 W
WThe African banded barb, Angola barb, blue-barred barb or fire barb is a ray-finned fish species in the family Cyprinidae.
 W
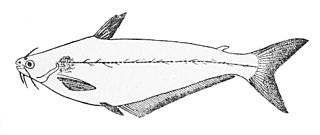
WThe African butter catfish is a species of fish in the family Schilbeidae. It is native to many major river systems in Africa. Other common names for the fish include butter fish, butter barbel, African glass catfish, lubangu, mystus catfish, silver barbel, and silver catfish. It was originally described as Silurus mystus by Carl Linnaeus in 1758.
 W
WAstatotilapia calliptera, the eastern happy or eastern river bream, is a species of haplochromine cichlid from southeastern Africa.
 W
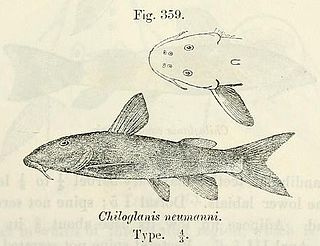
WChiloglanis neumanni, the Neumann's suckermouth, is a species of upside-down catfish native to Central Africa. This species grows to a length of 6.5 centimetres (2.6 in) SL.
 W
WThe Malawi squeaker is a species of upside-down catfish endemic to Lake Malawi. This species grows to a length of 19.2 centimetres (7.6 in) TL. This species is a minor component of local commercial fisheries and can also be found in the aquarium trade.
 W
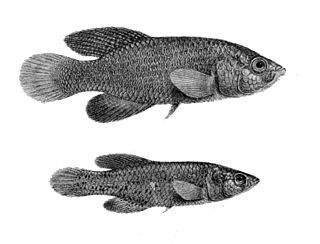
WNothobranchius furzeri, the turquoise killifish, is a species of killifish from the family Nothobranchiidae native to Africa where it is only known from Zimbabwe and Mozambique. This annual killifish inhabits ephemeral pools in semi-arid areas with scarce and erratic precipitations and have adapted to the routine drying of their environment by evolving desiccation-resistant eggs that can remain dormant in the dry mud for one and maybe more years by entering into diapause. Due to very short duration of the rain season, the natural lifespan of these animals is limited to a few months and their captive lifespan is likewise short, making them an attractive model system for ageing and disease research. Tandem repeats comprise 21% of the species' genome, an abnormally high proportion, which has been suggested as a factor in its fast ageing. Among vertebrates, the species has the fastest known sexual maturity – only 14 days after hatching, and shortest lifespan – ranging 3 to 12 months depending on the environment. More specifically, they are able to live 1–5 months in the wild and 3–16 months in captivity. They are able to live longer in captivity due to their diet, which is mostly bloodworms; this is due to dietary restrictions and antioxidant resveratrol supplements.
 W
WThe spotted killifish is a small, short lived species of fish, an African rivuline from the family Nothobranchiidae. These fish are native to many isolated freshwater pools located in the savannah depressions of east Africa, specifically Malawi, Mozambique, Zimbabwe, and South Africa. This species of fish occurs in ephemeral waters and killifish eggs can survive long periods of dehydration. The word killifish likely comes from the Dutch kil for kill.
 W
WSynodontis leopardinus, known as the leopard squeaker, is a species of upside-down catfish that is native to the Cunene, Okavango and upper Zambezi Rivers. It was first described by Jacques Pellegrin in 1914. The original specimens were obtained in Barotsés, on the Zambezi River in Zambia. The species name leopardinus means "leopard like", referring to the fish's small black spots on a yellowish body.
 W
WSynodontis nebulosus, known as the cloudy squeaker, or clouded squeaker, is a species of upside-down catfish that is native to the lower Zambezi River basin of Malawi, Mozambique, Zambia and Zimbabwe. It was first described by German naturalist and explorer Wilhelm Peters in 1852, from a specimen collected in the Zambezi River at Tete, Mozambique. The species name nebulosus is derived from the Latin word nebulosus, meaning "foggy", "cloudy", or "full of mist".
 W
WSynodontis nigromaculatus, known as the spotted squeaker, the blackspotted squeaker, or the speckled squeaker, is a species of upside-down catfish that is found widely in southern Africa. It has been identified in Angola, Botswana, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Mozambique, Namibia, South Africa, Zambia, and Zimbabwe. It was first described by British-Belgian zoologist George Albert Boulenger in 1905, from specimens collected in Lake Bangweulu in Zambia.
 W
WSynodontis woosnami, known as the Upper Zambezi squeaker, or bubblebarb squeaker, is a species of upside-down catfish that is native to Angola, Botswana, Namibia, Zambia and Zimbabwe where it is found in the upper Zambezi and Okavango River basins and the Cunene River. It was first described by British-Belgian zoologist George Albert Boulenger in 1911, from a specimen collected in the Okavango River in the Lake Ngami district of Botswana. The species name woosnami is derived from R. B. Woosnam, the collector of the first specimen.
 W
WSynodontis zambezensis, known as the brown squeaker, the korokoro, or the plain squeaker, is a species of upside-down catfish that is native to the middle and lower Zambezi River system of Mozambique, South Africa, Swaziland, Tanzania, Zambia and Zimbabwe. It was first described by German naturalist and explorer Wilhelm Peters in 1852, from specimens collected in the Zambezi River in Mozambique. The species name zambezensis is derived from the Zambezi River, where this species is found.