 W
WCell culture is the process by which cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside their natural environment. After the cells of interest have been isolated from living tissue, they can subsequently be maintained under carefully controlled conditions. These conditions vary for each cell type, but generally consist of a suitable vessel with a substrate or medium that supplies the essential nutrients (amino acids, carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals), growth factors, hormones, and gases (CO2, O2), and regulates the physio-chemical environment (pH buffer, osmotic pressure, temperature). Most cells require a surface or an artificial substrate (adherent or monolayer culture) whereas others can be grown free floating in culture medium (suspension culture). The lifespan of most cells is genetically determined, but some cell culturing cells have been “transformed” into immortal cells which will reproduce indefinitely if the optimal conditions are provided.
 W
WHydrogel from wood-based nanofibrillated cellulose (NFC) is used as a matrix for 3D cell culture. As plant based material, it does not contain any human- or animal-derived components.
 W
WAir liquid interface cell culture (ALI) is a method of cell culture by which basal stem cells are grown with their basal surfaces in contact with media, and the top of the cellular layer is exposed to the air. The cells are then lifted and media is changed until the development of a mucociliary phenotype of a pseudostratified epithelium, similar to the tracheal epithelium.
 W
WPlant callus is a growing mass of unorganized plant parenchyma cells. In living plants, callus cells are those cells that cover a plant wound. In biological research and biotechnology callus formation is induced from plant tissue samples (explants) after surface sterilization and plating onto tissue culture medium in vitro. The culture medium is supplemented with plant growth regulators, such as auxin, cytokinin, and gibberellin, to initiate callus formation or somatic embryogenesis. Callus initiation has been described for all major groups of land plants.
 W
W3D cell culture by the magnetic levitation method (MLM) is the application of growing 3D tissue by inducing cells treated with magnetic nanoparticle assemblies in spatially varying magnetic fields using neodymium magnetic drivers and promoting cell to cell interactions by levitating the cells up to the air/liquid interface of a standard petri dish. The magnetic nanoparticle assemblies consist of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles, gold nanoparticles, and the polymer polylysine. 3D cell culturing is scalable, with the capability for culturing 500 cells to millions of cells or from single dish to high-throughput low volume systems. Once magnetized cultures are generated, they can also be used as the building block material, or the "ink", for the magnetic 3D bioprinting process.
 W
WHyperhydricity is a physiological malformation that results in excessive hydration, low lignification, impaired stomatal function and reduced mechanical strength of tissue culture-generated plants. The consequence is poor regeneration of such plants without intensive greenhouse acclimation for outdoor growth. Additionally, it may also lead to leaf-tip and bud necrosis in some cases, which often leads to loss of apical dominance in the shoots. In general, the main symptom of hyperhydricity is translucent characteristics signified by a shortage of chlorophyll and high water content. Specifically, the presence of a thin or absent cuticular layer, reduced number of palisade cells, irregular stomata, less developed cell wall and large intracellular spaces in the mesophyll cell layer have been described as some of the anatomic changes associated with hyperhydricity.
 W
WAn immortalised cell line is a population of cells from a multicellular organism which would normally not proliferate indefinitely but, due to mutation, have evaded normal cellular senescence and instead can keep undergoing division. The cells can therefore be grown for prolonged periods in vitro. The mutations required for immortality can occur naturally or be intentionally induced for experimental purposes. Immortal cell lines are a very important tool for research into the biochemistry and cell biology of multicellular organisms. Immortalised cell lines have also found uses in biotechnology.
 W
WA microbiological culture, or microbial culture, is a method of multiplying microbial organisms by letting them reproduce in predetermined culture medium under controlled laboratory conditions. Microbial cultures are foundational and basic diagnostic methods used as a research tool in molecular biology.
 W
WPrimary cell culture is the ex vivo culture of cells freshly obtained from a multicellular organism, as opposed to the culture of immortalized cell lines. In general, primary cell cultures are considered more representative of in vivo tissues than cell lines, and this is recognized legally in some countries such as the UK. However, primary cells require adequate substrate and nutrient conditions to thrive and after a certain number of divisions they acquire a senescent phenotype, leading to irreversible cell cycle arrest. The generation of cell lines stems from these two reasons. Primary cells can become immortalized either spontaneously or by genetic modification, at which point they become cell lines which can be subcultured indefinitely.
 W
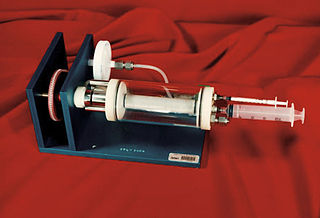
WThe Rotary Cell Culture System (RCCS) is a device designed to grow three-dimensional cell clusters in microgravity. In the early 1990s, NASA researchers began developing hardware that would let them study the cell tissues of mammals—including humans—in microgravity. They also needed it to protect the fragile cultures from the turbulence of Space Shuttle launch and landing. The resulting device enables the growth of tissue, cancer tumors and virus cultures outside the body, both in space and on Earth.
 W
WSomatic embryogenesis is an artificial process in which a plant or embryo is derived from a single somatic cell. Somatic embryos are formed from plant cells that are not normally involved in the development of embryos, i.e. ordinary plant tissue. No endosperm or seed coat is formed around a somatic embryo.
 W
WA stem cell line is a group of stem cells that is cultured in vitro and can be propagated indefinitely. Stem cell lines are derived from either animal or human tissues and come from one of three sources: embryonic stem cells, adult stem cells, or induced stem cells. They are commonly used in research and regenerative medicine.
 W
WTissue culture is the growth of tissues or cells in an artificial medium separate from the parent organism. This technique is also called micropropagation. This is typically facilitated via use of a liquid, semi-solid, or solid growth medium, such as broth or agar. Tissue culture commonly refers to the culture of animal cells and tissues, with the more specific term plant tissue culture being used for plants. The term "tissue culture" was coined by American pathologist Montrose Thomas Burrows.