 W
WThe alar fascia is a layer of fascia, sometimes described as part of the prevertebral fascia, and sometimes as in front of it.
 W
WThe buccopharyngeal fascia is a fascia in the head.
 W
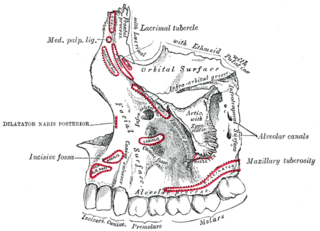
WThe canine space, is a fascial space of the head and neck. It is a thin potential space on the face, and is paired on either side. It is located between the levator anguli oris muscle inferiorly and the levator labii superioris muscle superiorly. The term is derived from the fact that the space is in the region of the canine fossa, and that infections originating from the maxillary canine tooth may spread to involve the space. Infra-orbital is derived from infra- meaning below and orbit which refers to the eye socket.
 W
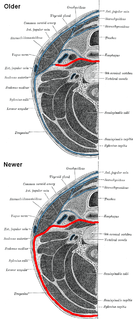
WThe deep cervical fascia lies under cover of the platysma, and invests the muscles of the neck; it also forms sheaths for the carotid vessels, and for the structures situated in front of the vertebral column. Its attachment to the hyoid bone prevents the formation of a dewlap.
 W
WThe deep temporal space is a fascial space of the head and neck. It is a potential space in the side of the head, and is paired on either side. It is located deep to the temporalis muscle
 W
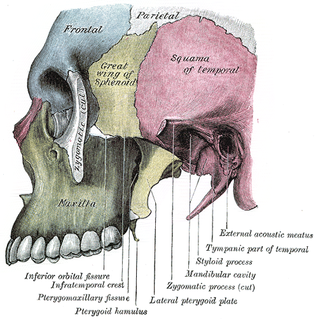
WThe Infratemporal space is a fascial space of the head and neck. It is a potential space in the side of the head, and is paired on either side. It is located posterior to the maxilla, between the lateral pterygoid plate of the sphenoid bone medially and by the base of skull superiorly. The term is derived from infra- meaning below and temporal which refers to the temporalis muscle.
 W
WThe Investing layer of deep cervical fascia is the most superficial part of the deep cervical fascia, and it encloses the whole neck.
 W
WThe masseteric fascia is a strong layer of fascia derived from the deep cervical fascia on the human head and neck. It covers the masseter, and is firmly connected to it. Above, this fascia is attached to the lower border of the zygomatic arch, and behind, it invests the parotid gland proceeding into the parotid fascia.
 W
WThe mental space is a fascial space of the head and neck. It is a potential space, bilaterally located in the chin, between the mentalis muscle superiorly and the platysma muscle inferiorly. These spaces may be created by pathology, e.g., the spread of odontogenic infection. Commonly the origin of the infection is an anterior mandibular tooth with associated periapical abscess which erodes through the buccal cortical plate of the mandibular at a level below the attachment of the mentalis muscle.
 W
WThe parapharyngeal space, is a potential space in the head and the neck. It has clinical importance in otolaryngology due to parapharyngeal space tumours and parapharyngeal abscess developing in this area. It is also a key anatomic landmark for localizing disease processes in the surrounding spaces of the neck; the direction of its displacement indirectly reflects the site of origin for masses or infection in adjacent areas, and consequently their appropriate differential diagnosis.
 W
WThe pretracheal fascia is a portion of the structure of the human neck. It extends medially in front of the carotid vessels and assists in forming the carotid sheath.
 W
WThe prevertebral fascia is a fascia in the neck.
 W
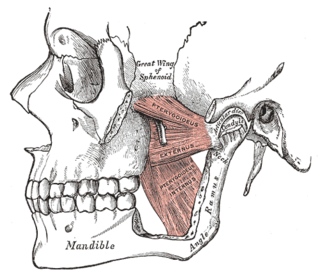
WThe pterygomandibular space is a fascial space of the head and neck. It is a potential space in the head and is paired on each side. It is located between the medial pterygoid muscle and the medial surface of the ramus of the mandible. The pterygomandibular space is one of the four compartments of the masticator space.
 W
WThe retropharyngeal space is a potential space of the head and neck, bounded by the buccopharyngeal fascia anteriorly and the alar fascia posteriorly.
 W
WThe sublingual space is a fascial space of the head and neck. It is a potential space located below the mouth and above the mylohyoid muscle, and is part of the suprahyoid group of fascial spaces.
 W
WThe submandibular space is a fascial space of the head and neck. It is a potential space, and is paired on either side, located on the superficial surface of the mylohyoid muscle between the anterior and posterior bellies of the digastric muscle. The space corresponds to the anatomic region termed the submandibular triangle, part of the anterior triangle of the neck.
 W
WThe submasseterric space is a fascial space of the head and neck. It is a potential space in the face over the angle of the jaw, and is paired on each side. It is located between the lateral aspect of the mandible and the medial aspect of the masseter muscle and its investing fascia. The term is derived from sub- meaning "under" in Latin and masseteric which refers to the masseter muscle. The submasseteric space is one of the four compartments of the masticator space. Sometimes the submasseteric space is described as a series of spaces, created because the masseter muscle has multiple insertions that cover most of the lateral surface of the ramus of the mandible.
 W
WThe submental space is a fascial space of the head and neck. It is a potential space located between the mylohyoid muscle superiorly, the platysma muscle inferiorly, under the chin in the midline. The space coincides with the anatomic region termed the submental triangle, part of the anterior triangle of the neck.
 W
WThe temporal fascia covers the temporalis muscle.
 W
WThe thoracolumbar fascia is a deep investing membrane throughout most of the posterior thorax and abdomen although it is a thin fibrous lamina in the thoracic region. Above, it is continuous with a similar investing layer on the back of the neck—the nuchal fascia.