 W
WMeridiungulata is an extinct clade with the rank of cohort or superorder, containing the South American ungulates Pyrotheria, Astrapotheria, Notoungulata and Litopterna. It is not known if it is a natural group; it is known that both Litopterna and Notoungulata form a clade based on collagen evidence, but the placement of the other members is uncertain. it was erected to distinguish the ungulates of South America from other ungulates. Relationships between the orders inside Meridiungulata remain unresolved and it could well be a "wastebasket taxon". Most Meridiungulata died out following the invasion of South America by North American ungulates and predators during the Great American Interchange, but a few of the largest species of notoungulates and litopterns survived until the end-Pleistocene extinctions. The notoungulate Mixotoxodon was able to invade North America to as far as present-day Texas.
 W
WAstraponotus is an extinct genus of herbivorous mammals, belonging to the family of astrapotherids. It lived during the late Late Eocene and its fossil remains have been found in the Sarmiento Formation of Argentina, South America.
 W
WAstrapotheria is an extinct order of South American and Antarctic hoofed mammals that existed from the Late Paleocene to the Middle Miocene, 59 to 11.8 million years ago. Astrapotheres were large and rhinoceros-like animals and have been called one of the most bizarre orders of mammals with an enigmatic evolutionary history.
 W
WAstrapotheriidae is an extinct family of herbivorous South American land mammals that lived from the Late Eocene to the Middle Miocene 37.8 to 15.97 million years ago. The most derived of the astrapotherians, they were also the largest and most specialized mammals in the Tertiary of South America. There are two sister taxa: Eoastrapostylopidae and Trigonostylopidae.
 W
WAstrapotherium is an extinct genus of South American mammals that vaguely resembled a cross between a small elephant, and a very large tapir. This peculiar-looking animal was unrelated to elephants or tapirs, and was instead related to other extinct South American ungulates. The beast lived in the Early to Middle Miocene. Fossil remains of the type species A. magnus have been found in the Santa Cruz Formation in Argentina. Other fossils have been found in the Deseado, Sarmiento, and Aisol Formations of Argentina and Chile.
 W
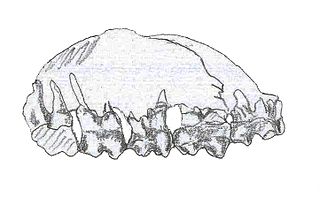
WCarodnia is an extinct genus of South American ungulate known from the Early Eocene of Brazil, Argentina, and Peru. Carodnia is placed in the order Xenungulata together with Etayoa and Notoetayoa.
 W
WColombitherium is an extinct mammal from Late Eocene Colombia. It has originally been assigned to the order Pyrotheria and the family Colombitheriidae, although a later detailed analysis of the fossil questions that classification. A fossil jawbone of approximately 9 centimetres (3.5 in) length of Colombitherium has been found by Texas Petroleum in 1945, in the Upper Eocene strata of the middle Gualanday Group in the department of Tolima, Central Ranges of the Colombian Andes.
 W
WGranastrapotherium is an extinct genus of ungulate mammals, described from remains found in rocks of the Honda Group in the Tatacoa Desert, in the Colombian departments of Huila and Tolima, at the Miocene fossil site La Venta. The only species formally recognized is Granastrapotherium snorki. Remains found in Bolivia and Peru, seem to belong to Granastrapotherium or a very similar animal.
 W
WHilarcotherium is an extinct genus of astrapotheriid mammals that lived in South America during the Middle Miocene (Laventan). The type species is H. castanedaii, found in sediments of the La Victoria Formation, part of the Honda Group in the department of Tolima in Colombia. In 2018, Carrillo et al. described a partial skull and mandible of a second species H. miyou from the Castilletes Formation in the Cocinetas Basin of northern Colombia, and estimated the body weight of the animal at 6,465 kilograms (14,253 lb).
 W
WParastrapotherium is an extinct genus of South American land mammal that existed from the Late Oligocene to the Early Miocene. The genus includes some of the largest and smallest known astrapotherian, but at present no generally recognized description can adequately characterize it.
 W
WPyrotheria is an order of extinct meridiungulate mammals. These mastodon-like ungulates include the genera Baguatherium, Carolozittelia, Colombitherium, Gryphodon, Propyrotherium, Proticia, and Pyrotherium.
 W
WPyrotheriidae is the only family in the order Pyrotheria, provided one does not include the Paleocene genus, Carodnia. These extinct, mastodon-like ungulates include the genera Baguatherium, Carolozittelia, Gryphodon, Propyrotherium, and Pyrotherium. Fossils of the family have been found in Argentina, Brazil, Bolivia and Peru.
 W
WPyrotherium is an extinct genus of South American ungulate, of the order Pyrotheria, that lived in what is now Argentina and Bolivia, during the Late Oligocene. It was named Pyrotherium because the first specimens were excavated from an ancient volcanic ash deposit. Fossils of the genus have been found in the Sarmiento Formation of Argentina and the Salla Formation of Bolivia.
 W
WTrigonostylops is an extinct genus of South American meridiungulatan ungulate, from the Late Paleocene to Late Eocene of South America and Antarctica. It is the only member of the family Trigonostylopidae.
 W
WXenastrapotherium is an extinct genus of astrapothere, a type of hoofed herbivorous mammal, native to South America, which lived in the Middle to Late Miocene period, typically during the Laventan stage. It is a member of the family Astrapotheriidae in the subfamily Uruguaytheriinae, large astrapotheres, equipped with a trunk-like nose and protruding teeth, similar to the elephants, but their tusks were the canine teeth, not the incisors. Xenastrapotherium was a genus widely distributed in northern South America, in contrast to other species of astrapotheres which lived in the area of the Southern Cone of the continent. It differed from other astrapotheres by having two lower incisors on each side of the jaw and the tusks have a pronounced longitudinal curvature, although their general shape and size are probably very similar to Astrapotherium, whose weight would be 900 to 1,500 kilograms, comparable to the current black rhino.
 W
WXenungulata is an order of extinct and primitive South American hoofed mammals that lived from the Late Paleocene to Early Eocene. Fossils of the order are known from deposits in Brazil, Argentina, Peru, and Colombia. The best known member of this enigmatic order is the genus Carodnia, a tapir-like and -sized animal with a gait similar to living African elephants.