 W
WBoreostemma is an extinct genus of glyptodonts from northern South America. Fossils assigned to the genus were first described as belonging to Asterostemma from southern South America, but have been placed in the new genus Boreostemma by Carlini et al. in 2008. The type species is B. pliocena. Fossils of Boreostemma have been found in the Honda Group of Colombia, in Peru and Venezuela.
 W
WDasypus bellus, the beautiful armadillo, is an extinct armadillo species endemic to North America and South America from the Pleistocene, living from 1.8 mya—11,000 years ago, existing for approximately 1.789 million years .
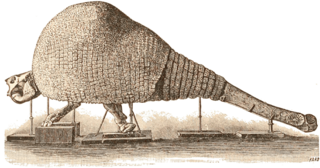 W
WDoedicurus, or Dædicurus, is an extinct genus of glyptodont from South America containing one species, D. clavicaudatus. Glyptodonts are a member of the family Chlamyphoridae, which also includes some modern armadillo species, and they are classified in the order Xenarthra alongside sloths and anteaters. Being a glyptodont, it was a rotund animal with heavy armor and a carapace. Averaging at an approximate 1,400 kg (3,100 lb), it was one of the largest glyptodonts to have ever lived. Though glyptodonts were quadrupeds, large ones like Doedicurus may have been able to stand on two legs like other xenarthrans. It notably sported a spiked tail club, which may have weighed 40 or 65 kg in life, and it may have swung this in defense against predators or in fights with other Doedicurus at speeds of perhaps 11 m/s.
 W
WEleutherocercus was a genus of glyptodonts that lived during the Late Miocene and Early Pliocene in South America. Fossils of the genus have been found in the Huayquerian Ituzaingó Formation and the Montehermosan Monte Hermoso Formation in Argentina.
 W
WEutatus is an extinct genus of large armadillos of the family Dasypodidae. It was endemic to South America from the Early Miocene to Late Pleistocene, living from 17.5 Ma-11,000 years ago, with possible survival into the early Holocene and existing for approximately 17.49 million years . Based on carbon isotope ratios, it is thought to have been an herbivore that fed on grasses.
 W
WGlyptodon was a genus of large, heavily armored mammals of the subfamily Glyptodontinae – relatives of armadillos – that lived during the Pleistocene epoch. It was roughly the same size and weight as a Volkswagen Beetle. With its rounded, bony shell and squat limbs, it superficially resembled a turtle, and the much earlier dinosaurian ankylosaur – providing an example of the convergent evolution of unrelated lineages into similar forms. In 2016 an analysis of Doedicurus mtDNA found it was, in fact, nested within the modern armadillos as the sister group of a clade consisting of Chlamyphorinae and Tolypeutinae. For this reason, glyptodonts and all armadillos but Dasypus were relocated to a new family, Chlamyphoridae, and glyptodonts were demoted from the former family Glyptodontidae to a subfamily.
 W
WGlyptodontinae is an extinct subfamily of large, heavily armored relatives of armadillos, members of the mostly South American mammalian superorder Xenarthra. They developed in South America around 20 million years ago and spread to southern North America after the continents became connected several million years ago. The best-known genus within the subfamily is Glyptodon.
 W
WGlyptotherium is an extinct genus of glyptodont, a group of extinct mammals related to the armadillos living from the Middle to Late Pleistocene, approximately 1.8 million to 12,000 years ago (AEO). The genus is considered an example of North American megafauna, of which most have become extinct. Glyptotherium may have been wiped out by changing climate or human interference.
 W
WHolmesina is a genus of pampathere, an extinct group of armadillo-like creatures that were distantly related to extant armadillos. Like armadillos, and unlike the other extinct branch of megafaunal cingulates, the glyptodonts, the shell was made up of flexible plates which allowed the animal to move more easily. Holmesina species were herbivores that grazed on coarse vegetation; armadillos are mostly insectivorous or omnivorous.
 W
WHoplophorus was an extinct genus of glyptodont, a family of mammals related to armadillo. The only known species was H. euphractus, found in Pleistocene deposits in Piauí, and Minas Gerais, in Brazil.
 W
WLomaphorus is an extinct genus of glyptodont that lived during the Pleistocene in eastern Argentina. Fossils of the genus were found in the Lagunilla del Plata Formation.
 W
WMacroeuphractus is a genus of extinct armadillos from the Late Miocene to Late Pliocene of South America. The genus is noted for its large size, with Macroeuphractus outesi being the largest non-pampathere or glyptodont armadillo discovered, as well as its specializations for carnivory, unique among all xenarthrans.
 W
WNeosclerocalyptus was an extinct genus of glyptodont that lived during the Pleistocene in northeastern Argentina.
 W
WPampatheriidae is an extinct family of large plantigrade armored xenarthrans related to armadillos. However, pampatheriids have existed as a separate lineage since at least the middle Eocene Mustersan age, 45 to 48 million years ago. Pampatheres evolved in South America during its long period of Cenozoic isolation. Although widespread, they were less diverse and abundant than the armadillos. Holmesina spread to North America after the formation of the Isthmus of Panama as part of the Great American Interchange. They finally disappeared on both continents in the end-Pleistocene extinctions, about 12,000 years ago.
 W
WPanochthus is an extinct genus of glyptodont, which lived in the Gran Chaco-Pampean region of Argentina, Brazil, Bolivia, Paraguay and Uruguay during the Pleistocene epoch.
 W
WPeltephilus, the horned armadillo, is an extinct genus of dog-sized, armadillo xenarthran mammals which first inhabited Argentina during the Oligocene epoch, and became extinct in the Miocene epoch. Notably, the scutes on its head were so developed that they formed horns. Aside from the horned gophers of North America, it is the only known fossorial horned mammal.
 W
WPropalaehoplophorus, also written as Propalaeohoplophorus, is an extinct genus of glyptodont, which lived in South America during the Early Miocene epoch.
 W
WSclerocalyptus was a glyptodont that lived during the Pleistocene in Argentina. Four species are described from the Ensenadan, S. pseudornatus, S. ornatus, S. perfectus and S. cordubensis, and two Lujanian taxa S. heusseri and S. evidens.
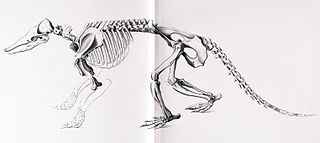 W
WStegotherium is an extinct genus of armadillo in the family Dasypodidae from Early Miocene Argentina.