 W
WIn the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, the South American nations of Argentina and Chile engaged in an expensive naval arms race to ensure the other would not gain supremacy in the Southern Cone.
 W
WThe Battle of Tocarema was a battle fought between an alliance of the troops of Spanish conquistador Gonzalo Jiménez de Quesada and zipa of the Muisca Sagipa of the southern Muisca Confederation and the indigenous Panche. The battle took place on the afternoon of August 19 and the morning of August 20, 1538 in the vereda Tocarema of Cachipay, Cundinamarca, Colombia and resulted in a victory for the Spanish and Muisca, when captains Juan de Céspedes and Juan de Sanct Martín commanded two flanks of the conquistadors.
 W
WThe Battle of Chocontá was one of a series of battles in the ongoing conflict between the northern and southern Muisca of pre-Columbian central Colombia. The battle was fought c. 1490 in the vicinity of Chocontá. An army of 50,000 southern Muisca guecha warriors, led by their ruler, or zipa, Saguamanchica, attacked 60,000 northern Muisca troops commanded by Zaque Michuá, who was supported by the Cacique of Guatavita.
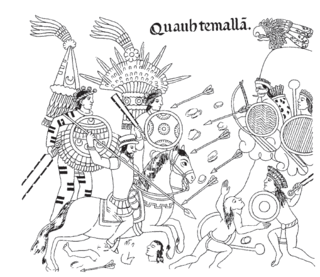 W
WIndian auxiliaries or indios auxiliares is the term used in old Spanish chronicles and historical texts for the indigenous peoples who were integrated into the armies of the Spanish conquistadors with the purpose of supporting their advance and combat operations during the Conquest of America. They acted as guides, translators, or porters and in this role were also called yanakuna, particularly within the old Inca Empire and Chile. The term was also used for formations composed of indigenous warriors or Indios amigos, which they used for reconnaissance, combat, and as reserve in battle. The auxiliary Indians remained in use after the conquest, during some revolts, in border zones and permanent military areas, as in Chile in the Arauco War.
 W
WThe Paraguayan War, also known as the War of the Triple Alliance was a South American war fought from 1864 to 1870, between Paraguay and the Triple Alliance of Argentina, the Empire of Brazil, and Uruguay. It was the deadliest and bloodiest inter-state war in Latin America's history. It particularly devastated Paraguay, which suffered catastrophic losses in population, and it was forced to cede territory in dispute with Argentina and Brazil.
 W
WThe Battle of Pasca was fought between the southern Muisca Confederation, led by their zipa (ruler), Saguamanchica, and an alliance between the Panche and the Sutagao, led by the Cacique of Fusagasugá. The battle took place c. 1470 in the vicinity of Pasca, in modern-day Cundinamarca, Colombia, and resulted in a victory for Saguamanchica.
 W
WA naval arms race among Argentina, Brazil and Chile—the most powerful and wealthy countries in South America—began in the early twentieth century when the Brazilian government ordered three dreadnoughts, formidable battleships whose capabilities far outstripped older vessels in the world's navies.
 W
WThe history of Latin America during World War II is important because of the significant economic, political, and military changes that occurred throughout much of the region as a result of the war. The war caused significant panic in Latin America over economics as a large portions of economy of the region depended on the European investment capital, which was shut down. Latin America tried to stay neutral but the warring countries were endangering their neutrality. Most countries used propaganda to turn the neutral countries to their side, while Berlin wanted Latin America neutral. In order to better protect the Panama Canal, combat Axis influence, and optimize the production of goods for the war effort, the United States through Lend-Lease and similar programs greatly expanded its interests in Latin America, resulting in large-scale modernization and a major economic boost for the countries that participated.