 W
WAldrin is an organochlorine insecticide that was widely used until the 1990s, when it was banned in most countries. Aldrin is a member of the so-called "classic organochlorines" (COC) group of pesticides. COCs enjoyed a very sharp rise in popularity during and after The Second World War. Other noteworthy examples of COCs include DDT. After research showed that organochlorines can be highly toxic to the ecosystem through bioaccumulation, most were banned from use. It is a colourless solid. Before the ban, it was heavily used as a pesticide to treat seed and soil. Aldrin and related "cyclodiene" pesticides became notorious as persistent organic pollutants.
 W
WAzinphos-ethyl was a broad-spectrum organophosphate insecticide.
 W
WBinapacryl was used as a miticide and fungicide. Chemically, it is an ester derivative of dinoseb. Although binapacryl has low toxicity itself, it is readily metabolized to form dinoseb, which is highly toxic.
 W
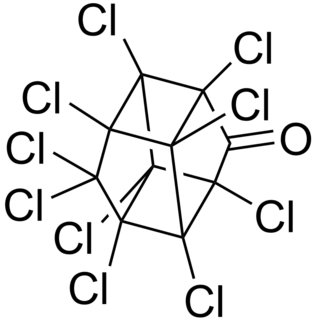
WChlordecone, better known under the brand name Kepone in the United States, is an organochlorine compound and a colourless solid. This compound is an obsolete insecticide related to Mirex and DDT. Its use was so disastrous that it is now prohibited in the western world, but only after many thousands of tonnes had been produced. Chlordecone is a known persistent organic pollutant (POP) that was banned globally by the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants in 2009.
 W
WDemeton was a phosphorothioate insecticide with the chemical formula C8H19O3PS2. While it was previously used as an insecticide, it is now largely obsolete due to its relatively high toxicity to humans. The chemical structure of demeton is closely related to military nerve agents such as VX, and a derivative with one of the ethoxy groups replaced by methyl was investigated by both the US and Soviet chemical weapons programs under the names "V.sub.X" and "GD-7".
 W
WDieldrin is an organochloride originally produced in 1948 by J. Hyman & Co, Denver, as an insecticide. Dieldrin is closely related to aldrin, which reacts further to form dieldrin. Aldrin is not toxic to insects; it is oxidized in the insect to form dieldrin which is the active compound. Both dieldrin and aldrin are named after the Diels-Alder reaction which is used to form aldrin from a mixture of norbornadiene and hexachlorocyclopentadiene.
 W
WDimefox was an organophosphate pesticide. In its pure form it is a colourless liquid with a fishy odour. Dimefox was first produced in 1940 by the group of Gerhard Schrader in Germany. It was historically used as a pesticide, but has been deemed obsolete or discontinued for use by the World Health Organization. However, they do not guarantee that all commercial use of this compound ceased. But in most countries it is no longer registered for use as a pesticide. It is considered an extremely hazardous substance as defined by the United States Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act.
 W
WEndrin is an organochloride with the chemical formula C12H8Cl6O that was first produced in 1950 by Shell and Velsicol Chemical Corporation. It was primarily used as an insecticide, as well as a rodenticide and piscicide. It is a colourless, odorless solid, although commercial samples are often off-white. Endrin was manufactured as an emulsifiable solution known commercially as Endrex. The compound became infamous as a persistent organic pollutant and for this reason it is banned in many countries.
 W
WFentin acetate is an organotin compound with the formula (C6H5)3SnO2CCH3. It is a colourless solid that was previously used as a fungicide.
 W
WHeptachlor is an organochlorine compound that was used as an insecticide. Usually sold as a white or tan powder, heptachlor is one of the cyclodiene insecticides. In 1962, Rachel Carson's Silent Spring questioned the safety of heptachlor and other chlorinated insecticides. Due to its highly stable structure, heptachlor can persist in the environment for decades. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency has limited the sale of heptachlor products to the specific application of fire ant control in underground transformers. The amount that can be present in different foods is regulated.
 W
WMercury(I) chloride is the chemical compound with the formula Hg2Cl2. Also known as the mineral calomel (a rare mineral) or mercurous chloride, this dense white or yellowish-white, odorless solid is the principal example of a mercury(I) compound. It is a component of reference electrodes in electrochemistry.
 W
WMethoxychlor is a synthetic organochloride insecticide, now obsolete.
 W
WMirex is an organochloride that was commercialized as an insecticide and later banned because of its impact on the environment. This white crystalline odorless solid is a derivative of cyclopentadiene. It was popularized to control fire ants but by virtue of its chemical robustness and lipophilicity it was recognized as a bioaccumulative pollutant. The spread of the red imported fire ant was encouraged by the use of Mirex, which also kills native ants that are highly competitive with the fire ants. The United States Environmental Protection Agency prohibited its use in 1976. It is prohibited by the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants.
 W
WOrganomercury refers to the group of organometallic compounds that contain mercury. Typically the Hg–C bond is stable toward air and moisture but sensitive to light. Important organomercury compounds are the methylmercury(II) cation, CH3Hg+; ethylmercury(II) cation, C2H5Hg+; dimethylmercury, (CH3)2Hg, diethylmercury, and merbromin ("Mercurochrome"). Thiomersal is used as a preservative for vaccines and intravenous drugs.
 W
WOrganotin compounds or stannanes are chemical compounds based on tin with hydrocarbon substituents. Organotin chemistry is part of the wider field of organometallic chemistry. The first organotin compound was diethyltin diiodide ((C2H5)2SnI2), discovered by Edward Frankland in 1849. The area grew rapidly in the 1900s, especially after the discovery of the Grignard reagents, which are useful for producing Sn-C bonds. The area remains rich with many applications in industry and continuing activity in the research laboratory.
 W
WParathion, also called parathion-ethyl or diethyl parathion and locally known as "Folidol", is an organophosphate insecticide and acaricide. It was originally developed by IG Farben in the 1940s. It is highly toxic to non-target organisms, including humans, so its use has been banned or restricted in most countries. The basic structure is shared by parathion methyl.
 W
WPromecarb (chemical formula: C12H17NO2) is a chemical compound previously used as an insecticide.
 W
WStockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants is an international environmental treaty, signed in 2001 and effective from May 2004, that aims to eliminate or restrict the production and use of persistent organic pollutants (POPs).
 W
WToxaphene was an insecticide used primarily for cotton in the southern United States during the late 1960s and 1970s. Toxaphene is a mixture of over 670 different chemicals and is produced by reacting chlorine gas with camphene. It can be most commonly found as a yellow to amber waxy solid.
 W
W2,4,5-Trichlorophenoxyacetic acid, a synthetic auxin, is a chlorophenoxy acetic acid herbicide used to defoliate broad-leafed plants. It was developed in the late 1940s and was widely used in the agricultural industry until being phased out, starting in the late 1970s due to toxicity concerns. Agent Orange, a defoliant used by the British in the Malayan Emergency and the U.S. in the Vietnam War, was equal parts 2,4,5-T and 2,4-D. 2,4,5-T itself is toxic with a NOAEL of 3 mg/kg/day and a LOAEL of 10 mg/kg/day. Additionally, the manufacturing process for 2,4,5-T contaminates this chemical with trace amounts of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD). TCDD is a carcinogenic persistent organic pollutant with long-term effects on the environment. With proper temperature control during production of 2,4,5-T, TCDD levels can be held to about .005 ppm. Before the TCDD risk was well understood, early production facilities lacked proper temperature controls and individual batches tested later were found to have as much as 60 ppm of TCDD.