 W
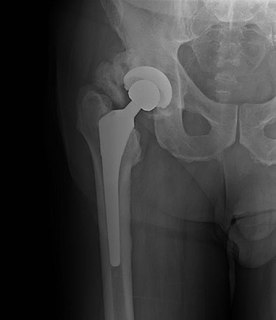
WAvascular necrosis (AVN), also called osteonecrosis or bone infarction, is death of bone tissue due to interruption of the blood supply. Early on, there may be no symptoms. Gradually joint pain may develop which may limit the ability to move. Complications may include collapse of the bone or nearby joint surface.
 W
WComplex regional pain syndrome (CRPS), also known as reflex sympathetic dystrophy (RSD), describes an array of painful conditions that are characterized by a continuing regional pain that is seemingly disproportionate in time or degree to the usual course of any known trauma or other lesion. Usually starting in a limb, it manifests as extreme pain, swelling, limited range of motion, and changes to the skin and bones. It may initially affect one limb and then spread throughout the body; 35% of affected people report symptoms throughout their whole bodies. Two subtypes exist. Having both types is possible.
 W
WFibrous dysplasia is a disorder where normal bone and marrow is replaced with fibrous tissue, resulting in formation of bone that is weak and prone to expansion. As a result, most complications result from fracture, deformity, functional impairment, and pain. Disease occurs along a broad clinical spectrum ranging from asymptomatic, incidental lesions, to severe disabling disease. Disease can affect one bone (monostotic), multiple (polyostotic), or all bones (panostotic) and may occur in isolation or in combination with café au lait skin macules and hyperfunctioning endocrinopathies, termed McCune–Albright syndrome. More rarely, fibrous dysplasia may be associated with intramuscular myxomas, termed Mazabraud's syndrome. Fibrous dysplasia is very rare, and there is no known cure. Fibrous dysplasia is not a form of cancer.
 W
WHeterotopic ossification (HO) is the process by which bone tissue forms outside of the skeleton.
 W
WHyperostosis is an excessive growth of bone. It may lead to exostosis. It occurs in many musculoskeletal disorders.
 W
WHyperostosis frontalis interna is a common, benign thickening of the inner side of the frontal bone of the skull. It is found predominantly in women after menopause and is usually asymptomatic. Mostly frequently it is found as an incidental finding discovered during an X-ray or CT scan of the skull.
 W
WHypertrophic osteoarthropathy is a medical condition combining clubbing and periostitis of the small hand joints, especially the distal interphalangeal joints and the metacarpophalangeal joints. Distal expansion of the long bones as well as painful, swollen joints and synovial villous proliferation are often seen. The condition may occur alone (primary), or it may be secondary to diseases like lung cancer. Among patients with lung cancer, it is most associated with adenocarcinoma and least associated with small cell lung cancer. These patients often get clubbing and increased bone deposition on long bones. Their presenting symptoms are sometimes only clubbing and painful ankles.
 W
WJuvenile osteoporosis is osteoporosis in children and adolescents. Osteoporosis is rare in children and adolescents. When it occurs, it is usually secondary to some other condition, e.g. osteogenesis imperfecta, rickets, eating disorders or arthritis. In some cases, there is no known cause and it is called idiopathic juvenile osteoporosis. Idiopathic juvenile osteoporosis usually goes away spontaneously.
 W
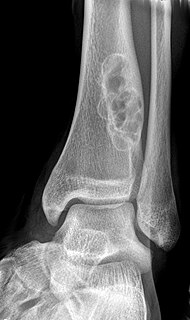
WA nonossifying fibroma is a common benign bone tumor in children and adolescents. However, it is controversial whether it represents a true neoplasm or rather a developmental disorder of growing bone. Radiographically, the tumor presents as a well marginated radiolucent lesion, with a distinct multilocular appearance. These foci consist of collagen rich connective tissue, fibroblasts, histiocytes and osteoclasts. They originate from the growth plate, and are located in adjacent parts of the metaphysis and diaphysis of long bones, most often of the legs. No treatment is needed in asymptomatic patients and spontaneous remission with replacement by bone tissue is to be expected.
 W
WNonunion is permanent failure of healing following a broken bone unless intervention is performed. A fracture with nonunion generally forms a structural resemblance to a fibrous joint, and is therefore often called a "false joint" or pseudoarthrosis. The diagnosis is generally made when there is no healing between two sets of medical imaging such as X-ray or CT scan. This is generally after 6–8 months.
 W
WOsteomalacia is a disease characterized by the softening of the bones caused by impaired bone metabolism primarily due to inadequate levels of available phosphate, calcium, and vitamin D, or because of resorption of calcium. The impairment of bone metabolism causes inadequate bone mineralization. Osteomalacia in children is known as rickets, and because of this, use of the term "osteomalacia" is often restricted to the milder, adult form of the disease. Signs and symptoms can include diffuse body pains, muscle weakness, and fragility of the bones. In addition to low systemic levels of circulating mineral ions necessary for bone and tooth mineralization, accumulation of mineralization-inhibiting proteins and peptides occurs in the extracellular matrix of bones and teeth, likely contributing locally to cause matrix hypomineralization (osteomalacia).
 W
WOsteomyelitis (OM) is an infection of bone. Symptoms may include pain in a specific bone with overlying redness, fever, and weakness. The long bones of the arms and legs are most commonly involved in children, while the feet, spine, and hips are most commonly involved in adults.
 W
WOsteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass, micro architectural deterioration of bone tissue leading to bone fragility, and consequent increase in fracture risk. It is the most common reason for a broken bone among the elderly. Bones that commonly break include the vertebrae in the spine, the bones of the forearm, and the hip. Until a broken bone occurs there are typically no symptoms. Bones may weaken to such a degree that a break may occur with minor stress or spontaneously. After a broken bone, chronic pain and a decreased ability to carry out normal activities may occur.
 W
WOsteosclerosis is a disorder that is characterized by abnormal hardening of bone and an elevation in bone density. It may predominantly affect the medullary portion and/or cortex of bone. Plain radiographs are a valuable tool for detecting and classifying osteosclerotic disorders. It can manifest in localized or generalized osteosclerosis. Localized osteosclerosis can be caused by Legg–Calvé–Perthes disease, sickle-cell disease and osteoarthritis among others. Osteosclerosis can be classified in accordance with the causative factor into acquired and hereditary.
 W
WPaget's disease of bone is a condition involving cellular remodeling and deformity of one or more bones. The affected bones show signs of dysregulated bone remodeling at the microscopic level, specifically excessive bone breakdown and subsequent disorganized new bone formation. These structural changes cause the bone to weaken, which may result in deformity, pain, fracture or arthritis of associated joints.
 W
WSclerostin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SOST gene.
 W
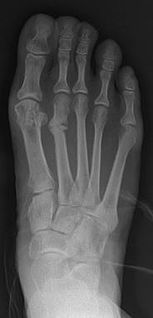
WSkeletal fluorosis is a bone disease caused by excessive accumulation of fluoride leading to weakened bones. In advanced cases, skeletal fluorosis causes painful damage to bones and joints.
 W
WA stress fracture is a fatigue-induced fracture of the bone caused by repeated stress over time. Instead of resulting from a single severe impact, stress fractures are the result of accumulated trauma from repeated submaximal loading, such as running or jumping. Because of this mechanism, stress fractures are common overuse injuries in athletes.
 W
WWeismann-Netter–Stuhl syndrome, also known as Weismann-Netter syndrome or tibioperoneal diaphyseal toxopachyosteosis, is a rare disorder characterized by bowing of the lower legs and an abnormal thickening of thinner bone in the leg.