 W
WThe environmental effects of pesticides describe the broad series of consequences of using pesticides. The unintended consequences of pesticides is one of the main drivers of the negative impact of modern industrial agriculture on the environment. Pesticides, because they are toxic chemicals meant to kill pest species, can effect non-target species, such as plants, animals and humans. Over 98% of sprayed insecticides and 95% of herbicides reach a destination other than their target species, because they are sprayed or spread across entire agricultural fields. Other agrochemicals, such as fertilizers, can also have negative effects on the environment.
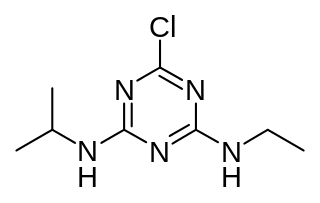 W
WAtrazine is a herbicide of the triazine class. It is used to prevent pre-emergence broadleaf weeds in crops such as maize (corn) and sugarcane and on turf, such as golf courses and residential lawns. Atrazine's primary manufacturer is Syngenta and it is one of the most widely used herbicides in the United States and Australian agriculture.
 W
WAttractive toxic sugar baits or ATSBs are oral insecticides designed to reduce malaria infections by killing the host vector - the mosquito - rather than the parasite itself.
Bees can suffer serious effects from toxic chemicals in their environments. These include various synthetic chemicals, particularly insecticides, as well as a variety of naturally occurring chemicals from plants, such as ethanol resulting from the fermentation of organic materials. Bee intoxication can result from exposure to ethanol from fermented nectar, ripe fruits, and manmade and natural chemicals in the environment.
 W
WDichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane, commonly known as DDT, is a colorless, tasteless, and almost odorless crystalline chemical compound, an organochloride. Originally developed as an insecticide, it became infamous for its environmental impacts. DDT was first synthesized in 1874 by the Austrian chemist Othmar Zeidler. DDT's insecticidal action was discovered by the Swiss chemist Paul Hermann Müller in 1939. DDT was used in the second half of World War II to limit the spread of the insect-born diseases malaria and typhus among civilians and troops. Müller was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1948 "for his discovery of the high efficiency of DDT as a contact poison against several arthropods".
 W
W1,2-Dibromo-3-chloropropane, (dibromochloropropane) better known as DBCP, is the organic compound with the formula BrCH(CH2Br)(CH2Cl). It is a dense colorless liquid although commercial samples often appear amber or even brown. It is the active ingredient in the nematicide Nemagon, also known as Fumazone.
 W
WGlobal distillation or the grasshopper effect is the geochemical process by which certain chemicals, most notably persistent organic pollutants (POPs), are transported from warmer to colder regions of the Earth, particularly the poles and mountain tops. Global distillation explains why relatively high concentrations of POPs have been found in the Arctic environment and in the bodies of animals and people who live there, even though most of the chemicals have not been used in the region in appreciable amounts.
 W
WThe light brown apple moth is a leafroller moth belonging to the lepidopteran family Tortricidae. The moth was confirmed to be present in mainland United States in 2007, principally along the West Coast. The State of California and the US Department of Agriculture quickly imposed quarantine measures and decided to use aerial spraying of cities with pesticides to try to eradicate the moth. This led to substantial public controversy and claims of adverse health effects. Aerial spraying was discontinued in 2008. Trapping, monitoring, and inspection efforts were reduced or eliminated in 2012 due to budget problems.
 W
WPersistent organic pollutants (POPs), sometimes known as "forever chemicals", are organic compounds that are resistant to environmental degradation through chemical, biological, and photolytic processes. They are toxic chemicals that adversely affect human health and the environment around the world. Because they can be transported by wind and water, most POPs generated in one country can and do affect people and wildlife far from where they are used and released. The effect of POPs on human and environmental health was discussed, with intention to eliminate or severely restrict their production, by the international community at the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants in 2001. The United States has taken strong domestic action to reduce emissions of POPs. For example, none of the original POPs pesticides listed in the Stockholm Convention is registered for sale and distribution in the United States today and in 1978, Congress prohibited the manufacture of PCBs and severely restricted the use of remaining PCB stocks. In addition, since 1987, EPA and the states have effectively reduced environmental releases of dioxins and furans to land, air, and water from U.S. sources.
 W
WPesticide drift refers to the unintentional diffusion of pesticides and the potential negative effects of pesticide application, including off-target contamination due to spray drift as well as runoff from plants or soil. This can lead to damage in human health, environmental contamination, and property damage.
 W
WA pesticide poisoning occurs when pesticides, chemicals intended to control a pest, affect non-target organisms such as humans, wildlife, plant, or bees. There are three types of pesticide poisoning. The first of the three is a single and short-term very high level of exposure which can be experienced by individuals who commit suicide, as well as pesticide formulators. The second type of poisoning is long-term high-level exposure, which can occur in pesticide formulators and manufacturers. The third type of poisoning is a long-term low-level exposure, which individuals are exposed to from sources such as pesticide residues in food as well as contact with pesticide residues in the air, water, soil, sediment, food materials, plants and animals.
 W
WSentinel Event Notification System for Occupational Risks (SENSOR)-Pesticides is a U.S. state-based surveillance program that monitors pesticide-related illness and injury. It is administered by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH), twelve state health agencies participate. NIOSH provides technical support to all participating states. It also provides funding to some states, in conjunction with the US Environmental Protection Agency.