 W
WOwls are birds from the order Strigiformes, which includes over 200 species of mostly solitary and nocturnal birds of prey typified by an upright stance, a large, broad head, binocular vision, binaural hearing, sharp talons, and feathers adapted for silent flight. Exceptions include the diurnal northern hawk-owl and the gregarious burrowing owl.
 W
WAn owl hole is a structural entrance built into buildings to allow predatory birds, typically Barn Owls, to enter. The birds prey on farm vermin, and therefore benefit the human owner of the structure in a symbiotic relationship.
 W
WThis list is not comprehensive, as not all Strigiformes have had their numbers quantified. For a simple list of all owl species, see the article "List of owl species".
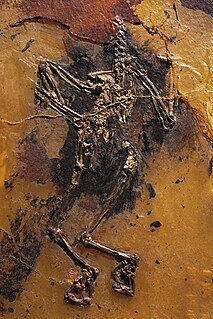 W
WPalaeoglaux is a genus of fossil owls from the Eocene epoch. The two known species are P. perrierensis from the Upper Eocene of Quercy, France, and P. artophoron from the Middle Eocene Messel shales, Germany. The holotype of P. perrierensis is a partial left coracoid in the Collection Université Montpellier, accession number PRR 2585. The four paratypes are the distal part of a left humerus (PRR2591), the proximal part of a left ulna, the distal part of a left ulna, and the distal part of a right tarsometatarsus. The type specimen of P. artophoron is a fossil slab and counterslab containing most of the postcranial skeleton and some feather impressions. This specimen is in the collection of the Forschunginstitut Senckenberg, accession number SMF-ME 1144 A and B.
 W
WBarn-owls are one of the two families of owls, the other being the true owls or typical owls, Strigidae. They are medium to large owls with large heads and characteristic heart-shaped faces. They have long, strong legs with powerful talons. They also differ from the Strigidae in structural details relating in particular to the sternum and feet.
 W
WThe Deutsche Arbeitsgemeinschaft zum Schutz der Eulen , translated German Association for the Protection of Owls, is a nationwide conservation organization that deals with the study and conservation of owls. The Owls Working Group (OWG) is a registered nonprofit association. It sees itself as an association of German-language owl experts. In addition to individuals, membership is open to groups, clubs, associations and institutions.
 W
WIn ornithology, the facial disc is the concave collection of feathers on the face of some birds—most notably owls—surrounding the eyes. The concavity of the facial disc forms a circular paraboloid that collects sound waves and directs those waves towards the owl's ears. The feathers making up this disc can be adjusted by the bird to alter the focal length of this sound collector, enabling the bird to focus at different distances and allowing it to locate prey by sound alone under snow, grass, and plant cover.
 W
WIn Greek mythology, a little owl traditionally represents or accompanies Athena, the virgin goddess of wisdom, or Minerva, her syncretic incarnation in Roman mythology. Because of such association, the bird – often referred to as the "owl of Athena" or the "owl of Minerva" – has been used as a symbol of knowledge, wisdom, perspicacity and erudition throughout the Western world.
 W
WThe Sophiornithidae are an extinct family of chicken-sized predatory birds that lived from the Paleocene to the Eocene periods of the Cenozoic, and were found primarily in Europe, and are thought to be primitive owls.
 W
WMost owls are nocturnal or crepuscular birds of prey. Because they hunt at night, they must rely on non-visual senses. Experiments by Roger Payne have shown that owls are sensitive to the sounds made by their prey, not the heat or the smell. In fact, the sound cues are both necessary and sufficient for localization of mice from a distant location where they are perched. For this to work, the owls must be able to accurately localize both the azimuth and the elevation of the sound source.
 W
WThe true owls or typical owls are one of the two generally accepted families of owls, the other being the barn owls (Tytonidae). The Sibley-Ahlquist taxonomy unites the Caprimulgiformes with the owl order; here, the typical owls are a subfamily Striginae. This is unsupported by more recent research, but the relationships of the owls in general are still unresolved. This large family comprises nearly 220 living species in 25 genera. The typical owls have a cosmopolitan distribution and are found on every continent except Antarctica. There are three accepted subfamilies of Strigidae including Striginae, Asioninae, and Surniinae.