 W
WAcrodus is an extinct genus of cartilaginous fish from the Permian to Paleocene periods. Acrodus anningiae was named by Louis Agassiz in honor of the pioneering English paleontologist Mary Anning.
 W
WBobasatrania is an extinct genus of prehistoric bony fish that survived the Permian-Triassic extinction event. Fossils of Bobasatrania were found in beds of Lopingian to Anisian age. It was most speciose during the Early Triassic. The genus was named after the locality Bobasatrana in northeast Madagascar, from where the type species was described.
 W
WCoelacanthus is a genus of extinct coelacanths that first appeared during the Permian period. It was the first genus of coelacanths described and the order Coelacanthiformes is named after it.
 W
WCretalamna is a genus of extinct otodontid shark that lived from the Late Cretaceous to Eocene epoch. It is considered by many to be the ancestor of the largest sharks to have ever lived, Carcharocles angustidens, and Carcharocles megalodon.
 W
WDiplomystus is an extinct genus of freshwater clupeomorph fish distantly related to modern-day extant herrings, alewives, and sardines. The genus was first named and described by Edward Drinker Cope in 1877. There are seven species of Diplomystus: D. dentatus, D. birdii, D. dubetreiti, D. shengliensis, D. kokuraensis, D. primotinus, and D. altiformis.
 W
WHelicoprion is a genus of extinct, shark-like eugeneodontid holocephalid fish. Almost all fossil specimens are of spirally arranged clusters of the individuals' teeth, called "tooth whorls"— the cartilaginous skull, spine, and other structural elements have not been preserved in the fossil record, leaving scientists to make educated guesses as to its anatomy and behavior. Helicoprion lived in the oceans of the early Permian 290 million years ago, with species known from North America, Eastern Europe, Asia, and Australia. The closest living relatives of Helicoprion are the chimaeras.
 W
WIschyodus is an extinct genus of cartilaginous fish belonging to the subclass Holocephali, which includes the modern-day chimaeras. Fossils are known from Europe, North America, and New Zealand.
 W
WListracanthus is a genus of extinct chondrichthyan with uncertain affinities. Species of Listracanthus are known primarily from their tremendous, feather-like denticles, which range up to four inches in length. The denticles had a large main spine, from which secondary spines emanate from the sides, like the barbs of a feather or a comb. Listracanthus first appeared in late Carboniferous strata in North America, and eventually disappear from the fossil record some time during the Early Triassic.
 W
WNotogoneus is an extinct genus of prehistoric ray-finned fish. A trace fossil attributed to Notogoneus osculus has been found in the Green River Formation.
 W
WPalaeocarcharodon, also known as the pygmy white shark, is a genus of shark within the family Otodontidae that lived about 61.7 to 55.8 Ma during the Paleocene. It currently contains a sole species P. orientalis.
 W
WPhareodus is a genus of freshwater fish from the Paleocene to the Eocene of Australia, Europe and North and South America.
 W
WPristis lathami is a species of extinct sawfish in the family Pristidae. It lived in the Eocene era, in areas in Egypt, Nigeria, Togo, the United Kingdom, the United States, and Western Sahara, in marine areas, estuaries, bays, open shallow subtidal areas, coastal, marginal marine areas, deep waters, offshore, and fluvial-deltaic areas. P. lathami has 53 occurrences, with 1 being found in Egypt with a rostal tooth about 10 cm in length.
 W
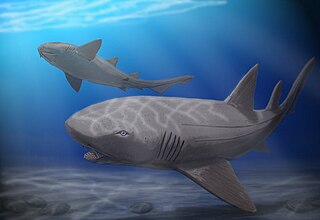
WPtychodus mortoni was a shark believed to be about 10 m long that probably crushed and ate large shelled animals such as giant clams.
 W
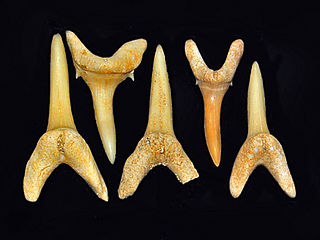
WStriatolamia is an extinct genus of sharks belonging to the family Odontaspididae. These extinct sharks lived from the Early Paleocene to Late Miocene.
 W
WThelodus is an extinct genus of thelodont agnathan that lived during the Silurian period. Fossils have been found in Europe, Asia and North America. Unlike many thelodonts, species of Thelodus are known not only from scales, but from impressions in rocks. Some species, such as the Canadian T. inauditus, are thought to be comparable in size to other thelodonts, i.e., from 5 to 15 centimeters in length. The scales of the type species, T. parvidens of Silurian Great Britain, however, reach the size of coins, and, if proportioned like other thelodonts, such as Loganellia, the living animal would have been about one meter in length.
 W
WTriodus is an extinct genus of xenacanthidan shark that lived from the Carboniferous to the Triassic. It was a freshwater shark, and fossils have been found in the Chinle Formation and Black Prince Limestone of Arizona, the Petrified Forest Member of New Mexico and the Tecovas Formation of Texas, United States. In 2017, a new species Triodus richterae was described from the Rio do Rasto Formation of Brazil.
 W
WXenacanthus is a genus of prehistoric sharks. The first species of the genus lived in the later Devonian period, and they survived until the end of the Triassic, 202 million years ago. Fossils of various species have been found worldwide.
 W
WXiphiorhynchus is an extinct genus of prehistoric swordfish that lived from the Eocene until the Miocene. Unlike the modern swordfish, both the upper and lower jaws of Xiphiorhynchus were extended into blade-like points.