 W
WMany conditions affect the human integumentary system—the organ system covering the entire surface of the body and composed of skin, hair, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier against the external environment. The skin weighs an average of four kilograms, covers an area of two square metres, and is made of three distinct layers: the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous tissue. The two main types of human skin are: glabrous skin, the hairless skin on the palms and soles, and hair-bearing skin. Within the latter type, the hairs occur in structures called pilosebaceous units, each with hair follicle, sebaceous gland, and associated arrector pili muscle. In the embryo, the epidermis, hair, and glands form from the ectoderm, which is chemically influenced by the underlying mesoderm that forms the dermis and subcutaneous tissues.
 W
WAcne, also known as acne vulgaris, is a long-term skin disease that occurs when dead skin cells and oil from the skin clog hair follicles. Typical features of the condition include blackheads or whiteheads, pimples, oily skin, and possible scarring. It primarily affects skin with a relatively high number of oil glands, including the face, upper part of the chest, and back. The resulting appearance can lead to anxiety, reduced self-esteem, and, in extreme cases, depression or thoughts of suicide.
 W
WBalanitis circinata is a skin condition of reactive arthritis comprising a serpiginous ring-shaped dermatitis of the glans penis. Circinate balanitis is one of the most common cutaneous manifestation of reactive arthritis. However, balanitis circinata can also occur independently. Topical corticosteroid therapy is the most commonly used treatment, and topical calcineurin inhibitors have also been used successfully.
 W
WDystonin (DST), also known as bullous pemphigoid antigen 1 (BPAG1), isoforms 1/2/3/4/5/8, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DST gene.
 W
WIn pathology, dermatopathic lymphadenopathy, is lymph node pathology due to skin disease.
 W
WAn eschar is a slough or piece of dead tissue that is cast off from the surface of the skin, particularly after a burn injury, but also seen in gangrene, ulcer, fungal infections, necrotizing spider bite wounds, tick bites associated with spotted fevers, and exposure to cutaneous anthrax. The term "eschar" is not interchangeable with "scab". An eschar contains necrotic tissue, whereas a scab is composed of dried blood and exudate.
 W
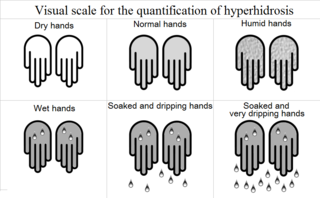
WFocal hyperhidrosis, also known as primary hyperhidrosis, is a disease characterized by an excessive sweating localized in certain body regions. Recent studies have shown that this condition, affecting between 1% and 3% of the general population, seems to have a genetic origin.
 W
WJaneway lesions are rare, non-tender, small erythematous or haemorrhagic macular, papular or nodular lesions on the palms or soles only a few millimeters in diameter that are associated with infective endocarditis and often indistinguishable from Osler's nodes.
 W
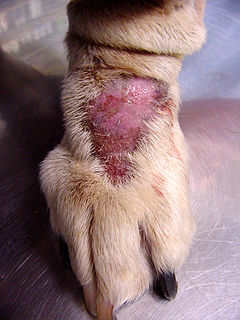
WA lick granuloma, also known as acral lick dermatitis, is a skin disorder found most commonly in dogs, but also in cats. In dogs, it results typically from the dog's urge to lick the lower portion of one of their legs.
 W
WMosquito bite allergies (MBA), also termed hypersensitivity to mosquito bites (HMB), are excessive reactions of varying severity to mosquito bites.
 W
WA non-blanching rash (NBR) is a skin rash that does not fade when pressed with, and viewed through, a glass.
 W
WPenile discharge is fluid that comes from the urethra at the end of the penis. This may occur with infections due to gonorrhea, chlamydia, or trichomoniasis. In gonorrhea the discharge may by white, yellow, or green.
 W
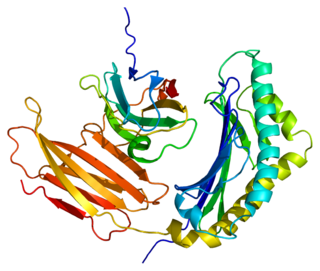
WProlactin-inducible protein also known as gross cystic disease fluid protein 15 (GCDFP-15), extra-parotid glycoprotein (EP-GP), gp17 seminal actin-binding protein (SABP) or BRST2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PIP gene. It is upregulated by prolactin and androgens and downregulated by estrogen.
 W
WPsoriasis is a long-lasting, noncontagious autoimmune disease characterized by raised areas of abnormal skin. These areas are typically red, or purple on some people with darker skin, dry, itchy, and scaly. Psoriasis varies in severity from small, localized patches to complete body coverage. Injury to the skin can trigger psoriatic skin changes at that spot, which is known as the Koebner phenomenon.
 W
WRosacea is a long-term skin condition that typically affects the face. It results in redness, pimples, swelling, and small and superficial dilated blood vessels. Often, the nose, cheeks, forehead, and chin are most involved. A red, enlarged nose may occur in severe disease, a condition known as rhinophyma.
 W
WSclerodactyly is a localized thickening and tightness of the skin of the fingers or toes. Sclerodactyly often leads to ulceration of the skin of the distal digits and is commonly accompanied by atrophy of the underlying soft tissues.
 W
WMaceration is defined as the softening and breaking down of skin resulting from prolonged exposure to moisture. It was first described by Jean-Martin Charcot in 1877. Maceration is caused by excessive amounts of fluid remaining in contact with the skin or the surface of a wound for extended periods.
 W
WSteroid-induced skin atrophy is thinning of the skin as a result of prolonged exposure to steroids. In people with psoriasis using topical steroids it occurs in up to 5% of people after a year of use.
 W
WTopical steroid withdrawal, also known as red burning skin and steroid dermatitis, has been reported in long-term users of topical steroids after they stop the use. Symptoms include redness of the skin, a burning sensation, and itchiness. This may then be followed by skin peeling. Itsan.org a reputable nonprofit are thought leaders in this area and work towards raising awareness and information for affected individuals. They also work with medical and regulatory bodies for policy changes of the drug use.
 W
WUremic frost is a colloquial description for crystallized urea deposits that can be found on the skin of those affected by chronic kidney disease. In states of prolonged kidney failure and subsequent uremia, the high level of urea in the bloodstream leads to high levels of urea secreted by eccrine sweat glands as a component of sweat. As water evaporates off of the skin, it results in crystallization of the remaining urea.
 W
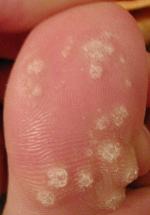
WWarts are typically small, rough, hard growths that are similar in color to the rest of the skin. They typically do not result in other symptoms, except when on the bottom of the feet, where they may be painful. While they usually occur on the hands and feet, they can also affect other locations. One or many warts may appear. They are not cancerous.