 W
WAntlers are extensions of an animal's skull found in members of the deer family. Antlers are a single structure composed of bone, cartilage, fibrous tissue, skin, nerves, and blood vessels. They are generally found only on males, with the exception of the reindeer/caribou. Antlers are shed and regrown each year and function primarily as objects of sexual attraction and as weapons in fights between males for control of harems.
 W
WArtificial bone refers to bone-like material created in a laboratory that can be used in bone grafts, to replace human bone that was lost due to severe fractures, disease, etc.
 W
WBone char is a porous, black, granular material produced by charring animal bones. Its composition varies depending on how it is made; however, it consists mainly of tricalcium phosphate 57–80%, calcium carbonate 6–10% and carbon 7–10%. It is primarily used for filtration and decolorisation.
 W
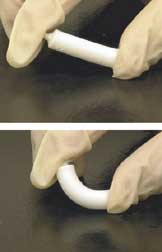
WA bone folder, bonefolder, or folding bone is a dull-edged hand tool used to fold and crease material in crafts such as bookbinding, cardmaking, origami, and other paper crafts that require a sharp crease or fold. The tool was also used when correspondence by letter writing was more formal and an art.
 W
WThe Ishango bone is a bone tool and possible mathematical object, dated to the Upper Paleolithic era. It is a dark brown length of bone, the fibula of a baboon, with a sharp piece of quartz affixed to one end, perhaps for engraving. It is thought by some to be a tally stick, as it has a series of what has been interpreted as tally marks carved in three columns running the length of the tool, though it has also been suggested that the scratches might have been to create a better grip on the handle or for some other non-mathematical reason. It has also been argued that the marks on the object are non-random and that it was likely a kind of counting tool and used to perform simple mathematical procedures.
 W
WBone mineral is the inorganic component of bone tissue. It gives bones their compressive strength. Bone mineral is formed from carbonated hydroxyapatite with lower crystallinity.
 W
WMineralized tissues are biological tissues that incorporate minerals into soft matrices. Typically these tissues form a protective shield or structural support. Bone, mollusc shells, deep sea sponge Euplectella species, radiolarians, diatoms, antler bone, tendon, cartilage, tooth enamel and dentin are some examples of mineralized tissues.
 W
WNeatsfoot oil is a yellow oil rendered and purified from the shin bones and feet of cattle. "Neat" in the oil's name comes from an Old English word for cattle. Neatsfoot oil is used as a conditioning, softening and preservative agent for leather. In the 18th century, it was also used medicinally as a topical application for dry scaly skin conditions.
 W
WA tabua is a polished tooth of a sperm whale that is an important cultural item in Fijian society. They were traditionally given as gifts for atonement or esteem, and were important in negotiations between rival chiefs. The dead men would be buried with their tabua, along with war clubs and even their strangled wives, to help them in the afterlife. Originally they were very rare items, available only from beached whales and from trade from neighbouring Tonga, but when the market became known in the early 19th century thousands of teeth, and fake teeth made from ivory and walrus tusks entered the market. This trade led to the development of the European art of scrimshaw.
 W
WTusks are elongated, continuously growing front teeth that protrude well beyond the mouth of certain mammal species. They are most commonly canine teeth, as with pigs, hippos, and walruses, or, in the case of elephants, elongated incisors. In most tusked species both the males and the females have tusks although the males' are larger. Most mammals with tusks have a pair of them growing out from either side of the mouth. Tusks are generally curved and have a smooth, continuous surface. The narwhal's straight single helical tusk, which grows out from the center of the mouth and is present only in the male, is an exception to the typical features of tusks described above. Continuous growth of tusks is enabled by formative tissues in the apical openings of the roots of the teeth. Prior to over hunting and proliferation of the ivory trade, elephant tusks weighing over 90 kg (200 lb) were not uncommon, though it is rare today to see any over 45 kg (100 lb).
 W
WYanik Tepe is a Chalcolithic and Bronze Age archaeological site in East Azarbaijan, Iran.