 W
WBack strain is the injury occurring to muscles or tendons. Due to back strain, the tendons and muscles supporting the spine are twisted or pulled. Chronic back strain occurs because of the sustained trauma and wearing out of the back muscles Acute back strain can occur following a single instance of over stressing of back muscles, as in lifting a heavy object. Chronic back strain is more common than the acute type.
 W
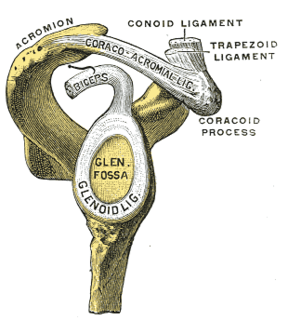
WA Bankart lesion is an injury of the anterior (inferior) glenoid labrum of the shoulder due to anterior shoulder dislocation. When this happens, a pocket at the front of the glenoid forms that allows the humeral head to dislocate into it. It is an indication for surgery and often accompanied by a Hill-Sachs lesion, damage to the posterior humeral head.
 W
WBlount's disease is a growth disorder of the tibia that causes the lower leg to angle inward, resembling a bowleg.It is also known as "tibia vara".
 W
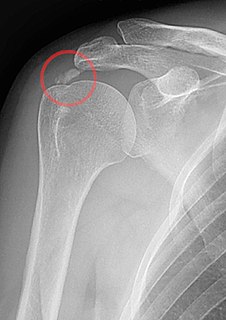
WCalcific tendinitis is a form of tendinitis, a disorder characterized by deposits of hydroxyapatite in any tendon of the body, but most commonly in the tendons of the rotator cuff (shoulder), causing pain and inflammation. The condition is related to and may cause adhesive capsulitis.
 W
WClay-shoveler's fracture is a stable fracture through the spinous process of a vertebra occurring at any of the lower cervical or upper thoracic vertebrae, classically at C6 or C7. In Australia in the 1930s, men digging deep ditches tossed clay 10 to 15 feet above their heads using long handled shovels. Instead of separating, the sticky clay would sometimes stick to the shovel; the worker would hear a pop and feel a sudden pain between the shoulder blades, unable to continue working. The mechanism of injury is believed to be secondary to muscle pull and reflex with force transmission through the supraspinous ligaments. The tremendous force pulls on the spinous process producing an avulsion fracture. The fracture is diagnosed by plain film examination.
 W
WDactylitis or sausage digit is inflammation of an entire digit, and can be painful.
 W
WFlat feet is a postural deformity in which the arches of the foot collapse, with the entire sole of the foot coming into complete or near-complete contact with the ground.
 W
WA flexion teardrop fracture is a fracture of the anteroinferior aspect of a cervical vertebral body due to flexion of the spine along with vertical axial compression. The fracture continues sagittally through the vertebral body, and is associated with deformity of the body and subluxation or dislocation of the facet joints at the injured level. A flexion teardrop fracture is usually associated with a spinal cord injury, often a result of displacement of the posterior portion of the vertebral body into the spinal canal.
 W
WGenu recurvatum is a deformity in the knee joint, so that the knee bends backwards. In this deformity, excessive extension occurs in the tibiofemoral joint. Genu recurvatum is also called knee hyperextension and back knee. This deformity is more common in women and people with familial ligamentous laxity. Hyperextension of the knee may be mild, moderate or severe.
 W
WA Hill–Sachs lesion, or Hill–Sachs fracture, is a cortical depression in the posterolateral head of the humerus. It results from forceful impaction of the humeral head against the anteroinferior glenoid rim when the shoulder is dislocated anteriorly.
 W
WKnee pain is pain in or around the knee.
 W
WLarsen syndrome (LS) is a congenital disorder discovered in 1950 by Larsen and associates when they observed dislocation of the large joints and face anomalies in six of their patients. Patients with Larsen syndrome normally present with a variety of symptoms, including congenital anterior dislocation of the knees, dislocation of the hips and elbows, flattened facial appearance, prominent foreheads, and depressed nasal bridges. Larsen syndrome can also cause a variety of cardiovascular and orthopedic abnormalities. This rare disorder is caused by a genetic defect in the gene encoding filamin B, a cytoplasmic protein that is important in regulating the structure and activity of the cytoskeleton. The gene that influences the emergence of Larsen syndrome is found in chromosome region, 3p21.1-14.1, a region containing human type VII collagen gene. Larsen syndrome has recently been described as a mesenchyme disorder that affects the connective tissue of an individual. Autosomal dominant and recessive forms of the disorder have been reported, although most cases are autosomal dominant. Reports have found that in Western societies, Larsen syndrome can be found in one in every 100,000 births, but this is most likely an underestimate because the disorder is frequently unrecognized or misdiagnosed.
 W
WOlecranon fracture is a fracture of the bony portion of the elbow. The injury is fairly common and often occurs following a fall or direct trauma to the elbow. The olecranon is the proximal extremity of the ulna which is articulated with the humerus bone and constitutes a part of the elbow articulation. Its location makes it vulnerable to direct trauma.
 W
WPerthes lesion is a variant of Bankart lesion, presenting as an anterior glenohumeral injury that occurs when the scapular periosteum remains intact but is stripped medially and the anterior labrum is avulsed from the glenoid but remains partially attached to the scapula by intact periosteum.
 W
WPlanovalgus deformity is a postural deformity, flat foot typology, very frequent in people with cerebral palsy and often due to muscle imbalance resulting in a predominance of the pronotory versus the supinatory forces.
 W
WRadioulnar synostosis is a rare condition where there is an abnormal connection between the radius and ulna bones of the forearm. This can be present at birth (congenital), when it is a result of a failure of the bones to form separately, or following an injury (post-traumatic).
 W
WSciatica is pain going down the leg from the lower back. This pain may go down the back, outside, or front of the leg. Onset is often sudden following activities like heavy lifting, though gradual onset may also occur. The pain is often described as shooting. Typically, symptoms are only on one side of the body. Certain causes, however, may result in pain on both sides. Lower back pain is sometimes present. Weakness or numbness may occur in various parts of the affected leg and foot.
 W
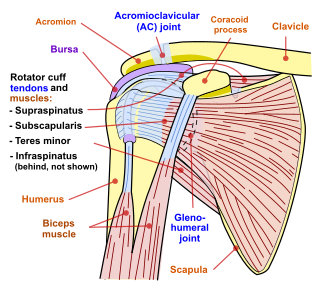
WShoulder problems including pain, are one of the more common reasons for physician visits for musculoskeletal symptoms. The shoulder is the most movable joint in the body. However, it is an unstable joint because of the range of motion allowed. This instability increases the likelihood of joint injury, often leading to a degenerative process in which tissues break down and no longer function well.
 W
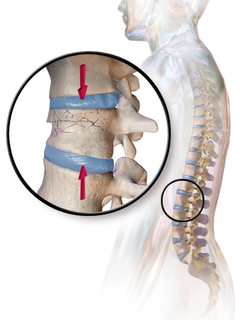
WA compression fracture is a collapse of a vertebra. It may be due to trauma or due to a weakening of the vertebra. This weakening is seen in patients with osteoporosis or osteogenesis imperfecta, lytic lesions from metastatic or primary tumors, or infection. In healthy patients, it is most often seen in individuals suffering extreme vertical shocks, such as ejecting from an ejection seat. Seen in lateral views in plain x-ray films, compression fractures of the spine characteristically appear as wedge deformities, with greater loss of height anteriorly than posteriorly and intact pedicles in the anteroposterior view.
 W
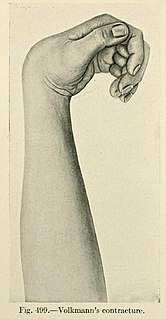
WVolkmann's contracture is a permanent flexion contracture of the hand at the wrist, resulting in a claw-like deformity of the hand and fingers. Passive extension of fingers is restricted and painful.