 W
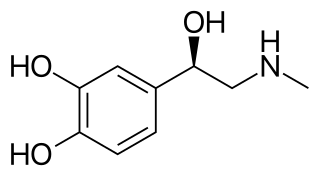
WAdrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication. Adrenaline is normally produced by both the adrenal glands and a small number of neurons in the medulla oblongata, where it acts as a neurotransmitter involved in regulating visceral functions. It plays an important role in the fight-or-flight response by increasing blood flow to muscles, output of the heart, pupil dilation response and blood sugar level. It does this by binding to alpha and beta receptors. It is found in many animals and some single-celled organisms. Polish physiologist Napoleon Cybulski first isolated adrenaline in 1895.
 W
WAmrinone, also known as inamrinone, and sold as Inocor, is a pyridine phosphodiesterase 3 inhibitor. It is a drug that may improve the prognosis in patients with congestive heart failure. Amrinone has been shown to increase the contractions initiated in the heart by high gain calcium induced calcium release (CICR). The positive inotropic effect of amrinone is mediated by the selective enhancement of high gain CICR which contributes to the contraction of myocytes by phosphorylation through cAMP dependent protein kinase A (PKA) and Ca2+ calmodulin kinase pathways.
 W
WAngiotensinamide is a potent vasoconstrictor used as a cardiac stimulant. It is a derivative of angiotensin II.
 W
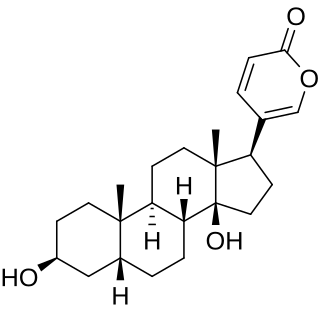
WBufalin, is a cardiotonic steroid originally isolated from the Chinese toad venom. It is a component found in many Chinese traditional medicine.
 W
WCafedrine (INN), also known as norephedrinoethyltheophylline, is a chemical linkage of norephedrine and theophylline and is a cardiac stimulant used to increase blood pressure in people with hypotension.
 W
WCocaine, also known as coke, is a strong stimulant most frequently used as a recreational drug. It is commonly snorted, inhaled as smoke, or dissolved and injected into a vein. Mental effects may include an intense feeling of happiness, sexual arousal, loss of contact with reality, or agitation. Physical symptoms may include a fast heart rate, sweating, and large pupils. High doses can result in very high blood pressure or body temperature. Effects begin within seconds to minutes of use and last between five and ninety minutes. Cocaine has a small number of accepted medical uses, such as numbing and decreasing bleeding during nasal surgery.
 W
WDimetofrine is a cardiac stimulant.
 W
WDopamine is a hormone and a neurotransmitter that plays several important roles in the brain and body. It is an organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. Dopamine constitutes about 80% of the catecholamine content in the brain. It is an amine synthesized by removing a carboxyl group from a molecule of its precursor chemical L-DOPA, which is synthesized in the brain and kidneys. Dopamine is also synthesized in plants and most animals. In the brain, dopamine functions as a neurotransmitter—a chemical released by neurons to send signals to other nerve cells. The brain includes several distinct dopamine pathways, one of which plays a major role in the motivational component of reward-motivated behavior. The anticipation of most types of rewards increases the level of dopamine in the brain, and many addictive drugs increase dopamine release or block its reuptake into neurons following release. Other brain dopamine pathways are involved in motor control and in controlling the release of various hormones. These pathways and cell groups form a dopamine system which is neuromodulatory.
 W
WDopexamine is a synthetic analogue of dopamine that is administered intravenously in hospitals to reduce exacerbations of heart failure and to treat heart failure following cardiac surgery. It is not used often, as more established drugs like epinephrine, dopamine, dobutamine, norepinephrine, and levosimendan work as well. It works by stimulating beta-2 adrenergic receptors and peripheral dopamine receptor D1 and dopamine receptor D2. It also inhibits the neuronal re-uptake of norepinephrine.
 W
WEnoximone is an imidazole phosphodiesterase inhibitor. It is used in the treatment of congestive heart failure and is selective for phosphodiesterase 3.
 W
WEtilefrine is a cardiac stimulant used as an antihypotensive. It is a sympathomimetic amine of the 3-hydroxy-phenylethanolamine series used in treating orthostatic hypotension of neurological, cardiovascular, endocrine or metabolic origin. Intravenous infusion of this compound increases cardiac output, stroke volume, venous return and blood pressure in man and experimental animals, suggesting stimulation of both α and β adrenergic receptors. However, in vitro studies indicate that etilefrine has a much higher affinity for β1 (cardiac) than for β2 adrenoreceptors.
 W
WMephentermine is a cardiac stimulant. It was formerly used in Wyamine nasal decongestant inhalers and before that as a stimulant in psychiatry.
 W
Wmeta-Hydroxynorephedrine or 3-hydroxynorephedrine, also known as 3,β-dihydroxyamphetamine, is an adrenergic drug of the amphetamine class which was patented as a vasopressor and nasal decongestant but was never marketed. It is the racemic form of the sympathomimetic drug metaraminol.
 W
WMetaraminol, also known as metaradrine, a stereoisomer of meta-hydroxynorephedrine (3,β-dihydroxyamphetamine), is a potent sympathomimetic amine used in the prevention and treatment of hypotension, particularly as a complication of anesthesia. It is an α1-adrenergic receptor agonist with some β effect.
 W
WMethamphetamine is a potent central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is mainly used as a recreational drug and less commonly as a second-line treatment for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and obesity. Methamphetamine was discovered in 1893 and exists as two enantiomers: levo-methamphetamine and dextro-methamphetamine. Methamphetamine properly refers to a specific chemical, the racemic free base, which is an equal mixture of levomethamphetamine and dextromethamphetamine in their pure amine forms. It is rarely prescribed over concerns involving human neurotoxicity and potential for recreational use as an aphrodisiac and euphoriant, among other concerns, as well as the availability of safer substitute drugs with comparable treatment efficacy. Dextromethamphetamine is a stronger CNS stimulant than levomethamphetamine.
 W
WMidodrine is a vasopressor/antihypotensive agent. Midodrine was approved in the United States by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1996 for the treatment of dysautonomia and orthostatic hypotension. In August 2010, the FDA proposed withdrawing this approval because the manufacturer, Shire plc, failed to complete required studies after the medicine reached the market.
 W
WNorepinephrine, also known as noradrenaline, is a medication used to treat people with very low blood pressure. It is the typical medication used in sepsis if low blood pressure does not improve following intravenous fluids. It is the same molecule as the hormone and neurotransmitter norepinephrine. It is given by slow injection into a vein.
 W
WNorfenefrine is an adrenergic agent used as a sympathomimetic drug which is marketed in Europe, Japan, and Mexico. Along with its structural isomer p-octopamine and the tyramines, norfenefrine is a naturally occurring, endogenous trace amine and plays a role as a minor neurotransmitter in the brain.
 W
WPhenylephrine is a medication primarily used as a decongestant, to dilate the pupil, to increase blood pressure, and to relieve hemorrhoids. While marketed as a decongestant, taken by mouth at recommended doses it is of unclear benefit for hay fever. It can be taken by mouth, given by injection into a vein or muscle, or applied to the skin.
 W
WPrenalterol is a cardiac stimulant which acts as a β1 adrenoreceptor agonist.
 W
WTheodrenaline (INN), also known as noradrenalinoethyltheophylline, is a chemical linkage of norepinephrine (noradrenaline) and theophylline used as a cardiac stimulant.