 W
WAn aecium is a specialised reproductive structure found in some plant pathogenic rust fungi that produce aeciospores. Aecia may also be referred to as "cluster cups". The term aecidium is used interchangeably but is not preferred.
 W
WThe cortical reaction is a process initiated during fertilization by the release of cortical granules from the egg, which prevents polyspermy, the fusion of multiple sperm with one egg. In contrast to the fast block of polyspermy which immediately but temporarily blocks additional sperm from fertilizing the egg, the cortical reaction gradually establishes a permanent barrier to sperm entry and functions as the main part of the slow block of polyspermy in many animals.
 W
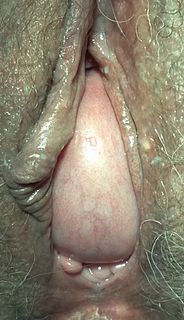
WA cystocele, also known as a prolapsed bladder, is a medical condition in which a woman's bladder bulges into her vagina. Some may have no symptoms. Other may have trouble starting urination, urinary incontinence, or frequent urination. Complications may include recurrent urinary tract infections and urinary retention. Cystocele and a prolapsed urethra often occur together and is called a cystourethrocele. Cystocele can negatively affect quality of life.
 W
WThe follicular phase, also known as the preovulatory phase or proliferative phase, is the phase of the estrous cycle during which follicles in the ovary mature from primary follicle to a fully mature graafian follicle. It ends with ovulation. The main hormones controlling this stage are secretion of gonadotropin-releasing hormone which are follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinising hormone. They are released by pulsatile secretion.
 W
WA gamete is a haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization in organisms that sexually reproduce. In species that produce two morphologically distinct types of gametes, and in which each individual produces only one type, a female is any individual that produces the larger type of gamete—called an ovum— and a male produces the smaller tadpole-like type—called a sperm. In short a gamete is an egg cell or a sperm. This is an example of anisogamy or heterogamy, the condition in which females and males produce gametes of different sizes. In contrast, isogamy is the state of gametes in a species being the same size and shape, in isogamy there is no male or female sex and given arbitrary designators for mating type. The name gamete was introduced by the German cytologist Eduard Strasburger. Gametes carry half the genetic information of an individual, one ploidy of each type, and are created through meiosis.
 W
WGametogenesis is a biological process by which diploid or haploid precursor cells undergo cell division and differentiation to form mature haploid gametes. Depending on the biological life cycle of the organism, gametogenesis occurs by meiotic division of diploid gametocytes into various gametes, or by mitosis. For example, plants produce gametes through mitosis in gametophytes. The gametophytes grow from haploid spores after sporic meiosis. The existence of a multicellular, haploid phase in the life cycle between meiosis and gametogenesis is also referred to as alternation of generations.
 W
WThe human reproductive system includes the male reproductive system which functions to produce and deposit sperm; and the female reproductive system which functions to produce egg cells, and to protect and nourish the fetus until birth. Humans have a high level of sexual differentiation. In addition to differences in nearly every reproductive organ, there are numerous differences in typical secondary sex characteristics.
 W
WHysterectomy is the surgical removal of the uterus. It may also involve removal of the cervix, ovaries (oophorectomy), Fallopian tubes (salpingectomy), and other surrounding structures.
 W
WOogamy is the familiar form of sexual reproduction. It is a form of anisogamy (heterogamy) in which the female gamete is significantly larger than the male gamete and is non-motile. The male gametes are typically highly motile and are usually tasked with all of the travel necessary to bring the respective gametes together. The prevalence of oogamy in higher animals leads to the conclusion that this specialization of the gametes results in their performing their respective tasks better and more efficiently than those tasks could be performed by generalist isogametes, particularly the ability to concentrate high-energy substances in a smaller number of ova.
 W
WThe placenta is a temporary organ that connects the developing fetus via the umbilical cord to the uterine wall to allow nutrient uptake, thermo-regulation, waste elimination, and gas exchange via the mother's blood supply; to fight against internal infection; and to produce hormones which support pregnancy. Placentas are a defining characteristic of placental mammals, but are also found in marsupials and some non-mammals with varying levels of development.
 W
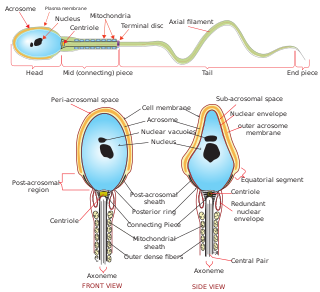
WSperm is the male reproductive cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction. Animals produce motile sperm with a tail known as a flagellum, which are known as spermatozoa, while some red algae and fungi produce non-motile sperm cells, known as spermatia. Flowering plants contain non-motile sperm inside pollen, while some more basal plants like ferns and some gymnosperms have motile sperm.
 W
WThe spermatid is the haploid male gametid that results from division of secondary spermatocytes. As a result of meiosis, each spermatid contains only half of the genetic material present in the original primary spermatocyte.
 W
WTubo-ovarian abscesses are one of the late complications of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) and can be life-threatening if the abscess ruptures and results in sepsis. It consists of an encapsulated or confined 'pocket of pus' with defined boundaries that forms during an infection of a fallopian tube and ovary. These abscesses are found most commonly in reproductive age women and typically result from upper genital tract infection. It is an inflammatory mass involving the fallopian tube, ovary and, occasionally, other adjacent pelvic organs. A TOA can also develop as a complication of a hysterectomy.
 W
WVaginoplasty is any surgical procedure that results in the construction or reconstruction of the vagina. It is a type of genitoplasty. Pelvic organ prolapse is often treated with one or more surgeries to repair the vagina. Sometimes a vaginoplasty is needed following the treatment or removal of malignant growths or abscesses in order to restore a normal vaginal structure and function. Surgery to the vagina is done to correct congenital defects to the vagina, urethra and rectum. It will correct protrusion of the urinary bladder into the vagina (cystocele) and protrusion of the rectum (rectocele) into the vagina. Often, a vaginoplasty is performed to repair the vagina and its attached structures due to trauma or injury.
 W
WThe zona pellucida is a glycoprotein layer surrounding the plasma membrane of mammalian oocytes. It is a vital constitutive part of the oocyte. The zona pellucida first appears in unilaminar primary oocytes. It is secreted by both the oocyte and the ovarian follicles. The zona pellucida is surrounded by the corona radiata. The corona is composed of cells that care for the egg when it is emitted from the ovary.
 W
WA zygote is a eukaryotic cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes. The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information necessary to form a new individual. In multicellular organisms, the zygote is the earliest developmental stage. In single-celled organisms, the zygote can divide asexually by mitosis to produce identical offspring.