 W
WThe coronal suture is a dense, fibrous connective tissue joint that separates the two parietal bones from the frontal bone of the skull.
 W
WThe frontal suture is a fibrous joint that divides the two halves of the frontal bone of the skull in infants and children. Typically, it completely fuses between three and nine months of age, with the two halves of the frontal bone being fused together. It is also called the metopic suture, although this term may also refer specifically to a persistent frontal suture.
 W
WThe frontoethmoidal suture is the suture between the ethmoid bone and the frontal bone.
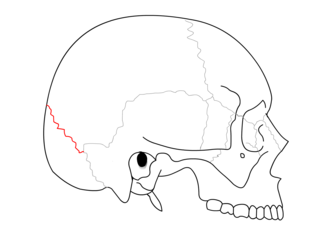 W
WThe lambdoid suture is a dense, fibrous connective tissue joint on the posterior aspect of the skull that connects the parietal bones with the occipital bone. It is continuous with the occipitomastoid suture.
 W
WThe occipitomastoid suture or occipitotemporal suture is the cranial suture between the occipital bone and the mastoid portion of the temporal bone.
 W
WThe sagittal suture is a dense, fibrous connective tissue joint between the two parietal bones of the skull. The term is derived from the Latin word sagitta, meaning arrow. The derivation of this term may be demonstrated by observing how the sagittal suture is notched posteriorly, like an arrow, by the lambdoid suture. The sagittal suture is also known as the interparietal suture, the sutura interparietalis.
 W
WThe Sphenoethmoidal suture is the cranial suture between the sphenoid bone and the ethmoid bone.
 W
WThe Sphenofrontal suture is the cranial suture between the sphenoid bone and the frontal bone.
 W
WThe Sphenoparietal suture is the cranial suture between the sphenoid bone and the parietal bone. It is one of the sutures that comprises the pterion.
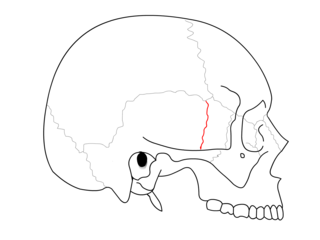 W
WThe Sphenosquamosal suture is a cranial suture between the sphenoid bone and the squama of the temporal bone.
 W
WThe sphenozygomatic suture is the cranial suture between the sphenoid bone and the zygomatic bone.
 W
WThe squamosal suture, or squamous suture, arches backward from the pterion and connects the temporal squama with the lower border of the parietal bone: this suture is continuous behind with the short, nearly horizontal parietomastoid suture, which unites the mastoid process of the temporal with the region of the mastoid angle of the parietal bone. The term parietotemporal suture may refer to both of these sutures or exclusively to the parietomastoid suture and its use is, therefore, best avoided.
 W
WThe zygomaticotemporal suture is the cranial suture between the zygomatic bone and the temporal bone.