 W
WAcanthurus nigricauda, the epaulette surgeonfish, black-barred surgeonfish, eye-line surgeonfish, shoulderbar surgeonfish, white-tail surgeonfish or blackstreak surgeonfish, is a tropical fish in the family Acanthuridae. It is native to the Indo-Pacific region.
 W
WAcanthurus nubilus is an herbivorous tropical fish also known as the bluelined surgeon or the pin-striped surgeon. It was first named by Fowler and Bean in 1929, and despite being a rare species, is used in aquariums.
 W
WAmphiprion mccullochi, also known as whitesnout anemonefish or McCulloch's anemonefish, is a species of anemonefish found in subtropical waters at Lord Howe Island and Norfolk Island.. It was named for Allan McCulloch, a former Curator of Fishes at the Australian Museum, Sydney. Like all anemonefishes it forms a symbiotic mutualism with sea anemones and is unaffected by the stinging tentacles of the host anemone. It is a sequential hermaphrodite with a strict sized based dominance hierarchy: the female is largest, the breeding male is second largest, and the male non-breeders get progressively smaller as the hierarchy descends. They exhibit protandry, meaning the breeding male will change to female if the sole breeding female dies, with the largest non-breeder becomes the breeding male.
 W
WAphyosemion splendopleure is a species of freshwater fish belonging to the family Aplocheilidae. It is found in brooks and streams in Cameroon, Equatorial Guinea and Gabon.
 W
WThe Arkansas River shiner is a species of ray-finned fish in the genus Notropis. It is native to part of the central United States. Historically this shiner was widespread and abundant throughout the western portions of the Arkansas River basin in Kansas, New Mexico, Oklahoma, and Texas. It is extirpated from the River in Kansas and Oklahoma. Recently, the species was almost entirely confined to about 820 km of the Canadian River in Oklahoma, Texas, and New Mexico, but it has been introduced and is now widely established in Pecos River in New Mexico.
 W
WThe Big Bend gambusia is a rare species of fish in the family Poeciliidae. It is endemic to the Big Bend region of the Rio Grande of the United States and Mexico. The only known remaining population is in a protected pond in the Big Bend National Park.
 W
WThe blacksail snake mackerel, known also as the black snoek, is a species of snake mackerel found in the Indo-Pacific from shallow water to a depth of at least 400 m (1,300 ft) where they appear to prefer slopes on seamounts and ridges. They are known for making diel vertical migrations to near-surface waters at night, feeding on fish, squid and crustaceans. This species reaches a total length of 2 m (6.6 ft) though most are around 1 m (3.3 ft). This species is of minor importance to local commercial fisheries. It is at the only member of the genus Thyrsitoides, making the genus monotypic.
 W
WThe brassy minnow is a species of fish belonging to the family Cyprinidae. The family Cyprinidae consists of mainly freshwater minnows and carps. The fish gets its scientific name from the Greek word Hybognathus, meaning bulging jaw, and hankinsoni from the American scientist, T.L. Hankinson. It is commonly found throughout the northern United States and Canada.
 W
WChauliodus danae, or dana viperfish, is a species of viperfish in the family Stomiidae. The Dana Viperfish is mostly found in the bathyal zone. The species was first caught and recognised on the Dana expeditions 1920-1922 and named after the research vessel Dana.
 W
WThe cherry barb is a tropical freshwater fish belonging to the family Cyprinidae. It is native to Sri Lanka, and introduced populations have become established in Mexico and Colombia. The cherry barb was named Puntius titteya by Paules Edward Pieris Deraniyagala in 1929. Synonyms include Barbus titteya and Capoeta titteya.
 W
WThe coffinfish is a species of sea toad of the family Chaunacidae, which consists of 17 species. It is found in salty temperate waters of southwestern Pacific, off east coast of Australia. The coffinfish was first discovered around February 1997 in Sicily, Italy by the skipper of the Libra, which was a trawler who was harbored in Mazara at the time. It can be also found in depths of 164–984.3 ft (50.0–300.0 m). Deep sea crab Fisher man off the east coast of Florida pull them up from depth ranging from 5,000-8,000 feet about 54–68 miles off the coast. They have a globose and spiny body that grows to a maximum length of 22.0 cm (8.7 in) and a black mouth lining and an illicium on the snout that can be lowered into a groove.
 W
WEconomidichthys pygmaeus, the Western Greece goby, is a species of freshwater goby endemic to western Greece where it is an inhabitant of streams and rivers. It is suspected to also occur in Albania. Males of this species can reach a length of 5.1 centimetres (2.0 in) TL while females can reach a length of 5.4 centimetres (2.1 in) TL.
 W
WThe eyespot gourami is a species of gourami endemic to Myanmar where it occurs in small, muddy streams and well vegetated shores of lakes.
 W
WHalicampus dunckeri or also commonly known as the Duncker's pipefish or ridgenose pipefish is a species of fish in the family Syngnathidae.
 W
WHaplochromis latifasciatus is a species of cichlid that is endemic to Uganda where restricted to the Lake Kyoga system, including Lake Bisina and Lake Nawampasa. This fish can reach a total length of 11 cm (4.3 in). It is also seen in the aquarium trade and it is easily bred in captivity. In the aquarium trade it is frequently labelled as Haplochromis "zebra obliquidens", which sometimes cause confusion with Haplochromis obliquidens, a separate species from Lake Victoria that is not known from the aquarium trade.
 W
WThe Olympic mudminnow is a fish native to the western lowlands of Washington: the Chehalis River basin, Deschutes River basin, and some Olympic Peninsula basins. It grows to 8 cm in length, and is Washington's only known endemic freshwater fish species. Although they strongly resemble killifish, mudminnows are more closely related to pike and muskellunge.
 W
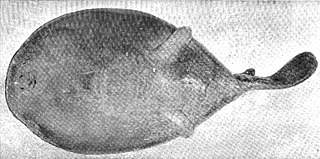
WThe oval electric ray is a little-known species of sleeper ray in the family Narkidae. It is endemic to New Zealand, where it is generally found on the sea floor at a depth of 300–400 m (980–1,310 ft). Seldom exceeding 30 cm (12 in) in length, this species has a thick, oval pectoral fin disc and a short, stout tail with a single dorsal fin. It is blind, as its tiny eyes are covered by skin. Its pelvic fins are divided in two, with the anterior portion forming a limb-like appendage. These appendages likely allow the ray, which may not be able to swim at all, to "walk" along the bottom. The claspers of adult males extend beyond the disc. Polychaete worms are known to be part of its diet, and its reproduction is aplacental viviparous. It can produce an electric shock for defense. The International Union for Conservation of Nature presently lacks the data to assess its conservation status.
 W
WThe sailfin roughshark is a species of dogfish shark in the family Oxynotidae, found in the eastern North Atlantic from Scotland to Senegal between latitudes 61°N and 11°N, at depths of between 265 and 720 m. Its length is up to 1.2 m (3.9 ft).