 W
WAn arbor press is a small hand-operated press. It is typically used to perform smaller jobs, such as staking, riveting, installing, configuring and removing bearings and other press fit work. Punches, inserters, or other tools/dies may be added to the end of the ram depending on the desired task. Arbor presses are usually rated by the ideal force that the leverage bar can apply. Typically common are presses with a leverage of 1–5 tons. This leverage is achieved when a force is applied to the lever arm or wheel.
 W
WAn astragal is a moulding profile composed of a half-round surface surrounded by two flat planes (fillets). An astragal is sometimes referred to as a miniature torus. It can be an architectural element used at the top or base of a column, but is also employed as a framing device on furniture and woodwork.
 W
WThe Black & Decker Workmate is a general purpose portable workbench and general carpentry tool manufactured under the brand Black & Decker. It is a folding table for portability, but when expanded stands about 3 feet (1 m) tall. The table top consists of two wooden jaws, one of which is fixed and the other able to be moved in and out on threaded rods operated by handles, so it can be used as a bench vice to hold wood, metal and other parts while working on them. The legs are designed to be strong enough to support the weight of a human so that it can be used as a stool to reach high surfaces, and has holes for retaining tools while working or for drilling. Its edges are printed with measures and angles, and although it cannot be used as a mitre saw the jaws are wide enough to hold one or take a mitre box.
 W
WA chainsaw mill or PortaMill or Alaskan mill is a type of sawmill incorporating a chainsaw, that is used by one or two operators to mill logs into lumber for use in furniture, construction and other uses.
 W
WA concealed hinge drilling jig is a type of support jig, designed for drilling 3 cm holes to fit concealed hinges into modern wardrobe doors. As many of the complementary tools used in woodworking, it uses an electric hand-drill for its operation, making a Forstner bit to turn.
 W
WDrill bits are cutting tools used to remove material to create holes, almost always of circular cross-section. Drill bits come in many sizes and shapes and can create different kinds of holes in many different materials. In order to create holes drill bits are usually attached to a drill, which powers them to cut through the workpiece, typically by rotation. The drill will grasp the upper end of a bit called the shank in the chuck.
 W
WA featherboard is a safety device used when working with stationary routers or power saws such as table saws or bandsaws. The purpose of a featherboard is to apply pressure against a workpiece, keeping it flat against a machine table or fence.
 W
WA jig is a type of custom-made tool used to control the location and/or motion of parts or other tools.
 W
WA jigsaw is a saw which uses a reciprocating blade to cut irregular curves, such as stenciled designs, in wood, metal, or other materials. Today they are electrically powered and known as scroll saws, and have been largely displaced by portable power jigsaws.
 W
WTools used in traditional timber framing date back thousands of years. Similar tools are used in many cultures, but the shapes vary and some are pulled rather than pushed.
 W
WA mandrel, mandril, or arbor is:a gently tapered cylinder against which material can be forged or shaped ; or a flanged or tapered or threaded bar that grips a workpiece to be machined in a lathe. A flanged mandrel is a parallel bar of a specific diameter with an integral flange towards one end, and threaded at the opposite end. Work is gripped between the flange and a nut on the thread. A tapered mandrel has a taper of approximately 0.005 inches per foot and is designed to hold work by being driven into an accurate hole on the work, gripping the work by friction. A threaded mandrel may have a male or female thread, and work which has an identical thread is screwed onto the mandrel. On a lathe, mandrels are commonly mounted between centres and driven by a lathe dog, but may also be gripped in a chuck (typically the threaded mandrels, where the outer face of work is to be machined. Threaded mandrels may also be mounted between centres. In addition to lathes, arbors are used to hold buffing wheels, circular saws, and sanding discs. Typically, these mandrels consist of a cylinder that is threaded on one end. There are many different types of mandrels for specialized applications. Examples include live chuck mandrels, live bull ring mandrels, and dead bull ring mandrels. a shaped bar of metal which is placed inside a workpiece to be formed, e.g. arbors used to bend the exhaust pipes for automobiles and in the production of molten glass, metal rings, threaded rods, and furniture legs.
 W
WThe Mästermyr chest is a Viking Age (793–1066) tool chest found in the Mästermyr mire west of Hemse on the island of Gotland, Sweden. It is the largest tool find from that era in Europe.
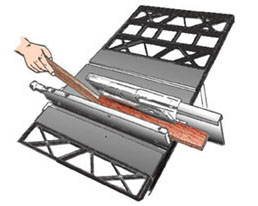 W
WA push stick, push shoe, or push block is a safety device used when working with stationary routers, jointers, or power saws such as table saws or bandsaws. The purpose of a push stick is to help the user safely maneuver a workpiece, keeping it flat against a machine table or fence while it is being cut.
 W
WA router is a hand tool or power tool that routs an area in hard material, such as wood or plastic. Routers are mainly used in woodworking, especially cabinetry. Usually they're handheld or fastened, with the cutting end up, in router tables.
 W
WA saw-horse or sawhorse is a beam with four legs used to support a board or plank for sawing. A pair of sawhorses can support a plank, forming a scaffold. In certain circles, it is also known as a mule and a short sawhorse is known as a pony. A sawhorse may also be a rack for supporting logs for sawing, known in the US as a sawbuck.
 W
WSharpening is the process of creating or refining a sharp edge of appropriate shape on a tool or implement designed for cutting. Sharpening is done by grinding away material on the implement with an abrasive substance harder than the material of the implement, followed sometimes by processes to polish the sharp surface to increase smoothness and to correct small mechanical deformations without regrinding.
 W
WA shaving horse is a combination of vice and workbench, used for green woodworking. Typical usage of the shaving horse is to create a round profile along a square piece, such as for a chair leg or to prepare a workpiece for the pole lathe. They are used in crafts such as coopering and bowyery.
 W
WA steam box is a long, sealed container used to steam wooden planks for the purpose of making them pliable. Once steamed and then fastened or clamped into the desired position and left to dry, the wood will hold the new shape. Steam boxes allow for much more efficient use of wood. Instead of cutting the desired shape away from a large and more expensive piece of wood and leaving much scrap to be discarded, steam boxes allow for a smaller piece to be bent in the general shape and leaving much less scrap. Steam boxes also allow the wood to bend beyond its dry breaking point, which is useful in making extreme curves with the wood. In many cases, the bent piece is stronger than an identical piece cut from larger stock. Steam bending wood allows the wood grain to follow the bend, leaving it strong where a piece cut from larger stock would snap across crosscut grains or laminated joints.
 W
WA stud finder is a handheld device used with wood buildings to locate framing studs located behind the final walling surface, usually drywall. While there are many different stud finders available, most fall into two main categories: magnetic stud detectors and electric stud finders. There are also some devices employing radar.
 W
WThe Takenaka Carpentry Tools Museum is a museum of carpentry tools in Kobe, Japan. The museum was opened in 1984 with the objective of collecting and conserving ancient tools as an example of Japanese cultural heritage, in order to pass them on to the next generation through research and exhibitions.