 W
WAmantadine, sold under the brand name Gocovri among others, is a medication used to treat dyskinesia associated with parkinsonism and influenza caused by type A influenzavirus, though its use for the latter is no longer recommended due to widespread drug resistance. It acts as a nicotinic antagonist, dopamine agonist, and noncompetitive NMDA antagonist. The antiviral mechanism of action is antagonism of the influenzavirus A M2 proton channel, which prevents endosomal escape.
 W
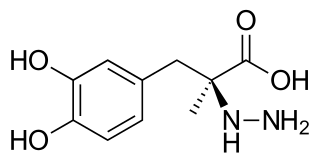
WBenserazide is a peripherally acting aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase or DOPA decarboxylase inhibitor, which is unable to cross the blood–brain barrier.
 W
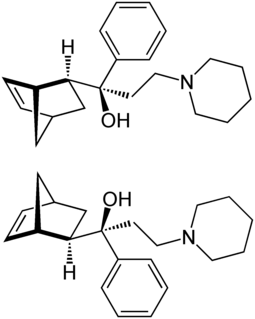
WBiperiden, sold under the brand name Akineton among others, is a medication used to treat Parkinson disease and certain drug-induced movement disorders. It is not recommended for tardive dyskinesias. It is taken by mouth, injection into a vein, or muscle.
 W
WBornaprine is a synthetic anticholinergic medication that is primarily used to treat Parkinson's disease. Additionally, bornaprine has been used to treat other disorders, including hyperhidrosis.
 W
WBudipine is an antiparkinson agent marketed for the treatment of Parkinson's disease.
 W
WCarbidopa (Lodosyn) is a drug given to people with Parkinson's disease in order to inhibit peripheral metabolism of levodopa. This property is significant in that it allows a greater proportion of peripheral levodopa to cross the blood–brain barrier for central nervous system effect.
 W
WCycrimine is a central anticholinergic drug designed to reduce the levels of acetylcholine in the treatment of Parkinson's disease. Its mechanism of action is to bind to the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M1.
 W
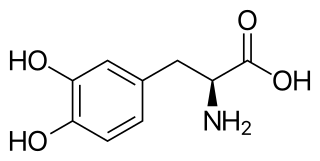
Wl-DOPA, also known as levodopa and l-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine, is an amino acid that is made and used as part of the normal biology of humans, as well as some animals and plants. Humans, as well as a portion of the other animals that utilize l-DOPA in their biology, make it via biosynthesis from the amino acid l-tyrosine. l-DOPA is the precursor to the neurotransmitters dopamine, norepinephrine (noradrenaline), and epinephrine (adrenaline), which are collectively known as catecholamines. Furthermore, l-DOPA itself mediates neurotrophic factor release by the brain and CNS. l-DOPA can be manufactured and in its pure form is sold as a psychoactive drug with the INN levodopa; trade names include Sinemet, Pharmacopa, Atamet, and Stalevo. As a drug, it is used in the clinical treatment of Parkinson's disease and dopamine-responsive dystonia.
 W
WEtanautine, also known as diphenhydramine monoacefyllinate, is an anticholinergic used as an antiparkinsonian agent. It is a 1:1 salt of diphenhydramine with acefylline, similar to the diphenhydramine/8-chlorotheophylline combination product dimenhydrinate.
 W
WEtybenzatropine (INN), also known as ethybenztropine and tropethydrylin, is an anticholinergic/antihistamine marketed under the trade names Panolid, Ponalid, and Ponalide, which is used as an antiparkinsonian agent. Like its analogue benzatropine, it may act as a dopamine reuptake inhibitor.
 W
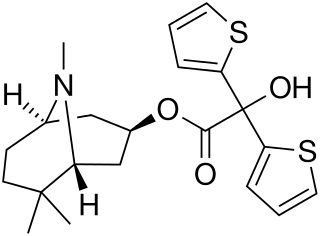
WMazaticol (Pentona) is an anticholinergic used as an antiparkinsonian agent in Japan.
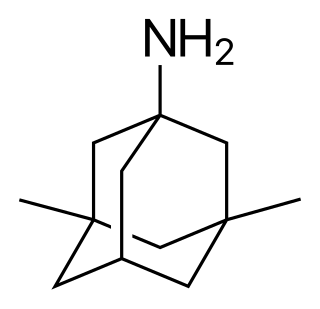 W
WMemantine is a medication used to treat moderate-to-severe Alzheimer's disease. It is less preferred than acetylcholinesterase inhibitors such as donepezil. Treatment should only be continued if beneficial effects are seen. It is taken by mouth.
 W
WMetixene, also known as methixene, is an anticholinergic used as an Management of Parkinson's disease#Medication}antiparkinsonian agent.
 W
WMofegiline (MDL-72,974) is a selective, irreversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B) and semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidase (SSAO) which was under investigation for the treatment of Parkinson's disease and Alzheimer's disease, but was never marketed.
 W
WPiroheptine is an anticholinergic and antihistamine used as an antiparkinsonian agent.
 W
WPridinol, sold under the brand name Myopridin, is a muscle relaxant that is used as an antiparkinsonian and anticholinergic drug.
 W
WRasagiline is an irreversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase-B used as a monotherapy to treat symptoms in early Parkinson's disease or as an adjunct therapy in more advanced cases.
 W
WSelegiline, also known as L-deprenyl and sold under the brand names Eldepryl and Emsam among others, is a medication which is used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease and major depressive disorder. It is provided in the form of a capsule or tablet taken by mouth for Parkinson's disease and as a patch applied to skin for depression.
 W
WTraxoprodil is a drug developed by Pfizer which acts as an NMDA antagonist, selective for the NR2B subunit. It has neuroprotective, analgesic, and anti-Parkinsonian effects in animal studies. Traxoprodil has been researched in humans as a potential treatment to lessen the damage to the brain after stroke, but results from clinical trials showed only modest benefit. The drug was found to cause EKG abnormalities and its clinical development was stopped. More recent animal studies have suggested traxoprodil may exhibit rapid-acting antidepressant effects similar to those of ketamine, although there is some evidence for similar psychoactive side effects and abuse potential at higher doses, which might limit clinical acceptance of traxoprodil for this application.
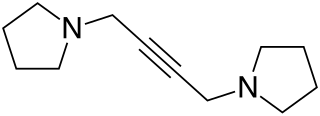 W
WTremorine is a drug which is used in scientific research to produce tremor in animals. This is used for the development of drugs for the treatment of Parkinson's disease, as tremor is a major symptom which is treated by anti-Parkinson's drugs. Beta blockers are also effective in counteracting the effects of tremorine.