 W
WNeuromuscular disease is a broad term that encompasses many diseases and ailments that impair the functioning of the muscles, either directly, being pathologies of the voluntary muscle, or indirectly, being pathologies of nerves or neuromuscular junctions.
 W
WBethlem myopathy is an autosomal dominant myopathy, classified as a congenital form of muscular dystrophy, that is caused by a mutation in one of the three genes coding for type VI collagen. These include COL6A1, COL6A2, and COL6A3. Gower's sign, tiptoe-walking and contractures of the joints are typical signs and symptoms of the disease. Bethlem myopathy could be diagnosed based on clinical examinations and laboratory tests may be recommended. Currently there is no cure for the disease and symptomatic treatment is used to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life. Bethlem myopathy affects about 1 in 200,000 people.
 W
WBotulism is a rare and potentially fatal illness caused by a toxin produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. The disease begins with weakness, blurred vision, feeling tired, and trouble speaking. This may then be followed by weakness of the arms, chest muscles, and legs. Vomiting, swelling of the abdomen, and diarrhea may also occur. The disease does not usually affect consciousness or cause a fever.
 W
WCentral core disease (CCD), also known as central core myopathy, is an autosomal dominantly inherited muscle disorder present from birth that negatively affects the skeletal muscles. It was first described by Shy and Magee in 1956. It is characterized by the appearance of the myofibril under the microscope.
 W
WCentronuclear myopathies (CNM) are a group of congenital myopathies where cell nuclei are abnormally located in the center of skeletal muscle cells instead of their normal location at the periphery.
 W
WHypokalemic periodic paralysis (hypoKPP), also known as familial hypokalemic periodic paralysis (FHPP), is a rare, autosomal dominant channelopathy characterized by muscle weakness or paralysis when there is a fall in potassium levels in the blood. In individuals with this mutation, attacks sometimes begin in adolescence and most commonly occur with individual triggers such as rest after strenuous exercise, high carbohydrate meals, meals with high sodium content, sudden changes in temperature, and even excitement, noise, flashing lights, cold temperatures and stress. Weakness may be mild and limited to certain muscle groups, or more severe full-body paralysis. During an attack, reflexes may be decreased or absent. Attacks may last for a few hours or persist for several days. Recovery is usually sudden when it occurs, due to release of potassium from swollen muscles as they recover. Some patients may fall into an abortive attack or develop chronic muscle weakness later in life.
 W
WLambert–Eaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS) is a rare autoimmune disorder characterized by muscle weakness of the limbs.
 W
WInjuries to the arm, forearm or wrist area can lead to various nerve disorders. One such disorder is median nerve palsy. The median nerve controls the majority of the muscles in the forearm. It controls abduction of the thumb, flexion of hand at wrist, flexion of digital phalanx of the fingers, is the sensory nerve for the first three fingers, etc. Because of this major role of the median nerve, it is also called the eye of the hand. If the median nerve is damaged, the ability to abduct and oppose the thumb may be lost due to paralysis of the thenar muscles. Various other symptoms can occur which may be repaired through surgery and tendon transfers. Tendon transfers have been very successful in restoring motor function and improving functional outcomes in patients with median nerve palsy.
 W
WMERRF syndrome is a mitochondrial disease. It is extremely rare, and has varying degrees of expressivity owing to heteroplasmy. MERRF syndrome affects different parts of the body, particularly the muscles and nervous system. The signs and symptoms of this disorder appear at an early age, generally childhood or adolescence. The causes of MERRF syndrome are difficult to determine, but because it is a mitochondrial disorder, it can be caused by the mutation of nuclear DNA or mitochondrial DNA. The classification of this disease varies from patient to patient, since many individuals do not fall into one specific disease category. The primary features displayed on a person with MERRF include myoclonus, seizures, cerebellar ataxia, myopathy, and ragged red fibers (RRF) on muscle biopsy, leading to the disease's name. Secondary features include dementia, optic atrophy, bilateral deafness, peripheral neuropathy, spasticity, or multiple lipomata. Mitochondrial disorders, including MERRFS, may present at any age.
 W
WMitochondrial myopathies are types of myopathies associated with mitochondrial disease. On biopsy, the muscle tissue of patients with these diseases usually demonstrate "ragged red" muscle fibers. These ragged-red fibers contain mild accumulations of glycogen and neutral lipids, and may show an increased reactivity for succinate dehydrogenase and a decreased reactivity for cytochrome c oxidase. Inheritance was believed to be maternal. It is now known that certain nuclear DNA deletions can also cause mitochondrial myopathy such as the OPA1 gene deletion. There are several subcategories of mitochondrial myopathies.
 W
WMuscular dystrophy (MD) is a group of muscle diseases that results in increasing weakening and breakdown of skeletal muscles over time. The disorders differ in which muscles are primarily affected, the degree of weakness, how fast they worsen, and when symptoms begin. Many people will eventually become unable to walk. Some types are also associated with problems in other organs.
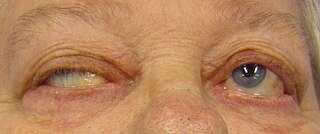 W
WMyasthenia gravis (MG) is a long-term neuromuscular disease that leads to varying degrees of skeletal muscle weakness. The most commonly affected muscles are those of the eyes, face, and swallowing. It can result in double vision, drooping eyelids, trouble talking, and trouble walking. Onset can be sudden. Those affected often have a large thymus or develop a thymoma.
Myotonic dystrophy is a long-term genetic disorder that affects muscle function. It is a type of muscular dystrophy. Symptoms include gradually worsening muscle loss and weakness. Muscles often contract and are unable to relax. Other symptoms may include cataracts, intellectual disability and heart conduction problems. In men, there may be early balding and an inability to have children.
 W
WParamyotonia congenita (PC), is a rare congenital autosomal dominant neuromuscular disorder characterized by “paradoxical” myotonia. This type of myotonia has been termed paradoxical because it becomes worse with exercise whereas classical myotonia, as seen in myotonia congenita, is alleviated by exercise. PC is also distinguished as it can be induced by cold temperatures. Although more typical of the periodic paralytic disorders, patients with PC may also have potassium-provoked paralysis. PC typically presents within the first decade of life and has 100% penetrance. Patients with this disorder commonly present with myotonia in the face or upper extremities. The lower extremities are generally less affected. While some other related disorders result in muscle atrophy, this is not normally the case with PC. This disease can also present as hyperkalemic periodic paralysis and there is debate as to whether the two disorders are actually distinct.
 W
WUllrich congenital muscular dystrophy is a form of congenital muscular dystrophy. It is associated with variants of type VI collagen, it is commonly associated with muscle weakness and respiratory problems, though cardiac issues are not associated with this type of CMD. It is named after Otto Ullrich, who is also known for the Ullrich-Turner syndrome.
 W
WX-linked myotubular myopathy (MTM) is a form of centronuclear myopathy (CNM) associated with myotubularin 1.
 W
WZaspopathy, also called ZASP-related myofibril myopathy, is a novel autosomal dominant form of progressive muscular dystrophy, first described in 2005.