 W
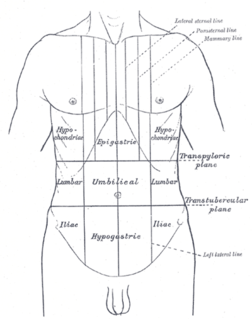
WAbdominal distension occurs when substances, such as air (gas) or fluid, accumulate in the abdomen causing its expansion. It is typically a symptom of an underlying disease or dysfunction in the body, rather than an illness in its own right. People suffering from this condition often describe it as "feeling bloated". Sufferers often experience a sensation of fullness, abdominal pressure, and sometimes nausea, pain, or cramping. In the most extreme cases, upward pressure on the diaphragm and lungs can also cause shortness of breath. Through a variety of causes, bloating is most commonly due to buildup of gas in the stomach, small intestine, or colon. The pressure sensation is often relieved, or at least lessened, by belching or flatulence. Medications that settle gas in the stomach and intestines are also commonly used to treat the discomfort and lessen the abdominal distension.
 W
WAbdominal pain, also known as a stomach ache, is a symptom associated with both non-serious and serious medical issues.
 W
WAscites is the abnormal buildup of fluid in the abdomen. Technically, it is more than 25 ml of fluid in the peritoneal cavity, although volumes greater than 1 liter may occur. Symptoms may include increased abdominal size, increased weight, abdominal discomfort, and shortness of breath. Complications can include spontaneous bacterial peritonitis.
 W
WBad breath, also known as halitosis, is a symptom in which a noticeably unpleasant breath odour is present. It can result in anxiety among those affected. It is also associated with depression and symptoms of obsessive compulsive disorder.
 W
WCancer and nausea are associated in about fifty percent of people affected by cancer. This may be as a result of the cancer itself, or as an effect of the treatment such as chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or other medication such as opiates used for pain relief. About 70 to 80% of people undergoing chemotherapy experience nausea or vomiting. Nausea and vomiting may also occur in people not receiving treatment, often as a result of the disease involving the gastrointestinal tract, electrolyte imbalance, or as a result of anxiety. Nausea and vomiting may be experienced as the most unpleasant side effects of cytotoxic drugs and may result in patients delaying or refusing further radiotherapy or chemotherapy.
 W
WCastell's sign is a medical sign assessed to evaluate splenomegaly and typically part of an abdominal examination. It is an alternative physical examination maneuver to percussion over Traube's space.
 W
WDefecation is the final act of digestion, by which organisms eliminate solid, semisolid, or liquid waste material from the digestive tract via the anus.
 W
WDiarrhea, also spelled diarrhoea, is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements each day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration due to fluid loss. Signs of dehydration often begin with loss of the normal stretchiness of the skin and irritable behaviour. This can progress to decreased urination, loss of skin color, a fast heart rate, and a decrease in responsiveness as it becomes more severe. Loose but non-watery stools in babies who are exclusively breastfed, however, are normal.
 W
WDysphagia is difficulty in swallowing. Although classified under "symptoms and signs" in ICD-10, in some contexts it is classified as a condition in its own right.
 W
WFecal incontinence (FI), or in some forms encopresis, is a lack of control over defecation, leading to involuntary loss of bowel contents, both liquid stool elements and mucus, or solid feces. When this loss includes flatus (gas) it is referred to as anal incontinence. FI is a sign or a symptom, not a diagnosis. Incontinence can result from different causes and might occur with either constipation or diarrhea. Continence is maintained by several interrelated factors, including the anal sampling mechanism, and usually there is more than one deficiency of these mechanisms for incontinence to develop. The most common causes are thought to be immediate or delayed damage from childbirth, complications from prior anorectal surgery, altered bowel habits, and receptive anal sex. An estimated 2.2% of community dwelling adults are affected.
 W
WFlatulence is defined in the medical literature as "flatus expelled through the anus" or the "quality or state of being flatulent", which is defined in turn as "marked by or affected with gases generated in the intestine or stomach; likely to cause digestive flatulence". The root of these words is from the Latin flatus – "a blowing, a breaking wind". Flatus is also the medical word for gas generated in the stomach or bowels. Despite these standard definitions, a proportion of intestinal gas may be swallowed environmental air, and hence flatus is not totally generated in the stomach or bowels. The scientific study of this area of medicine is termed flatology.
 W
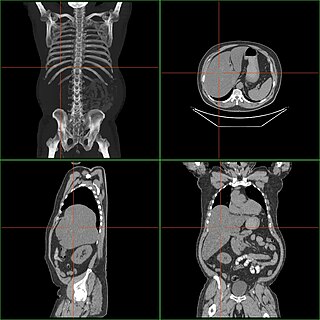
WHepatomegaly is the condition of having an enlarged liver. It is a non-specific medical sign having many causes, which can broadly be broken down into infection, hepatic tumours, or metabolic disorder. Often, hepatomegaly will present as an abdominal mass. Depending on the cause, it may sometimes present along with jaundice.
 W
WJaundice, also known as icterus, is a yellowish or greenish pigmentation of the skin and whites of the eyes due to high bilirubin levels. Jaundice in adults is typically a sign indicating the presence of underlying diseases involving abnormal heme metabolism, liver dysfunction, or biliary tract obstruction. The prevalence of jaundice in adults is rare, while jaundice in babies is common with an estimated 80% affected during their first week of life. The most commonly associated symptoms of jaundice are itchiness, pale feces, and dark urine.
 W
WNausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, often perceived as an urge to vomit. While not painful, it can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged, and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, upper abdomen, or back of the throat.
 W
WOmental infarction, or omental torsion, is an acute vascular disorder which compromises tissue of the greater omentum—the largest peritoneal fold in the abdomen.
 W
WSplenomegaly is an enlargement of the spleen. The spleen usually lies in the left upper quadrant (LUQ) of the human abdomen. Splenomegaly is one of the four cardinal signs of hypersplenism which include: some reduction in number of circulating blood cells affecting granulocytes, erythrocytes or platelets in any combination; a compensatory proliferative response in the bone marrow; and the potential for correction of these abnormalities by splenectomy. Splenomegaly is usually associated with increased workload, which suggests that it is a response to hyperfunction. It is therefore not surprising that splenomegaly is associated with any disease process that involves abnormal red blood cells being destroyed in the spleen. Other common causes include congestion due to portal hypertension and infiltration by leukemias and lymphomas. Thus, the finding of an enlarged spleen, along with caput medusae, is an important sign of portal hypertension.
 W
WA stomach rumble, also known as a bowel sound, peristaltic sound, abdominal sound or bubble gut, is a rumbling, growling or gurgling noise produced by movement of the contents of the gastro-intestinal tract as they are propelled through the small intestine by a series of muscle contractions called peristalsis. A trained healthcare provider can listen to these intestinal noises with a stethoscope, but they may be audible enough to be heard with the naked ear and are known as stomach rumble or borborygmus as the fluid and gas moves forward in the intestines. The lack of bowel sounds is indicative of ileus, intestinal obstruction, or some other serious pathology.
 W
WTympanites is a medical condition in which excess gas accumulates in the gastrointestinal tract and causes abdominal distension. The term is from the Greek τύμπανο, "drum".
 W
WVomiting is the involuntary, forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose.
 W
WXerostomia, also known as dry mouth, is dryness in the mouth, which may be associated with a change in the composition of saliva, or reduced salivary flow, or have no identifiable cause.