 W
WHuman impact on the environment or anthropogenic impact on the environment includes changes to biophysical environments and ecosystems, biodiversity, and natural resources caused directly or indirectly by humans, including global warming, environmental degradation, mass extinction and biodiversity loss, ecological crisis, and ecological collapse. Modifying the environment to fit the needs of society is causing severe effects, which become worse as the problem of human overpopulation continues. Some human activities that cause damage to the environment on a global scale include population growth, overconsumption, overexploitation, pollution, and deforestation, to name but a few. Some of the problems, including global warming and biodiversity loss pose an existential risk to the human race, and human overpopulation is strongly correlated with those problems.
 W
WHydraulic fracturing, also called fracking, fracing, hydrofracking, fraccing, frac'ing, and hydrofracturing, is a well stimulation technique involving the fracturing of bedrock formations by a pressurized liquid. The process involves the high-pressure injection of 'fracking fluid' into a wellbore to create cracks in the deep-rock formations through which natural gas, petroleum, and brine will flow more freely. When the hydraulic pressure is removed from the well, small grains of hydraulic fracturing proppants hold the fractures open.
 W
WIndustrialisation is the period of social and economic change that transforms a human group from an agrarian society into an industrial society. This involves an extensive re-organisation of an economy for the purpose of manufacturing. Historically industrialization is associated with increase of polluting industries heavily dependent on fossil fuels; however, with the increasing focus on sustainable development and green industrial policy practices, industrialization increasingly includes technological leapfrogging, with direct investment in more advanced, cleaner technologies.
 W
WLand degradation is a process in which the value of the biophysical environment is affected by a combination of human-induced processes acting upon the land. It is viewed as any change or disturbance to the land perceived to be deleterious or undesirable. Natural hazards are excluded as a cause; however human activities can indirectly affect phenomena such as floods and bush fires.
 W
WA lawn is an area of soil-covered land planted with grasses and other durable plants such as clover which are maintained at a short height with a lawnmower and used for aesthetic and recreational purposes. Lawns are usually composed only of grass species, subject to weed and pest control, maintained in a green color, and are regularly mowed to ensure an acceptable length. Lawns are used around houses, apartments, commercial buildings and offices. Many city parks also have large lawn areas. In recreational contexts, the specialised names turf, pitch, field or green may be used, depending on the sport and the continent.
 W
WLogistics is generally the detailed organization and implementation of a complex operation. In a general business sense, logistics is the management of the flow of things between the point of origin and the point of consumption to meet the requirements of customers or corporations. The resources managed in logistics may include tangible goods such as materials, equipment, and supplies, as well as food and other consumable items. The logistics of physical items usually involves the integration of information flow, materials handling, production, packaging, inventory, transportation, warehousing, and often security.
 W
WOff-roading is the activity of driving or riding a vehicle on unsurfaced roads or tracks, made of materials such as sand, gravel, riverbeds, mud, snow, rocks, and other natural terrain. Types of off-roading range in intensity, from leisure drives with unmodified vehicles to competitions with customized vehicles and professional drivers. Off-roaders have been met with criticism for the environmental damage caused by their vehicles. There have also been extensive debates over the role of government in regulating the sport, including a Supreme Court case brought against the Bureau of Land Management.
 W
WOverconsumption is a situation where resource use has outpaced the sustainable capacity of the ecosystem. A prolonged pattern of overconsumption leads to environmental degradation and the eventual loss of resource bases.
 W
WSoil conservation is the prevention of loss of the top most layer of the soil from erosion or prevention of reduced fertility caused by over usage, acidification, salinization or other chemical soil contamination.
 W
WUrban ecology is the scientific study of the relation of living organisms with each other and their surroundings in the context of an urban environment. The urban environment refers to environments dominated by high-density residential and commercial buildings, paved surfaces, and other urban-related factors that create a unique landscape dissimilar to most previously studied environments in the field of ecology. The goal of urban ecology is to achieve a balance between human culture and the natural environment.
 W
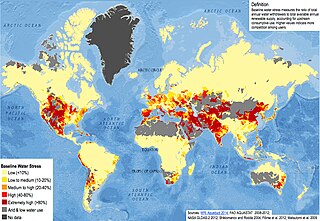
WWater scarcity is the lack of fresh water resources to meet the standard water demand. Water scarcity can also be caused by droughts, lack of rainfall, or pollution. This was listed in 2019 by the World Economic Forum as one of the largest global risks in terms of potential impact over the next decade. It is manifested by partial or no satisfaction of expressed demand, economic competition for water quantity or quality, disputes between users, irreversible depletion of groundwater, and negative impacts on the environment. Two-thirds of the global population live under conditions of severe water scarcity at least 1 month of the year. Half a billion people in the world face severe water scarcity all year round. Half of the world's largest cities experience water scarcity.