 W
WThe military history of South America can be divided into two major periods - pre- and post-Columbian - divided by the entrance of European forces to the region. The sudden introduction of steel, gunpowder weapons and horses into the Americas would revolutionize warfare. Within the post-Columbian period, the events of the early 19th century, when almost all of South America was marked by wars of independence, also forms a natural historical juncture. Throughout its history, South America has had distinct military features: it has been geographically separated from many major military powers by large oceans; its unique terrain has imposed major logistical challenges, and privileged naval lines of communications.
 W
WThe American Theater was a theater of operations during World War II including all continental American territory, and extending 200 miles (320 km) into the ocean.
 W
WThe British Legion or British Legions were foreign volunteer units that fought under Simón Bolívar against Spain for the independence of Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador and José de San Martín for the independence of Peru in the Spanish American wars of independence. Venezuelans generally called them the Albion Legion. They were composed of over seven thousand volunteers, mainly Napoleonic War veterans from Great Britain and Ireland, as well as some German veterans and some locals recruited after arriving in South America. Volunteers in the British Legion were motivated by a combination of both genuine political motives and mercenary motives.
 W
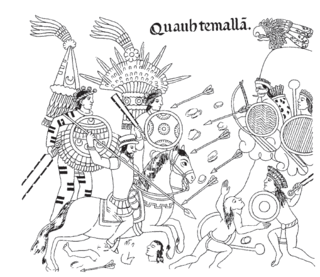
WIndian auxiliaries or indios auxiliares is the term used in old Spanish chronicles and historical texts for the indigenous peoples who were integrated into the armies of the Spanish conquistadors with the purpose of supporting their advance and combat operations during the Conquest of America. They acted as guides, translators, or porters and in this role were also called yanakuna, particularly within the old Inca Empire and Chile. The term was also used for formations composed of indigenous warriors or Indios amigos, which they used for reconnaissance, combat, and as reserve in battle. The auxiliary Indians remained in use after the conquest, during some revolts, in border zones and permanent military areas, as in Chile in the Arauco War.
 W
WMalón is the name given to plunder raids carried out by Mapuche warriors, who rode horses into Spanish, Chilean and Argentine territories from the 17th to the 19th centuries, as well as to their attacks on rival Mapuche factions. Historian Juan Ignacio Molina said the Mapuche considered the malón to be a means of obtaining justice:The injured family often assumes the right of pursuing the aggressor or his relations, and of punishing them. From this abuse are derived the denominations and distinctions, so much used in their jurisprudence, of genguerin, genguman, gerila, &c. denoting the principal connections of the aggressor, of the injured, or the deceased, who are supposed to be authorized, by the laws of nature, to support by force the rights of their relatives. When those who are at enmity have a considerable number of adherents, they mutually make incursions upon each other's possessions, where they destroy or burn all that they cannot carry off. These private quarrels, called malones, resemble much the feuds of the ancient Germans, and are very dreadful when the Ulmenes are concerned, in which case they become real civil wars. But it must be acknowledged that they are generally unaccompanied with the effusion of blood, and are confined to pillage alone. This people, notwithstanding their propensity to violence, rarely employ arms in their private quarrels, but decide them with the fist or with the club.
 W
WThe Paraguayan War, also known as the War of the Triple Alliance was a South American war fought from 1864 to 1870, between Paraguay and the Triple Alliance of Argentina, the Empire of Brazil, and Uruguay. It was the deadliest and bloodiest inter-state war in Latin America's history. It particularly devastated Paraguay, which suffered catastrophic losses in population, and it was forced to cede territory in dispute with Argentina and Brazil.
 W
WThe number of people who died in the Paraguayan War (1864–1870) is unknown. Widely diverging estimates have been made. "Determining the size of Paraguay's population has always been an exercise in frustration." However, there is a widespread impression that the casualties were immense; there was also some population loss from non-lethal causes such as migration. The Dutch human geographer Jan Kleinpenning thought that Paraguay lost between a quarter and a half of its population, but much higher and lower estimates have been made. No academic demographic scholarship makes it less than 7% or greater than 69%.
 W
WA naval arms race among Argentina, Brazil and Chile—the most powerful and wealthy countries in South America—began in the early twentieth century when the Brazilian government ordered three dreadnoughts, formidable battleships whose capabilities far outstripped older vessels in the world's navies.