 W
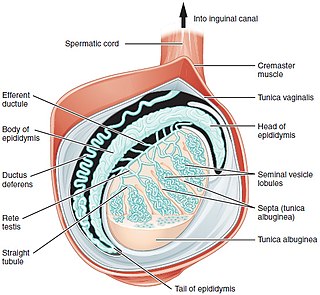
WTesticle or testis is the male reproductive gland or gonad in all animals, including humans. It is homologous to the female ovary. The functions of the testes are to produce both sperm and androgens, primarily testosterone. Testosterone release is controlled by the anterior pituitary luteinizing hormone; whereas sperm production is controlled both by the anterior pituitary follicle-stimulating hormone and gonadal testosterone.
 W
WThe testicular artery is a branch of the abdominal aorta that supplies blood to the testis. It is a paired artery, with one for each of the testes.
 W
WThe scrotum is an anatomical male reproductive structure located caudal to the penis that consists of a suspended dual-chambered sack of skin and smooth muscle. It is present in most terrestrial male mammals. The scrotum contains the external spermatic fascia, testes, epididymis, and ductus deferens. It is a distention of the perineum and carries some abdominal tissues into its cavity including the testicular artery, testicular vein, and pampiniform plexus. The perineal raphe is a small, vertical, slightly raised ridge of scrotal skin under which is found the scrotal septum. It appears as a thin longitudinal line that runs front to back over the entire scrotum. In humans and some other mammals the scrotum becomes covered with pubic hair at puberty. The scrotum will usually tighten during penile erection and when exposed to cold temperature. One testis is typically lower than the other to avoid compression in the event of impact.
 W
WThe blood–testis barrier is a physical barrier between the blood vessels and the seminiferous tubules of the animal testes. The name "blood-testis barrier" is misleading in that it is not a blood-organ barrier in a strict sense, but is formed between Sertoli cells of the seminiferous tubule and as such isolates the further developed stages of germ cells from the blood. A more correct term is the "Sertoli cell barrier" (SCB).
 W
WCock and ball torture (CBT), penis torture or dick torture is a sexual activity involving application of pain or constriction to the penis or testicles. This may involve directly painful activities, such as genital piercing, wax play, genital spanking, squeezing, ball-busting, genital flogging, urethral play, tickle torture, erotic electrostimulation, kneeing or kicking. The recipient of such activities may receive direct physical pleasure via masochism, or emotional pleasure through erotic humiliation, or knowledge that the play is pleasing to a sadistic dominant. Many of these practices carry significant health risks.
 W
WLamb fries are lamb testicles used as food. Historically they were parboiled, cut in half, and seasoned. Lamb testicles are served in a variety of cuisines, including Italian, Basque, breaded and fried in some barbecue restaurants, Chinese, Caucasian, Persian and Iranian Armenian, and Turkish. The dish is rarely served at restaurants in the United States, but can occasionally be found at Iranian restaurants.
 W
WAn orchidometer is a medical instrument used to measure the volume of the testicles.
 W
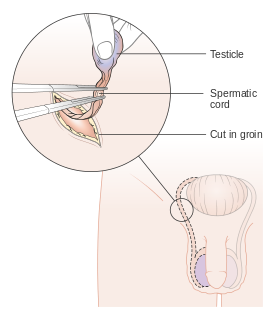
WOrchiectomy is a surgical procedure in which one or both testicles are removed, as a form of castration. The surgery is typically performed as treatment for testicular cancer, in some cases of testicular torsion, as a gender-affirming procedure for trans women, and is sometimes used in the management of advanced prostate cancer.
 W
WOrchiopexy is a surgery to move an undescended (cryptorchid) testicle into the scrotum and permanently fix it there. Orchiopexy typically also describes the surgery used to resolve testicular torsion.
 W
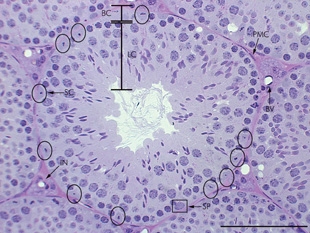
WA peritubular myoid (PTM) cell is one of the smooth muscle cells which surround the seminiferous tubules in the testis. These cells are present in all mammals but their organisation and abundance varies between species. The exact role of PTM cells is still somewhat uncertain and further work into this is needed. However, a number of functions of these cells have been established. They are contractile cells which contain actin filaments and are primarily involved in transport of spermatozoa through the tubules. They provide structural integrity to the tubules through their involvement in laying down the basement membrane. This has also been shown to affect Sertoli cell function and PTM cells also communicate with Sertoli cells through the secretion of growth factors and ECM components. Studies have shown PTM cells to be critical in achieving normal spermatogenesis. Overall, PTM cells have a role in both maintaining the structure of the tubules and regulating spermatogenesis through cellular interaction.
 W
WPolyorchidism is the incidence of more than two testicles. It is a very rare congenital disorder, with fewer than 200 cases reported in medical literature and six cases in veterinary literature.
 W
WRocky Mountain oysters, or mountain oysters, or meat balls, also known as prairie oysters in Canada, is a dish made of bull testicles. The organs are often deep-fried after being skinned, coated in flour, pepper and salt, and sometimes pounded flat. This delicacy is most often served as an appetizer.
 W
WThe scrotum is an anatomical male reproductive structure located caudal to the penis that consists of a suspended dual-chambered sack of skin and smooth muscle. It is present in most terrestrial male mammals. The scrotum contains the external spermatic fascia, testes, epididymis, and ductus deferens. It is a distention of the perineum and carries some abdominal tissues into its cavity including the testicular artery, testicular vein, and pampiniform plexus. The perineal raphe is a small, vertical, slightly raised ridge of scrotal skin under which is found the scrotal septum. It appears as a thin longitudinal line that runs front to back over the entire scrotum. In humans and some other mammals the scrotum becomes covered with pubic hair at puberty. The scrotum will usually tighten during penile erection and when exposed to cold temperature. One testis is typically lower than the other to avoid compression in the event of impact.
 W
WSeminiferous tubules are located within the testes, and are the specific location of meiosis, and the subsequent creation of male gametes, namely spermatozoa.
 W
WA Sertoli cell is a "nurse" cell of the testicles that is part of a seminiferous tubule and helps in the process of spermatogenesis, the production of sperm.
 W
WA testicle festival is an event held at several small towns where the featured activity is the consumption of animal testicles, usually battered and fried.
 W
WThe testicles of calves, lambs, roosters, turkeys, and other animals are eaten in many parts of the world, often under euphemistic culinary names. Testicles are a by-product of the castration of young animals raised for meat, so they were probably a late-spring seasonal specialty, though nowadays they are generally frozen and available year-round.
 W
WTruck nuts, also called truck nutz, are vehicular vanity accessories resembling a dangling scrotum. They are attached under the rear bumper or trailer hitch making them plainly visible to other vehicles behind.