 W
WHomo is the genus that emerged in the genus Australopithecus that encompasses the extant species Homo sapiens, plus several extinct species classified as either ancestral to or closely related to modern humans, most notably Homo erectus and Homo neanderthalensis. The genus emerged with the appearance of Homo habilis just over 2 million years ago. Homo, together with the genus Paranthropus, is probably sister to Australopithecus africanus, which itself had previously split from the lineage of Pan, the chimpanzees.
 W
WHomo antecessor is an archaic human species recorded in the Spanish Sierra de Atapuerca from 1.2 to 0.8 million years ago during the Early Pleistocene. Populations may have been present elsewhere in Western Europe, and were among the first to colonise that region of the world. The first fossils were found in the Gran Dolina cave in 1994, and the species was formally described in 1997 as the last common ancestor of modern humans and Neanderthals, supplanting the more conventional H. heidelbergensis in this position. H. antecessor has since been reinterpreted as an offshoot, though probably one branching off just before the modern human/Neanderthal split.
 W
WHomo bodoensis is the species name for extinct archaic humans that lived during the Chibanian in Africa. It relies on the fossil specimen known as Bodo cranium, which was discovered in 1976 from the Awash River in Ethiopia and is estimated to have lived around 500,000 years ago. Following the comparative analysis of the fossil with those of other Homo falling on the same geological age, the name was formally introduced in 2021.
 W
WHomo erectus is an extinct species of archaic human from the Pleistocene, with its earliest occurrence about 2 million years ago, and its specimens are among the first recognizable members of the genus Homo. H. erectus was the first human ancestor to spread throughout Eurasia, with a continental range extending from the Iberian Peninsula to Java. African populations of H. erectus are likely to be the ancestors to several human species, such as H. heidelbergensis and H. antecessor, with the former generally considered to have been the ancestor to Neanderthals, Denisovans, and modern humans. Asian populations of H. erectus may be ancestral to H. floresiensis and possibly to H. luzonensis. As a chronospecies, the time of the disappearance of H. erectus is a matter of contention. There are also several proposed subspecies with varying levels of recognition. The last known population of H. erectus is H. e. soloensis from Java, around 117,000–108,000 years ago.
 W
WHomo ergaster is an extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Africa in the Early Pleistocene. Whether H. ergaster constitutes a species of its own or should be subsumed into H. erectus is an ongoing and unresolved dispute within palaeoanthropology. Proponents of synonymisation typically designate H. ergaster as "African Homo erectus" or "Homo erectus ergaster". The name Homo ergaster roughly translates to "working man", a reference to the more advanced tools used by the species in comparison to those of their ancestors. The fossil range of H. ergaster mainly covers the period of 1.7 to 1.4 million years ago, though a broader time range is possible. Though fossils are known from across East and Southern Africa, most H. ergaster fossils have been found along the shores of Lake Turkana in Kenya. There are later African fossils, some younger than 1 million years ago, that indicate long-term anatomical continuity, though it is unclear if they can be formally regarded as H. ergaster specimens. As a chronospecies, H. ergaster may have persisted to as late as 600,000 years ago, when new lineages of Homo arose in Africa.
 W
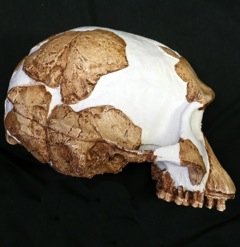
WHomo floresiensis is a species of small archaic human that inhabited the island of Flores, Indonesia, until the arrival of modern humans about 50,000 years ago.
 W
WHomo gautengensis is a species name proposed by anthropologist Darren Curnoe in 2010 for South African hominin fossils otherwise attributed to H. habilis, H. ergaster, or, in some cases, Australopithecus or Paranthropus. The fossils assigned to the species by Curnoe cover a vast temporal range, from about 1.8 million years ago to potentially as late as 0.8 million years ago, meaning that if the species is considered valid, H. gautengensis would be both one of the earliest and one of the longest lived species of Homo.
 W
WHomo habilis is an extinct species of archaic human from the Early Pleistocene of East and South Africa about 2.3 to 1.65 million years ago (mya). Upon species description in 1964, H. habilis was highly contested, with many researchers recommending it be synonymised with Australopithecus africanus, the only other early hominin known at the time, but H. habilis received more recognition as time went on and more relevant discoveries were made. By the 1980s, H. habilis was proposed to have been a human ancestor, directly evolving into Homo erectus which directly led to modern humans. This viewpoint is now debated. Several specimens with insecure species identification were assigned to H. habilis, leading to arguments for splitting, namely into "H. rudolfensis" and "H. gautengensis" of which only the former has received wide support.
 W
WHomo luzonensis, also locally called "Ubag" after a mythical caveman, is an extinct, possibly pygmy, species of archaic human from the Late Pleistocene of Luzon, the Philippines. Their remains, teeth and phalanges, are known only from Callao Cave in the northern part of the island dating to before 50,000 years ago. They were initially identified as belonging to modern humans in 2010, but in 2019, after the discovery of more specimens, they were placed into a new species based on the presence of a wide range of traits similar to modern humans as well as to Australopithecus and early Homo.
 W
WHomo naledi is a species of archaic human discovered in the Rising Star Cave, Cradle of Humankind, South Africa dating to the Middle Pleistocene 335,000–236,000 years ago. The initial discovery comprises 1,550 specimens, representing 737 different elements, and at least 15 different individuals. Despite this exceptionally high number of specimens, their classification with other Homo remains unclear.
 W
WHomo rudolfensis is a species of archaic human from the Early Pleistocene of East Africa about 2 million years ago (mya). Because H. rudolfensis coexisted with several other hominins, it is debated what specimens can be confidently assigned to this species beyond the lectotype skull KNM-ER 1470 and other partial skull aspects. No bodily remains are definitively assigned to H. rudolfensis. Consequently, both its generic classification and validity are debated without any wide consensus, with some recommending the species to actually belong to the genus Australopithecus as A. rudolfensis or Kenyanthropus as K. rudolfensis, or that it is synonymous with the contemporaneous and anatomically similar H. habilis.
 W
WPeking Man is a subspecies of H. erectus which inhabited the Zhoukoudian Cave of northern China during the Middle Pleistocene. The first fossil, a tooth, was discovered in 1921, and the Zhoukoudian has since become the most productive H. erectus site in the world. Peking Man was instrumental in the foundation of Chinese anthropology, and fostered an important dialogue between Western and Eastern science for decades to come. The fossils became the centre of anthropological discussion, and were classified as a direct human ancestor, propping up the Out of Asia hypothesis that humans evolved in Asia. Peking Man also played a vital role in the restructuring of the Chinese identity following the Chinese Communist Revolution, and was intensively communicated to working class and peasant communities to introduce them to Marxism and science. As a consequence of the former, early models of Peking Man society strongly leaned towards communist or nationalist ideals, leading to discussions on primitive communism and polygenism. This produced a strong schism between Western and Eastern interpretations, especially as the West adopted the Out of Africa hypothesis by the late 20th century, and Peking Man's role in human evolution diminished as merely an offshoot of the human line. Now that the hypothesis is ubiquitous, Peking Man interbreeding with human ancestors is frequently discussed especially in Chinese circles.
 W
WPenghu 1 is a fossil jaw (mandible) belonging to an extinct hominin species of the genus Homo from Taiwan which lived in the middle-late Pleistocene. The precise classification of the mandible is disputed, some arguing that it represents a new species, Homo tsaichangensis, whereas others believe it to be the fossil of a H. erectus, an archaic H. sapiens or possibly a Denisovan.
 W
WHomo rhodesiensis is the species name proposed by Arthur Smith Woodward (1921) to classify Kabwe 1, a Middle Stone Age fossil recovered from a cave at Broken Hill, or Kabwe, Northern Rhodesia .. In 2020, the skull was dated to 324,000 to 274,000 years ago. Other similar older specimens also exist.
 W
WSinanthropus is an archaic genus in the scientific classification system to which the early hominid fossils of Peking man, Lantian Man, Nanjing Man, and Yuanmou Man were once assigned. All of them have now been reclassified as Homo erectus, and the genus Sinanthropus is disused. Beginning in the year 1928 to the year 1937, 14 fragmented skulls belonging to the hominids were found in various locations in China. Peking and Chou K’ou-tien are two notable places with fossils found. It has been noted by researchers that it is likely that the found fragmented skulls were brought to the cave after being severed from the bodies they belonged to. This is very likely, because most of the found pieces are teeth and jaws. Some skulls are missing large parts which indicates separation before they were fossilized, not the loss of pieces due to fossilization process.
 W
WWushan Man is a set of fossilised remains of an extinct, undetermined non-hominin ape found in central China in 1985. The remains are dated to around 2 million years ago and were originally considered to represent a subspecies of Homo erectus.