 W
WSubstance abuse, also known as drug abuse, is use of a drug in amounts or by methods which are harmful to the individual or others. It is a form of substance-related disorder. Differing definitions of drug abuse are used in public health, medical and criminal justice contexts. In some cases criminal or anti-social behaviour occurs when the person is under the influence of a drug, and long term personality changes in individuals may occur as well. In addition to possible physical, social, and psychological harm, use of some drugs may also lead to criminal penalties, although these vary widely depending on the local jurisdiction.
 W
WAlcohol abuse encompasses a spectrum of unhealthy alcohol drinking behaviors, ranging from binge drinking to alcohol dependence, in extreme cases resulting in health problems for individuals and large scale social problems such as alcohol-related crimes.
 W
WResearch data indicates that steroids affect the serotonin and dopamine neurotransmitter systems of the brain. In an animal study, male rats developed a conditioned place preference to testosterone injections into the nucleus accumbens, an effect blocked by dopamine antagonists, which suggests that androgen reinforcement is mediated by the brain. Moreover, testosterone appears to act through the mesolimbic dopamine system, a common substrate for drugs of abuse. Nonetheless, androgen reinforcement is not comparable to that of cocaine, nicotine, or heroin. Instead, testosterone resembles other mild reinforcers, such as caffeine, or benzodiazepines. The potential for androgen addiction remains to be determined.
 W
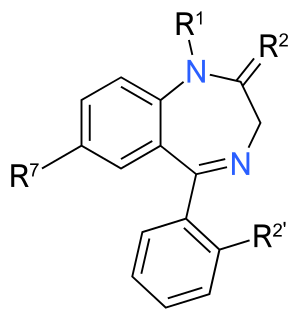
WThe Benadryl challenge is an internet challenge which emerged in 2020, and revolves around the deliberate consumption, abuse and overdose of the antihistamine medicine diphenhydramine, commonly sold in the United States under the brand name Benadryl. The challenge, which spread via the social media platform TikTok, instructs participants to film themselves consuming large doses of Benadryl for the purpose of 'tripping', or hallucinating.
 W
WBenzodiazepine use disorder (BUD), also called misuse or abuse, is the use of benzodiazepines without a prescription, often for recreational purposes, which poses risks of dependence, withdrawal and other long-term effects. Benzodiazepines are one of the more common prescription drugs used recreationally. When used recreationally benzodiazepines are usually administered orally but sometimes they are taken intranasally or intravenously. Recreational use produces effects similar to alcohol intoxication.
 W
WProtein fosB, also known as FosB and G0/G1 switch regulatory protein 3 (G0S3), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FBJ murine osteosarcoma viral oncogene homolog B (FOSB) gene.
 W
WA drug overdose is the ingestion or application of a drug or other substance in quantities greater than are recommended. Typically it is used for cases when a risk to health will potentially result. An overdose may result in a toxic state or death.
 W
WHarm reduction, or harm minimization, refers to a range of public health policies designed to lessen the negative social and/or physical consequences associated with various human behaviors, both legal and illegal. Harm reduction policies are used to manage behaviors such as recreational drug use and sexual activity in numerous settings that range from services through to geographical regions.
 W
WInhalants are a broad range of household and industrial chemicals whose volatile vapors or pressurized gases can be concentrated and breathed in via the nose or mouth to produce intoxication, in a manner not intended by the manufacturer. They are inhaled at room temperature through volatilization or from a pressurized container, and do not include drugs that are sniffed after burning or heating. For example, amyl nitrite (poppers), nitrous oxide and toluene – a solvent widely used in contact cement, permanent markers, and certain types of glue – are considered inhalants, but smoking tobacco, cannabis, and crack are not, even though these drugs are inhaled as smoke.
 W
WPolysubstance dependence refers to a type of substance dependence disorder in which an individual uses at least three different classes of substances indiscriminately and does not have a favorite drug that qualifies for dependence on its own. Although any combination of three drugs can be used, studies have shown that alcohol is commonly used with another substance. This is supported by one study on polysubstance use that separated participants who used multiple substances into groups based on their preferred drug. The results of a long-term or longitudinal study on substance use led the researchers to observe that excessively using or relying on one drug increased the probability of excessively using or relying on another drug.
 W
WDextromethorphan, or DXM, a common active ingredient found in many over-the-counter cough suppressant cold medicines, is used as a recreational drug and entheogen for its dissociative effects. It has almost no psychoactive effects at medically recommended doses. However, dextromethorphan has powerful dissociative properties when administered in doses well above those considered therapeutic for cough suppression. Recreational use of DXM is sometimes referred to in slang form as "robo-tripping", whose prefix derives from the Robitussin brand name, or "Triple Cs", which derives from the Coricidin brand. However, this brand presents a danger when used at recreational doses due to the presence of chlorpheniramine.
 W
WSubstance Abuse Prevention, also known as drug abuse prevention, is a process that attempts to prevent the onset of substance use or limit the development of problems associated with using psychoactive's substances. Prevention efforts may focus on the individual or their surroundings. A concept known as "environmental prevention" focuses on changing community conditions or policies so that the availability of substances is reduced as well as the demand.
 W
WThe United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has data on drug overdose death rates and totals. 945,877 US residents died from drug overdoses from 1968 to 2018. From 1999 to Feb 2019 over 770,000 people died from drug overdoses. 21 people out of every 100,000 died from drug overdoses in 2018 in the US.