 W
WAcanthocephalus is a genus of parasitic worms. One of the species in this genus is Acanthocephalus anguillae, a fish parasite. Acanthocephalans are also found in humans and primates, causing a common zoonotic infection called "human acanthocephaliasis". While pathogens can be transferred among animals and humans, the main source of human acanthocephaliasis is the diet of infected raw fish and insects.
 W
WCorynosoma is a genus of parasitic worms belonging to the family Polymorphidae.
 W
WEchinorhynchida is an order of parasitic worms in the phylum Acanthocephala. It contains the following families:Arhythmacanthidae Yamaguti, 1935 Cavisomidae Meyer, 1932 Diplosentidae Tubangui and Masiluñgan, 1937 Echinorhynchidae Cobbold, 1876 Fessisentidae Van Cleave, 1931 Gymnorhadinorhynchidae Braicovich, Lanfranchi, Farber, Marvaldi, Luque and Timi, 2014 Heteracanthocephalidae Petrochenko, 1956 Illiosentidae Golvan, 1960 Isthmosacanthidae Smales, 2012 Pomphorhynchidae Yamaguti, 1939 Rhadinorhynchidae Lühe, 1912 Sauracanthorhynchidae Bursey, Goldberg and Kraus, 2007 Transvenidae Pichelin and Cribb, 2001
 W
WEoacanthocephala is a class of parasitic worms, within the phylum Acanthocephala. They feed on any aquatic cold-blooded creature such as turtles and fish. Their proboscis spines arranged radially, no protonephridia, persistent ligament sacs in female. The only reliable way to identify the group is that they only have one cement gland. This is a primitive characteristic and hence the name. The class contains 2 orders:Gyracanthocephala Van Cleave, 1936 Neoechinorhynchida Southwell and Macfie, 1925
 W
WMacracanthorhynchus, also known as the giant thorny-headed worm of swine, is a member of the Oligacanthorhynchidae which contains many species. One species, M. hirudinaceus, is a parasite which lives in the intestines of pigs and other suids, and very occasionally in humans or dogs. It causes enteritis, gastritis or peritonitis. Its life cycle includes beetles of the genus Melolontha as intermediate hosts. This species has many synonyms which include: Echinorhynchus gigas, Macracanthorhynchus gigas, Echinorhynchus hirundinacea, Gigantorhynchus hirundinaceus, Gigantorhynchus gigas, Hormorhynchus gigas, Taenia haeruca, and Taenia hirundinaceus The complete mitochondrial genome of M. hirudinaceus has been sequenced. The eggs have 4 membranes are 98 um long and have an elongation ratio of 1.85.
 W
WNeoandracantha is a genus of parasitic worms from the phylum Acanthocephala. The genus was created in 2017 by Amin & Heckmann for the single species Neoandracantha peruensis.
 W
WNeoechinorhynchida is an order of parasitic worms from the. It contains 3 families:Dendronucleatidae Sokolovskaja, 1962 Neoechinorhynchidae Ward, 1917 Tenuisentidae Van Cleave, 1936
 W
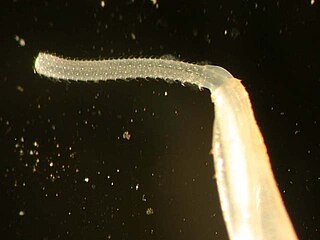
WPalaeacanthocephala is a class within the phylum Acanthocephala. The adults of these parasitic platyzoans feed mainly on fish, aquatic birds and mammals. This order is characterized by the presence of lateral longitudinal lacunar canals and a double-walled proboscis receptacle. The nuclei of the hypodermis are fragmented and the males have two to seven cement glands, unlike their relatives the Archiacanthocephala which always have eight.
 W
WPolymorphida are an order of thorny-headed worms. The adults of these parasitic platyzoans feed mainly on fish and aquatic birds.
 W
WTelosentis is a genus of acanthocephalans. The representatives of the genus are distributed in tropical waters of Indian ocean, Pacific coast of Australia and Mediterranean. Consists of four species:Telosentis australiensis Edmond, 1964 Telosentis exiguus Telosentis lutianusi Gupta & Gupta, 1990 Telosentis mizellei Gupta & Fatma, 1988