 W
WActinobacillus suis is a beta-haemolytic, Gram-negative bacterium of the family Pasteurellaceae.
 W
WAfrican swine fever virus (ASFV) is a large, double-stranded DNA virus in the Asfarviridae family. It is the causative agent of African swine fever (ASF). The virus causes a hemorrhagic fever with high mortality rates in domestic pigs; some isolates can cause death of animals as quickly as a week after infection. It persistently infects its natural hosts, warthogs, bushpigs, and soft ticks of the genus Ornithodoros, which likely act as a vector, with no disease signs. It does not cause disease in humans. ASFV is endemic to sub-Saharan Africa and exists in the wild through a cycle of infection between ticks and wild pigs, bushpigs, and warthogs. The disease was first described after European settlers brought pigs into areas endemic with ASFV, and as such, is an example of an emerging infectious disease.
 W
WAscaris suum, also known as the large roundworm of pig, is a parasitic nematode that causes ascariasis in pigs. While roundworms in pigs and humans are today considered as two species with different hosts, cross-infection between humans and pigs is possible; some researchers have thus argued they are the same species. Ascariasis is associated with contact to pigs and pig manure in Denmark.
 W
WBrucella suis is a bacterium that causes swine brucellosis, a zoonosis that affects pigs. The disease typically causes chronic inflammatory lesions in the reproductive organs of susceptible animals or orchitis, and may even affect joints and other organs. The most common symptom is abortion in pregnant susceptible sows at any stage of gestation. Other manifestations are temporary or permanent sterility, lameness, posterior paralysis, spondylitis, and abscess formation. It is transmitted mainly by ingestion of infected tissues or fluids, semen during breeding, and suckling infected animals.
 W
WJapanese encephalitis (JE) is an infection of the brain caused by the Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV). While most infections result in little or no symptoms, occasional inflammation of the brain occurs. In these cases, symptoms may include headache, vomiting, fever, confusion and seizures. This occurs about 5 to 15 days after infection.
 W
WLeptospirosis is a blood infection caused by the bacteria Leptospira. Signs and symptoms can range from none to mild to severe. Weil's disease, the acute, severe form of leptospirosis, causes the infected individual to become jaundiced, develop kidney failure, and bleed. Bleeding from the lungs associated with leptospirosis is known as "severe pulmonary haemorrhage syndrome".
 W
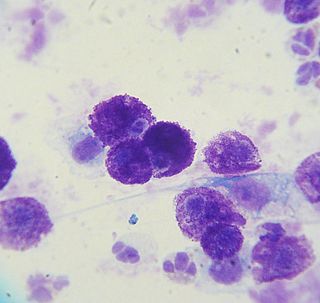
WA mastocytoma or mast cell tumor is a type of round-cell tumor consisting of mast cells. It is found in humans and many animal species; it also can refer to an accumulation or nodule of mast cells that resembles a tumor.
 W
WA Nipah virus infection is a viral infection caused by the Nipah virus. Symptoms from infection vary from none to fever, cough, headache, shortness of breath, and confusion. This may worsen into a coma over a day or two, and 50% to 75% of those infected die. Complications can include inflammation of the brain and seizures following recovery.
 W
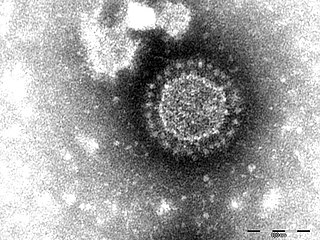
WPasteurellosis is an infection with a species of the bacterial genus Pasteurella, which is found in humans and other animals.
 W
WPorcine epidemic diarrhea virus is a coronavirus that infects the cells lining the small intestine of a pig, causing porcine epidemic diarrhoea, a condition of severe diarrhea and dehydration. Older hogs mostly get sick and lose weight after being infected, whereas newborn piglets usually die within five days of contracting the virus. PEDV cannot be transmitted to humans, nor contaminate the human food supply.
 W
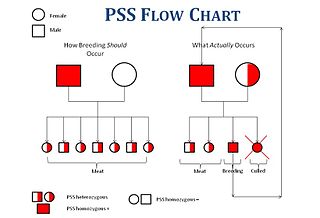
WPorcine stress syndrome, also known as malignant hyperthermia or PSS, is a condition in pigs. It is characterised by hyperthermia triggered by stress, anaesthesia with halothane or intense exercise. PSS may appear as sudden death in pigs, often after transport. It is an inherited, autosomal recessive disorder due to a defective ryanodine receptor leading to huge calcium influx, muscle contracture and increase in metabolism.
 W
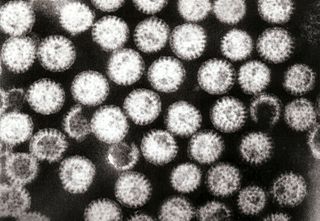
WRotavirus gastroenteritis is the most common cause of severe diarrhoea among infants and young children. It is caused by Rotavirus, a genus of double-stranded RNA virus in the family Reoviridae. By the age of five, nearly every child in the world has been infected with rotavirus at least once. However, with each infection, immunity develops, and subsequent infections are less severe; adults are rarely affected. There are five species of this virus, referred to as A, B, C, D, and E. Rotavirus A, the most common, causes more than 90% of infections in humans.
 W
WSalmonellosis is a symptomatic infection caused by bacteria of the Salmonella type. The most common symptoms are diarrhea, fever, abdominal cramps, and vomiting. Symptoms typically occur between 12 hours and 36 hours after exposure, and last from two to seven days. Occasionally more significant disease can result in dehydration. The old, young, and others with a weakened immune system are more likely to develop severe disease. Specific types of Salmonella can result in typhoid fever or paratyphoid fever.
 W
WSavaging is a term used in the study of ethology that refers to aggressive behaviour displayed by the mother towards the offspring. Aggressive behaviour includes being rough with, injuring, biting, attacking, crushing and killing of the offspring. While savaging behaviour has been seen in multiple species, it is predominantly demonstrated in domestic pigs. As the definition of savaging is so broad, research on the prevalence of savaging behaviour varies with reports of little savaging of offspring to savaging of offspring up to the 20th percentile. Prevalence of aggressive, non-fatal savaging is greater in gilts as piglet-focused aggression is more frequent in young animals than sows. Occurrence of savaging demonstrated by sows is greater if the sow has previously savaged her offspring either as a gilt or sow. Savaging behaviour usually occurs during the first two days after parturition. Prevalence of savaging is similar among first and second farrowing cycles. Savaging behaviour has a significant impact on both agricultural economy and animal welfare which is why it is currently a subject of interest in the pig industry.
 W
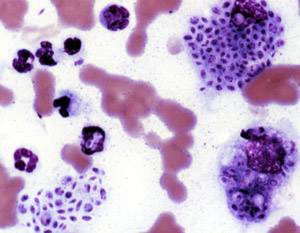
WSporotrichosis is a disease caused by the infection of the fungus Sporothrix schenckii. This fungal disease usually affects the skin, although other rare forms can affect the lungs, joints, bones, and even the brain. Because roses can spread the disease, it is one of a few diseases referred to as rose-thorn or rose-gardeners' disease. The species was named for Benjamin Schenck, a medical student who in 1896 was the first to isolate it from a human specimen.
 W
WSwine influenza is an infection caused by any one of several types of swine influenza viruses. Swine influenza virus (SIV) or swine-origin influenza virus (S-OIV) is any strain of the influenza family of viruses that is endemic in pigs. As of 2009, the known SIV strains include influenza C and the subtypes of influenza A known as H1N1, H1N2, H2N1, H3N1, H3N2, and H2N3.
 W
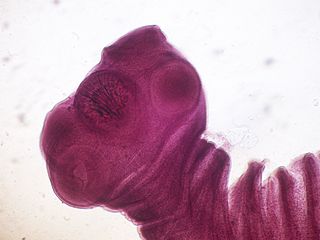
WThe pork tapeworm, Taenia solium, belongs to the cyclophyllid cestode family Taeniidae. It is found throughout the world and is most common in countries where pork is eaten. It is a tapeworm which has humans as its definitive host and often pigs as intermediate or secondary host. It may be transmitted to pigs through human faeces contaminating their fodder, and back to humans through consumption of uncooked, or under-cooked, pork that contains tapeworm cysts. Pigs ingest tapeworm eggs, which develop into larvae, then into oncospheres, and ultimately into infective tapeworm cysts. An ingested tapeworm cyst grows into an adult worm in human small intestines.
 W
WTransmissible gastroenteritis virus or Transmissible gastroenteritis coronavirus (TGEV) is a coronavirus which infects pigs. It is an enveloped, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA virus which enters its host cell by binding to the APN receptor. The virus is a member of the genus Alphacoronavirus, subgenus Tegacovirus, species Alphacoronavirus 1.