 W
WAminophenazone is a pyrazolone with analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic properties but has risk of agranulocytosis. A breath test with 13C-labeled aminopyrine has been used as a non-invasive measure of cytochrome P-450 metabolic activity in liver function tests. It is also used in measuring the total body water in the human body system. Production and use have been banned in France, Thailand and India.
 W
WAmpyrone is a metabolite of aminopyrine with analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic properties. Due to the risk of agranulocytosis its use as a drug is discouraged. It is used as a reagent for biochemical reactions producing peroxides or phenols. Ampyrone stimulates liver microsomes and is also used to measure extracellular water.
 W
WBenorilate (INN), or benorylate, is an ester-linked codrug of aspirin with paracetamol. It is used as an anti-inflammatory and antipyretic medication. In the treatment of childhood fever, it has been shown to be inferior to paracetamol and aspirin taken separately. In addition, because it is converted to aspirin, benorylate is not recommended in children due to concerns about Reye syndrome.
 W
WBucetin is an analgesic and antipyretic that is no longer marketed. Chemically, it is similar to phenacetin with which it shares the risk of carcinogenesis. Bucetin was withdrawn from use in 1986 due to renal toxicity.
 W
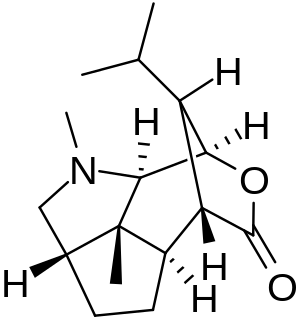
WDendrobine is an alkaloid found in Dendrobium nobile at an average of 0.5% by weight. It is a colorless solid at room temperature. It is related to the picrotoxin family of natural products. When given a fatal dose, death is usually caused by convulsions. It possesses a molecular structure that attracted interest in its total synthesis by organic chemists.
 W
WDipyrocetyl is a pharmaceutical drug used as an analgesic and antipyretic.
 W
WKairine is a derivative of tetrahydroquinoline which was first described by Wilhelm Fischer in 1883. Its name comes from the Greek kairos, meaning "the right time". It is an antipyretic, formerly used against typhoid fever, but now largely obsolete due to severe side effects. Both kairine and its N-ethyl homolog show similar antipyretic activity.
 W
WMetacetamol, also known as 3-hydroxyacetanilide and AMAP, is a non-toxic regioisomer of paracetamol with analgesic and antipyretic properties, but has never been marketed as a drug.
 W
WMetamizole, or dipyrone, is a painkiller, spasm reliever, and fever reliever that also has anti-inflammatory effects. It is most commonly given by mouth or by injection.
 W
WNaproxen, sold under the brand name Aleve among others, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to treat pain, menstrual cramps, inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, and fever. It is taken orally. It is available in immediate and delayed release formulations. Onset of effects is within an hour and last for up to twelve hours.
 W
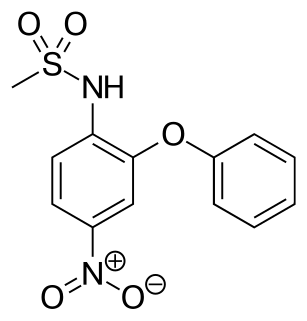
WNimesulide is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) with pain medication and fever reducing properties. Its approved indications are the treatment of acute pain, the symptomatic treatment of osteoarthritis, and primary dysmenorrhoea in adolescents and adults above 12 years old.
 W
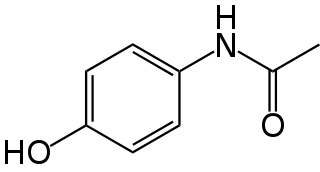
WParacetamol, also known as acetaminophen, is a medication used to treat pain and fever. It is typically used for mild to moderate pain relief. Evidence is mixed for its use to relieve fever in children. It is often sold in combination with other medications, such as in many cold medications. Paracetamol is also used for severe pain, such as cancer pain and pain after surgery, in combination with opioid pain medication. It is typically used either by mouth or rectally, but is also available by injection into a vein. Effects last between two and four hours.
 W
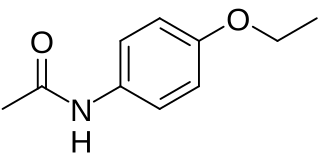
WPhenacetin is a pain-relieving and fever-reducing drug, which was widely used following its introduction in 1887. It was withdrawn from medicinal use as dangerous from the 1970s.
 W
WPhenazone is an analgesic, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) and an antipyretic.
 W
WPiperylone is a pyrazolone with analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic properties.
 W
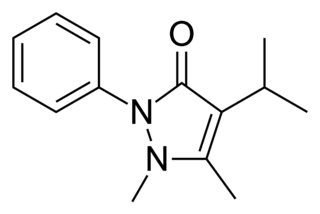
WPropyphenazone is a derivative of phenazone with similar analgesic and antipyretic effects. It is known as isopropylantipyrine in Japan. It was patented in 1931. The drug is marketed as a combination of (Paracetamol-Caffeine-Propyphenazone) tablets in effective treatment for primary headache disorder. It is marketed globally by Bayer, and in India as "Saridon" by Piramal, and "Dart" by Juggat Pharma.
 W
WSalicylamide is a non-prescription drug with analgesic and antipyretic properties. Its medicinal uses are similar to those of aspirin. Salicylamide is used in combination with both aspirin and caffeine in the over-the-counter pain remedy PainAid. It was also an ingredient in the over-the-counter pain remedy BC Powder but was removed from the formulation in 2009, and Excedrin used the ingredient from 1960 to 1980 in conjunction with aspirin, acetaminophen, and caffeine. It was used in later formulations of Vincent's powders in Australia as a substitute for phenacetin.
 W
WTolfenamic acid is a member of the anthranilic acid derivatives class of NSAID drugs discovered by scientists at Medica Pharmaceutical Company in Finland. Like other members of the class, it is a COX inhibitor and prevents formation of prostaglandins.
 W
WTylenol is a brand of drugs advertised for reducing pain, reducing fever, and relieving the symptoms of allergies, cold, cough, headache, and influenza. The active ingredient of its original flagship product is paracetamol, an analgesic and antipyretic. Like the words paracetamol and acetaminophen, the brand name Tylenol is derived from a chemical name for the compound, N-acetyl-para-aminophenol (APAP). The brand name is owned by McNeil Consumer Healthcare, a subsidiary of Johnson & Johnson.