 W
WThe abdominal aortic plexus is formed by branches derived, on either side, from the celiac plexus and ganglia, and receives filaments from some of the lumbar ganglia.
 W
WThe anterior vagal trunk is a branch of the vagus nerve which contributes to the esophageal plexus. It consists primarily of fibers from the left vagus, but also contains a few fibers from the right vagus nerve.
 W
WThe cardiac plexus is a plexus of nerves situated at the base of the heart that innervates the heart.
 W
WThe celiac plexus or coeliac plexus, also known as the solar plexus because of its radiating nerve fibers, is a complex network of nerves located in the abdomen, near where the celiac trunk, superior mesenteric artery, and renal arteries branch from the abdominal aorta. It is behind the stomach and the omental bursa, and in front of the crura of the diaphragm, on the level of the first lumbar vertebra.
 W
WThe superior gastric plexus accompanies the left gastric artery along the lesser curvature of the stomach, and joins with branches from the left vagus nerve.
 W
WThe hepatic plexus, the largest offset from the celiac plexus, receives filaments from the left vagus and right phrenic nerves.
 W
WThe inferior hypogastric plexus is a network (plexus) of nerves that supplies the organs of the pelvic cavity. The inferior hypogastric plexus gives rise to the prostatic plexus in males and the uterovaginal plexus in females.
 W
WThe inferior mesenteric plexus is derived chiefly from the aortic plexus.
 W
WThe posterior vagal trunk is a branch of the vagus nerve which contributes to the esophageal plexus. It consists primarily of fibers from the right vagus, but also contains a few fibers from the left vagus.
 W
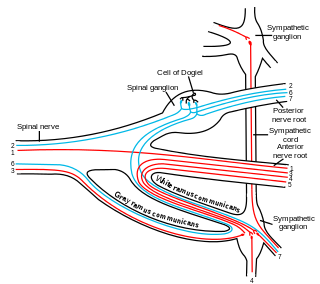
WRamus communicans is the Latin term used for a nerve which connects two other nerves, and can be translated as "communicating branch".
 W
WThe renal plexus is formed by filaments from the celiac ganglia and plexus, aorticorenal ganglia, lower thoracic splanchnic nerves and first lumbar splanchnic nerve and aortic plexus.
 W
WThe spermatic plexus is derived from the renal plexus, receiving branches from the aortic plexus. It accompanies the internal spermatic artery to the testis.
 W
WThe splenic plexus is formed by branches from the celiac plexus, the left celiac ganglion, and from the right vagus nerve.
 W
WThe superior hypogastric plexus is a plexus of nerves situated on the vertebral bodies anterior to the bifurcation of the abdominal aorta.
 W
WThe superior mesenteric plexus is a continuation of the lower part of the celiac plexus, receiving a branch from the junction of the right vagus nerve with the plexus.
 W
WThe suprarenal plexus is formed by branches from the celiac plexus, from the celiac ganglion, and from the phrenic and greater splanchnic nerves, a ganglion being formed at the point of junction with the latter nerve.
 W
WThe white ramus communicans from Latin ramus (branch) and communicans (communicating) is the preganglionic sympathetic outflow nerve tract from the spinal cord.