 W
WThe mind is the set of faculties responsible for mental phenomena. Often the term is also identified with the phenomena themselves. These faculties include thought, imagination, memory, will and sensation. They are responsible for various mental phenomena, like perception, pain experience, belief, desire, intention and emotion. Various overlapping classifications of mental phenomena have been proposed. Important distinctions group them together according to whether they are sensory, propositional, intentional, conscious or occurrent. Minds were traditionally understood as substances but it is more common in the contemporary perspective to conceive them as properties or capacities possessed by humans and higher animals. Various competing definitions of the exact nature of the mind or mentality have been proposed. Epistemic definitions focus on the privileged epistemic access the subject has to these states. Consciousness-based approaches give primacy to the conscious mind and allow unconscious mental phenomena as part of the mind only to the extent that they stand in the right relation to the conscious mind. According to intentionality-based approaches, the power to refer to objects and to represent the world is the mark of the mental. For behaviorism, whether an entity has a mind only depends on how it behaves in response to external stimuli while functionalism defines mental states in terms of the causal roles they play. Central questions for the study of mind, like whether other entities besides humans have minds or how the relation between body and mind is to be conceived, are strongly influenced by the choice of one's definition.
 W
W"Cartesian theater" is a derisive term coined by philosopher and cognitive scientist Daniel Dennett to refer pointedly to a defining aspect of what he calls Cartesian materialism, which he considers to be the often unacknowledged remnants of Cartesian dualism in modern materialist theories of the mind.
 W
WConcepts are defined as abstract ideas. They are understood to be the fundamental building blocks of the concept behind principles, thoughts and beliefs. They play an important role in all aspects of cognition. As such, concepts are studied by several disciplines, such as linguistics, psychology, and philosophy, and these disciplines are interested in the logical and psychological structure of concepts, and how they are put together to form thoughts and sentences. The study of concepts has served as an important flagship of an emerging interdisciplinary approach called cognitive science.
 W
WEcstasy is a subjective experience of total involvement of the subject, with an object of their awareness. In classical Greek literature it refers to removal of the mind or body "from its normal place of function."
 W
WIn common usage and in philosophy, ideas are the results of thought. Also in philosophy, ideas can also be mental representational images of some object. Many philosophers have considered ideas to be a fundamental ontological category of being. The capacity to create and understand the meaning of ideas is considered to be an essential and defining feature of human beings. In a popular sense, an idea arises in a reflexive, spontaneous manner, even without thinking or serious reflection, for example, when we talk about the idea of a person or a place. A new or an original idea can often lead to innovation.
 W
WIn the study of the human mind, intellect refers to, describes, and identifies the ability of the human mind to reach correct conclusions about what is true and what is false in reality; and how to solve problems. Derived from the Ancient Greek philosophy term nous, intellect derived from the Latin intelligere, from which derives the term intelligence in the French and English languages. The discussion of intellect is in two areas of knowledge that concern the relation between intelligence and intellect.In classical philosophy and in mediaeval philosophy the intellect (nous) is the subject of the question: How do people know things? In Late Antiquity and in the Middle Ages, the intellect was the conceptual means of reconciling the religious faith of monotheism with the facts of philosophy and science about Nature, a reconciliation that would make the intellect the conduit between the human soul, and the divine intellect of the cosmos. In the Late Middle Ages, philosophers developed the distinction that intelligence is in two modes passive intellect and active intellect.In psychology and in neuroscience, the Theory of Multiple Intelligences applies the terms intelligence (emotion) and intellect (mind) to describe how people understand the world and reality.
 W
WIntuition is the ability to acquire knowledge without recourse to conscious reasoning. Different fields use the word "intuition" in very different ways, including but not limited to: direct access to unconscious knowledge; unconscious cognition; inner sensing; inner insight to unconscious pattern-recognition; and the ability to understand something instinctively, without any need for conscious reasoning.
 W
WThe mental lexicon is defined as a mental dictionary that contains information regarding a word's meaning, pronunciation, syntactic characteristics, and so on.
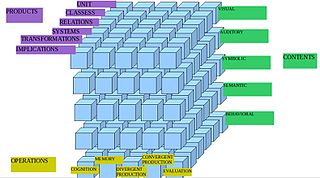 W
WMental operations are operations that affect mental contents. Initially, operations of reasoning have been the object of logic alone. Pierre Janet was one of the first to use the concept in psychology. Mental operations have been investigated at a developmental level by Jean Piaget, and from a psychometric perspective by J. P. Guilford. There is also a cognitive approach to the subject, as well as a systems view of it.
 W
WMental substance, according to the idea held by dualists and idealists, is a non-physical substance of which minds are composed. This substance is often referred to as consciousness.
 W
WNous, sometimes equated to intellect or intelligence, is a term from classical philosophy for the faculty of the human mind necessary for understanding what is true or real. English words such as "understanding" are sometimes used, but three commonly used philosophical terms come directly from classical languages: νοῦς or νόος, intellēctus and intellegentia. To describe the activity of this faculty, the word intellection is sometimes used in philosophical contexts, as well as the Greek words noēsis and noeîn. This activity is understood in a similar way to the modern concept of intuition.
 W
WThe study of the mind in Eastern philosophy has parallels to the Western study of the Philosophy of mind as a branch of philosophy that studies the nature of the mind. Dualism and monism are the two central schools of thought on the mind–body problem in the Western tradition, although nuanced views have arisen that do not fit one or the other category neatly. Dualism is found in both Eastern and Western traditions but its entry into Western philosophy was thanks to René Descartes in the 17th century. This article on mind in eastern philosophy deals with this subject from the standpoint of eastern philosophy which is historically strongly separated from the Western tradition and its approach to the Western philosophy of mind.
 W
WPhilosophy of mind is a branch of philosophy that studies the ontology and nature of the mind and its relationship with the body. The mind–body problem is a paradigmatic issue in philosophy of mind, although a number of other issues are addressed, such as the hard problem of consciousness and the nature of particular mental states. Aspects of the mind that are studied include mental events, mental functions, mental properties, consciousness, the ontology of the mind, the nature of thought, and the relationship of the mind to the body.
 W
WTabula rasa is the theory that individuals are born without built-in mental content, and therefore all knowledge comes from experience or perception. Epistemological proponents of tabula rasa disagree with the doctrine of innatism, which holds that the mind is born already in possession of certain knowledge. Proponents of the tabula rasa theory also favour the "nurture" side of the nature versus nurture debate when it comes to aspects of one's personality, social and emotional behaviour, knowledge, and sapience.
 W
WIn their most common sense, the terms thought and thinking refer to conscious cognitive processes that can happen independently of sensory stimulation. Their most paradigmatic forms are judging, reasoning, concept formation, problem solving, and deliberation. But other mental processes, like considering an idea, memory, or imagination, are also often included. These processes can happen internally independent of the sensory organs, unlike perception. But when understood in the widest sense, any mental event may be understood as a form of thinking, including perception and unconscious mental processes. In a slightly different sense, the term thought refers not to the mental processes themselves but to mental states or systems of ideas brought about by these processes.