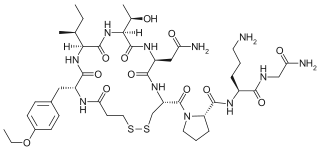
 W
WAtosiban, sold under the brand name Tractocile among others, is an inhibitor of the hormones oxytocin and vasopressin. It is used as an intravenous medication as a labour repressant (tocolytic) to halt premature labor. It was developed by Ferring Pharmaceuticals in Sweden and first reported in the literature in 1985. Originally marketed by Ferring Pharmaceuticals, it is licensed in proprietary and generic forms for the delay of imminent preterm birth in pregnant adult women.
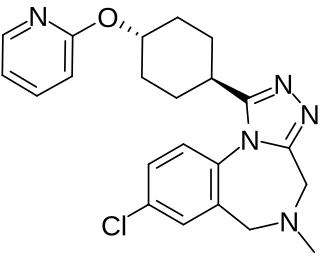 W
WBalovaptan, is a selective small molecule antagonist of the vasopressin V1A receptor which is under development by Roche for the treatment of autism. As of August 2019, it is in a phase III clinical trial for adults and a phase II clinical trial for children for this indication. On 29 January 2018, Roche announced that the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) had granted Breakthrough Therapy Designation for balovaptan in individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). The FDA granted this based on the results of the adult phase II clinical trial called VANILLA study. The currently-recruiting phase III adult study is called V1aduct and the currently-closed phase II child study is called Av1ation.
 W
WConivaptan, sold under the brand name Vaprisol, is a non-peptide inhibitor of the receptor for anti-diuretic hormone, also called vasopressin. It was approved in 2004 for hyponatremia. The compound was discovered by Astellas and marked in 2006. The drug is now marketed by Cumberland Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
 W
WLixivaptan (VPA-985) is a phase III pharmaceutical being developed by Cardiokine, Inc., a specialty pharmaceutical company based in Philadelphia, PA, focused on the development of pharmaceuticals for the treatment and prevention of cardiovascular diseases. Lixivaptan is, as of May 2010, in Phase III clinical trials involving patients with hyponatremia, including those with concomitant heart failure. Hyponatremia is an electrolyte disturbance in which the sodium concentration in the serum is lower than normal. Lixivaptan may help some patients eliminate excess fluids while retaining electrolytes.
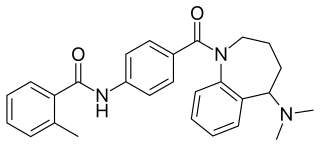 W
WMozavaptan (INN) is a vasopressin receptor antagonist marketed by Otsuka. In Japan, it was approved in October 2006 for hyponatremia caused by syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH) due to ADH producing tumors.
 W
WNelivaptan (INN) is a selective, orally active, non-peptide vasopressin receptor antagonist selective for the V1B subtype. The drug had entered clinical trials for treatment of anxiety and depression. In July 2008, Sanofi-Aventis announced that further development of this drug had been halted.
 W
WPF-184563 is a potent, selective non-peptidic antagonist of the V1a receptor. The compound was discovered by Pfizer in its Sandwich, Kent research center, as a potential treatment for dysmenorrhoea, an indication for which V1a antagonists have shown efficacy.
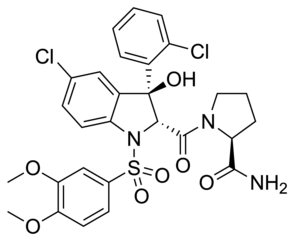 W
WRelcovaptan (SR-49059) is a non-peptide vasopressin receptor antagonist, selective for the V1a subtype. It has shown positive initial results for the treatment of Raynaud's disease and dysmenorrhoea, and as a tocolytic, although it is not yet approved for clinical use.
 W
WSatavaptan is a vasopressin-2 receptor antagonist which was investigation by Sanofi-Aventis and was under development for the treatment of hyponatremia. It was also being studied for the treatment of ascites. Development was discontinued in 2009.
 W
WSRX246, also known as API-246, is a small-molecule, centrally-active, highly-selective vasopressin V1A receptor antagonist which is under investigation by Azevan Pharmaceuticals for the treatment of affective and anger disorders. It is an azetidinone derivative, and was developed from LY-307174 as a lead compound. A phase II activity trial of the drug in the treatment of adults with intermittent explosive disorder is ongoing. It is also being studied for the treatment of post-traumatic stress disorder.
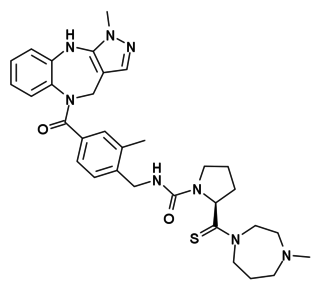 W
WTC OT 39 is a non-peptide partial agonist of the oxytocin and vasopressin V2 receptors (Ki = 147 nM and >1000 nM, respectively) and antagonist of the vasopressin V1A receptor (Ki = 330 nM).
 W
WTolvaptan (trade names Samsca, Jinarc, and others) is an aquaretic drug that functions as a selective, competitive vasopressin receptor 2 (V2) antagonist used to treat hyponatremia (low blood sodium levels) associated with congestive heart failure, cirrhosis, and the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH). Tolvaptan was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) on May 19, 2009, and is sold by Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co. under the trade name Samsca. Tolvaptan, as Jynarque, was granted approval for medical use in the United States in April 2018.
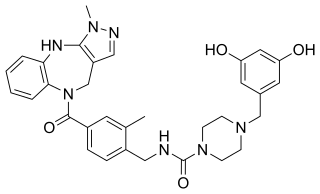 W
WWAY-267464 is a potent, selective, non-peptide agonist for the oxytocin receptor, with negligible affinity for the vasopressin receptors. Contradictorily however, though originally described as selective for the oxytocin receptor and lacking affinity for the vasopressin receptors, it has since been reported to also act as a potent vasopressin V1A receptor antagonist. WAY-267464 has been shown to cross the blood-brain-barrier to a significantly greater extent than exogenously applied oxytocin, and in animal tests produces centrally-mediated oxytocinergic actions such as anxiolytic effects, but with no antidepressant effect evident. It was developed by a team at Ferring Pharmaceuticals.