, launched at Cherbourg in 1809. In December of the next year she captured HMS Africaine. The Royal Navy captured Astrée in 1810 and took her into service under her French name, rating her as a 38-gun frigate, but then in 1811 recommissioned her as HMS Pomone. She served during the War of 1812 and was broken up in 1816.
 W
WHMS Belle Poule was a Royal Navy fifth-rate frigate, formerly Belle Poule, a Virginie-class frigate of the French Navy, which was built by the Crucy family's shipyard at Basse-Indre to a design by Jacques-Noël Sané. She was launched on 17 April 1802, and saw active service in the East, but in 1806 a British squadron under Sir John Borlase Warren captured her off La Palma in the Canary Islands. The Admiralty commissioned her into the Royal Navy as HMS Belle Poule. She was sold in 1816.
 W
WBelle-Poule was a Surveillante-class 60-gun first rank frigate of the French Navy. She achieved fame for bringing the remains of Napoleon from Saint Helena back to France, in what became known as the Retour des cendres.
 W
WBellone was a 44-gun Consolante-class frigate of the French Navy.
 W
WBordelois was a 56-gun ship of the line of the French Navy, lead ship of her class. She was funded by a don des vaisseaux donation from the city of Bordeaux, and built by engineer Léon Guignace on a design by Antoine Groignard. Complete too late to serve in the Seven Years' War, she was razéed into a frigate and used as an East Indiaman. She was rebuilt into a frigate to serve in the War of American Independence. Captured by HMS Romney, she was brought into British service as HMS Artois.
 W
WBoudeuse was a 26-gun, 12-pounder-armed sailing frigates named Boudeuse on 6 June 1765. She is most famous for being the exploration ship of Louis Antoine de Bougainville between 1766 and 1769. She also served in the American and French Revolutionary Wars, during which she captured two enemy vessels. She was broken up for firewood at Malta in early 1800.
 W
WCarrère was a French frigate that served briefly in the French navy before the British captured her in 1801, naming her HMS Carrere. She seems never to have seen any meaningful active duty after her capture as she was laid up in 1802 and finally sold in 1814.
 W
WCléopâtre was a 32-gun Vénus class frigate of the French Navy. She was designed by Jacques-Noël Sané, and had a coppered hull. She was launched in 1781, and the British captured her in 1793. She then served the Royal Navy as HMS Oiseau until she was broken up in 1816.
 W
WHMS Coventry was a 28-gun sixth-rate frigate of the Royal Navy, launched in 1757 and in active service as a privateer hunter during Seven Years' War, and as part of the British fleet in India during the Anglo-French War. After seventeen years' in British service she was captured by the French in 1783, off Ganjam in the Bay of Bengal. Thereafter she spent two years as part of the French Navy until January 1785 when she was removed from service at the port of Brest. She was broken up in 1786.
 W
WHMS Crescent was a 28-gun Enterprise-class sixth-rate frigate of the Royal Navy. Crescent was launched in 1779. The French captured her in 1781. She was wrecked in 1786.
 W
WDescartes was a wooden-hulled paddle frigate of the French Navy. Laid down as Gomer, she was renamed Descartes in 1841 while still on the stocks.
 W
WDiana was a 54-gun frigate of the Portuguese Navy. She was captured at the Battle of the Tagus and incorporated in the French Navy as Diane.
 W
WThe Didon was a 60-gun Dryade-class first rank frigate of the French Navy.
 W
WEmbuscade ("Ambush") was a 32-gun frigate. She served in the French Navy during the War of the First Coalition before being captured by the British. Renamed HMS Ambuscade and later HMS Seine, she participated in the Napoleonic Wars in the Royal Navy. She was broken up in 1813.
 W
WEngageante was a 26-gun frigate of the French Navy, only ship of her class, built to a design by Jean-François Etienne. The British captured her in 1794 and converted her to a hospital ship. She served as a hospital ship until she was broken up in 1811.
 W
WFranchise was launched in 1798 as a 40-gun Coquille-class frigate of the French Navy. The British captured her in 1803 and took her into the Royal Navy under her existing name. In the war on commerce during the Napoleonic Wars she was more protector than prize-taker, capturing many small privateers but apparently few commercial prizes. She was also at the battle of Copenhagen. She was broken up in 1815.
 W
WThe FREMM is a class of multi-purpose frigates designed by Naval Group and Fincantieri for the navies of France and Italy. The lead ship of the class, Aquitaine, was commissioned in November 2012 by the French Navy. In France the class is known as the Aquitaine class, while in Italy they are known as the Bergamini class. Italy has ordered six general purpose variants and four anti-submarine variants. France has ordered six anti-submarine variants, and two air-defense variants. The US Navy selected the class to fulfill the FFG(X) requirement, and Fincantieri was given a $795 million contract for the lead ship.
 W
WGomer was a paddle frigate of the French Navy, lead ship of her class.
 W
WGracieuse was a 32-gun Charmante-class frigate of the French Navy. Renamed to Unité in 1793, she took part in the French Revolutionary Wars. The Royal Navy captured her in 1796 off Île d'Yeu and brought her into British service as HMS Unite. She was sold in 1802
 W
WHMS Guadeloupe, was a 28-gun sixth-rate Coventry-class frigate of the Royal Navy. The ship was designed by Sir Thomas Slade, and was initially contracted to be built with the Pembrokeshire shipwright John Williams of Neyland; however he became bankrupt and the Admiralty transferred the order to the Plymouth Naval Dockyard.
 W
WIndien (1778), often L'Indien, was a frigate built for the U.S. Commissioners in France – Benjamin Franklin, Silas Deane, and Arthur Lee – to a design by the French naval architect Jacques Boux. She was laid down early in 1777 by a private shipyard in Amsterdam and launched in February 1778. Apparently she was built with the scantlings and lines of a small 74-gun Third Rate ship of the line but was a frigate in construction. In 1780 the Duke of Luxembourg chartered her to the navy of South Carolina and she sailed as South Carolina.
 W
WL'Insurgente was a 40-gun Sémillante-class frigate of the French Navy, launched in 1793. During the Quasi War with the United States, the United States Navy frigate USS Constellation, with Captain Thomas Truxtun in command, captured her off the island of Nevis. After her capture she served in the United States Navy as USS Insurgent, patrolling the waters in the West Indies. In September 1800 she was caught up in a severe storm and was presumed lost at sea.
 W
WHMS Iphigenia was a Royal Navy 36-gun Perseverance-class fifth-rate frigate. She was built at Chatham Dockyard by Master Shipwright Robert Seppings.
 W
WThe French frigate Iphigénie was a Pallas-class frigate of a nominal 44 guns, launched in 1810. The British captured her in 1814. The British named her HMS Palma, and then renamed her HMS Gloire. She was sold in 1817, never having been commissioned into the Royal Navy.
 W
WThe French frigate Iphigénie was a first rank frigate of the French Navy. Launched in Toulon in 1827, she took part in the Battle of Veracruz, and was eventually broken up in 1900.
 W
WThe French frigate Iris was a Magicienne-class frigate, one of seven, launched at Toulon in 1781 for the French Navy. Note: Between 1781 and 1784, there were two French frigates Iris, this newly launched frigate, and the former USS Hancock, which the British had captured in 1781 in the American theatre and renamed Iris, and which the French had captured in 1781 and sold in 1784. The British captured the new Iris at Toulon on 28 August 1793, and burned her on their evacuation of the city in December.
 W
WLoire was a 38-gun frigate of the French Navy. She was captured following the Battle of Tory Island by a Royal Navy frigate squadron and subsequently taken into British service as HMS Loire.
 W
WHMS Madagascar was a 38-gun Piémontaise-class frigate originally of the French Navy. Her French name had been Néréide, and she had been built to a design by François Pestel.
 W
WHMS Melpomene was a 38-gun frigate of the Royal Navy. Originally a French vessel, she was captured at Calvi on 10 August 1794 and first saw British service in the English Channel, where she helped to contain enemy privateering. In October 1798, she chased a French frigate squadron sent to find the French fleet under Jean-Baptiste-François Bompart, that was routed at the Battle of Tory Island and in August 1799, she joined Andrew Mitchell's squadron for the Anglo-Russian invasion of Holland.
 W
WMelpomène was a Surveillante class 60-gun first rank frigate of the French Navy.
 W
WHMS Milan was a 38-gun fifth rate frigate of the Royal Navy. She had previously been Ville de Milan, a 40-gun frigate of the French Navy, but served for only a year before being chased down and engaged by the smaller 32-gun frigate HMS Cleopatra. Ville de Milan defeated and captured her opponent, but suffered so much damage that she was forced to surrender without a fight several days later when both ships encountered HMS Leander, a British fourth rate. Milan went on to serve with the Royal Navy for another ten years, before being broken up in 1815, after the conclusion of the Napoleonic Wars.
 W
WMinerve was a 40-gun Minerve-class frigate of the French Navy. The British captured her twice and the French recaptured her once. She therefore served under four names before being broken up in 1814:Minerve, 1794–1795 HMS Minerve, 1795–1803 Canonnière, 1803–1810 HMS Confiance, 1810–1814
 W
WMinerve was the 48-gun Portuguese Navy frigate Nossa Senhora da Vitória, a Minerva, launched in 1788. The French captured her in November 1809 off India and took her into service as Minerve. The British captured her shortly thereafter and had her broken up.
 W
WMinerve was a Téméraire-class 74-gun ship of the line, later razeed and commissioned as a frigate. Started during the Empire, she was launched during the Bourbon Restoration, rebuilt during the reign of Louis-Philip, and served as a gunnery school through the French Second Republic and the Second French Empire, only to be broken up shortly after the advent of the French Third Republic.
 W
WHMS Modeste was a 36-gun fifth rate frigate of the Royal Navy. She had previously been a ship of the French Navy under the name Modeste. Launched in France in 1786, she served during the first actions of the French Revolutionary Wars until being captured while in harbour at Genoa, in circumstances disputed by the French and British, and which created a diplomatic incident. Taken into British service she spent the rest of the French Revolutionary and most of the Napoleonic Wars under the white ensign. She served with distinction in the East Indies, capturing several privateers and enemy vessels, including the French corvette Iéna. She also saw service in a variety of roles, as a troopship, a receiving ship, and a floating battery, until finally being broken up in 1814, as the Napoleonic Wars drew to a close.
 W
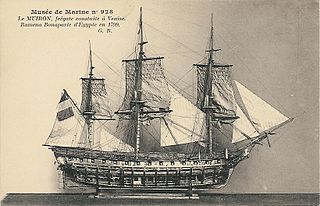
WMuiron was a frigate of the French Navy, famous for ferrying Bonaparte on the 22 August 1799 under the flagship of Admiral Ganteaume from Egypt to France after the Battle of the Nile.
 W
WThe French frigate Némésis was an Artémise class screw-powered 50-gun second rate frigate of the French Navy in the 19th century. She was launched in 1847 at Brest, and participated in campaigns in Asia.
 W
WHMS Madagascar was a 38-gun Piémontaise-class frigate originally of the French Navy. Her French name had been Néréide, and she had been built to a design by François Pestel.
 W
WThe Pélican was a French warship from the late 17th century. Built in Bayonne, France, the original Pélican was launched in January 1693. A 500-ton ship fitted with 50 guns and commanded by Captain Pierre Le Moyne d'Iberville, she ran aground on the shores of Hudson Bay a few days after a heroic battle in 1697, badly damaged by the encounter and by a fierce storm. In five short months the ship's place in history had been assured, as the victor in the greatest naval battle in the history of New France.
 W
WThe Piémontaise was a 40-gun Consolante-class frigate of the French Navy. She served as a commerce raider in the Indian Ocean until her capture in March 1808. She then served with the British Royal Navy in the East Indies until she was broken up in Britain in 1813.
 W
WHMS Pique was a 38-gun fifth rate frigate of the Royal Navy. She had formerly served with the French Navy, initially as the Fleur-de-Lys, and later as the Pique. HMS Blanche captured her in 1795 in a battle that left the Blanche's commander, Captain Robert Faulknor, dead. HMS Pique was taken into service under her only British captain, David Milne, but served for just three years with the Royal Navy before being wrecked in an engagement with the French ship Seine in 1798. The Seine had been spotted heading for a French port and Pique and another British ship gave chase. All three ships ran aground after a long and hard-fought pursuit. The arrival of a third British ship ended French resistance, but while the Seine and Jason were both refloated, attempts to save Pique failed; she bilged and had to be abandoned.
 W
WPsyché was a 36-gun vessel built between February 1798 and 1799 at Basse-Indre (Nantes) as a privateer. As a privateer she had an inconclusive but bloody encounter with HMS Wilhelmina of the Royal Navy, commanded by Commander Henry Lambert, off the Indian coast in April 1804. The French then brought her into service in June 1804 as the frigate Psyché. In February 1805 she encountered San Fiorenzo, under the command of the same Henry Lambert, now an acting captain. After a sanguinary engagement of over three hours, Psyché surrendered. The British took her into service as HMS Psyche. In British service she captured several prizes and took part in the capture of Mauritius and in an operation in Java. She was broken up at Ferrol in 1812.
 W
WThe Railleuse was an 18-gun frigate of the French Navy, launched in 1689.
 W
WHMS Java was a British Royal Navy 38-gun fifth-rate frigate. She was originally laid down in 1805 as Renommée, described as a 40-gun Pallas-class French Navy frigate, but the vessel actually carried 46 guns. The British captured her in 1811 in a noteworthy action during the Battle of Tamatave, but she is most famous for her defeat on 29 December 1812 in a three-hour single-ship action against USS Constitution. Java had a crew of about 277 but during her engagement with Constitution her complement was 475.
 W
WLa Réunion was a 36-gun French warship launched in 1786. During the French Revolutionary War she was stationed at Cherbourg and was successfully employed harassing British merchant shipping in the English Channel until the British captured her off the Cotentin Peninsula during the action of 20 October 1793. Renamed HMS Reunion, she served for three years in the Royal Navy helping to counter the threat from the new Batavian Navy, before she was wrecked in the Thames Estuary in December 1796.
 W
WMinerve was a 40-gun frigate of the French Navy, lead ship of her class. She operated in the Mediterranean during the French Revolutionary Wars. Her crew scuttled her at Saint-Florent to avoid capture when the British invaded Corsica in 1794, but the British managed to raise her and recommissioned her in the Royal Navy as the 38-gun fifth rate HMS St Fiorenzo.
 W
WHMS Thames was a 32-gun Richmond-class fifth-rate frigate of the Royal Navy built by Henry Adams and launched at Bucklers Hard in 1758. She served in several wars, including for some four years in French service after her capture. She was recaptured in 1796 and was broken up in 1803.
 W
WThe French frigate Trave was a Pallas-class frigate of the French Navy, launched at Amsterdam in 1812. After the Royal Navy captured her in 1813 in the North Sea, it took her into service as the troopship HMS Trave. She served in the Potomac and her boats participated in the Battle of Lake Borgne during the War of 1812. She was sold on 7 June 1821.
 W
WUranie was a frigate of the French Navy launched in 1788. She took part in a frigate action in 1793, capturing HMS Thames, and was renamed Tartu in honour of her captain, Jean-François Tartu, who was killed in the action. The Royal Navy captured her in 1797. She served as HMS Uranie until the Royal Navy sold her in 1807.
 W
WThe Vénus was a 32-gun frigate of the French Navy, lead ship of her class.
 W
WVertu was a 40-gun French frigate designed by engineer Segondat. She served in Sercey's squadron in the Indian Ocean, and in Saint-Domingue. She was captured by the Royal Navy at the end of the Blockade of Saint-Domingue when the island surrendered to the British. After her capture the Navy sailed her to Britain but never commissioned her, and finally sold her in 1810.