 W
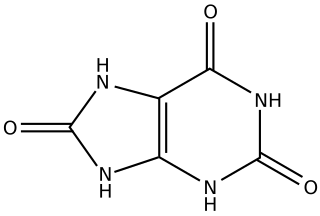
WExcretion is a process by which metabolic waste is eliminated from an organism. In vertebrates this is primarily carried out by the lungs, kidneys and skin. This is in contrast with secretion, where the substance may have specific tasks after leaving the cell. Excretion is an essential process in all forms of life. For example, in mammals urine is expelled through the urethra, which is part of the excretory system. In unicellular organisms, waste products are discharged directly through the surface of the cell.
 W
WAsher yatzar is a blessing in Judaism. It is recited after engaging in an act of excretion or urination, but is also included in many Jewish prayer books as a part of daily prayer prior to birkot hashachar.
 W
W"The Crabfish" is a ribald humorous folk song of the English oral tradition. It dates back to the seventeenth century, appearing in Bishop Percy's Folio Manuscript as a song named "The Sea Crabb" based on an earlier tale. The moral of the story is that one should look in the chamber pot before using it.
 W
WDefecation is the final act of digestion, by which organisms eliminate solid, semisolid, or liquid waste material from the digestive tract via the anus.
 W
WDried nasal mucus, colloquially known as a boogie, booger, bogey, or snot is found in the nose. It is a result of drying of the normally viscous colloidal mucus, commonly known as snot.
 W
WDrooling, or slobbering, is the flow of saliva outside the mouth. Drooling can be caused by excess production of saliva, inability to retain saliva within the mouth, or problems with swallowing.
 W
WIn pharmacology the elimination or excretion of a drug is understood to be any one of a number of processes by which a drug is eliminated from an organism either in an unaltered form or modified as a metabolite. The kidney is the main excretory organ although others exist such as the liver, the skin, the lungs or glandular structures, such as the salivary glands and the lacrimal glands. These organs or structures use specific routes to expel a drug from the body, these are termed elimination pathways:Urine, Tears, Perspiration Saliva Respiration Milk Faeces Bile
 W
WHainuwele, "The Coconut Girl", is a figure from the Wemale and Alune folklore of the island of Seram in the Maluku Islands, Indonesia. Her story is an origin myth.
 W
WIslamic hygienical jurisprudence includes a number of regulations involving cleanliness during salat through wudu and ghusl, as well as dietary laws and toilet etiquette for Muslims. The fiqh is based on admonitions in the Quran for Muslims to be ritually clean whenever possible, as well as in hadith literature.
 W
WIslamic toilet etiquette is a set of personal hygiene rules in Islam followed when going to the toilet. This code of Muslim hygienical jurisprudence is known as Qadaa' al-Haajah.
 W
WMucus is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both serous and mucous cells. It is a viscous colloid containing inorganic salts, antimicrobial enzymes, immunoglobulins, and glycoproteins such as lactoferrin and mucins, which are produced by goblet cells in the mucous membranes and submucosal glands. Mucus serves to protect epithelial cells in the linings of the respiratory, digestive, and urogenital systems, and structures in the visual and auditory systems from pathogenic fungi, bacteria and viruses. Most of the mucus in the body is produced in the gastrointestinal tract.
 W
WPerspiration, also known as sweating, is the production of fluids secreted by the sweat glands in the skin of mammals.
 W
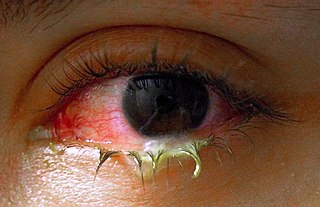
WPus is an exudate, typically white-yellow, yellow, or yellow-brown, formed at the site of inflammation during bacterial or fungal infection. An accumulation of pus in an enclosed tissue space is known as an abscess, whereas a visible collection of pus within or beneath the epidermis is known as a pustule, pimple or spot.
 W
WReuse of excreta refers to the safe, beneficial use of treated animal or human excreta after applying suitable treatment steps and risk management approaches that are customized for the intended reuse application. Beneficial uses of the treated excreta may focus on using the plant-available nutrients that are contained in the treated excreta. They may also make use of the organic matter and energy contained in the excreta. To a lesser extent, reuse of the excreta's water content might also take place, although this is better known as water reclamation from municipal wastewater. The intended reuse applications for the nutrient content may include: soil conditioner or fertilizer in agriculture or horticultural activities. Other reuse applications, which focus more on the organic matter content of the excreta, include use as a fuel source or as an energy source in the form of biogas.
 W
WSaliva is an extracellular fluid produced and secreted by salivary glands in the mouth. In humans, saliva is 99.5% water plus electrolytes, mucus, white blood cells, epithelial cells, enzymes, antimicrobial agents such as secretory IgA, and lysozymes.
 W
WSpitting is the act of forcibly ejecting saliva or other substances from the mouth. The act is often done to get rid of unwanted or foul-tasting substances in the mouth or to get rid of a large buildup of saliva.
 W
WUrination is the release of urine from the urinary bladder through the urethra to the outside of the body. It is the urinary system's form of excretion. It is also known medically as micturition, voiding, uresis, or, rarely, emiction, and known colloquially by various names including peeing, weeing, and pissing.
 W
W