 W
WThe Australian grey smooth-hound or grey gummy shark is a species of houndshark, belonging to the family Triakidae, native to the Pacific Ocean and Indian Ocean waters surrounding Australia. The shark is widespread in deep coastal waters.
 W
WBetta ferox is a species of gourami endemic to Thailand. It is only found in rivers in Songkhla Province, where it resides along shallow riverbanks among vegetation. This species grows to a length of 6.3 centimetres (2.5 in) SL. This species is closely related to Betta pugnax and is also a paternal mouthbrooder. Males and females are dimorphic, with males displaying elongated ventral fins, elongated caudal fins, and green coloration on the gill plates. Females typically display two horizontal brown bars across their bodies, shorter fins, and a more rounded body shape.
 W
WBodianus busellatus is a species of wrasse native to tropical and warm temperate waters of the south central Pacific, particularly the Marquesas Islands. This species was described by Martin F. Gomon of the Australian Museum in 2006 with the type locality given as northeast of Matakumu Point on Fatu Hiva in the Marquesas Islands. This species is found only in the Marquesas and Pitcairn Islands.
 W
WBodianus dictynna, is a species of wrasse native to tropical and warm temperate waters of the Western Pacific, from the Indo-Malaysian Archipelago east to Tonga, as far north as Japan and as far south as Australia. It is most frequently recorded in association with living coral reefs and the juvenile fish usually occur near black coral and gorgonians, although they sometimes are found in caves near the ceiling. It feeds mainly on benthic invertebrates such as molluscs and crustaceans. The juveniles regularly behave as cleaner fish, removing parasites from other fish. The specific name dictynna is an alternative name for Diana, the Roman goddess of hunting, and refers to the close relationship between this species and Bodianus diana of the Indian Ocean, and a proposed common name of Pacific Diana's pigfish also reflects this relationship.
 W
WCentropyge abei is a small marine angelfish of the genus Centropyge.
 W
WThe crescent-tail hogfish, also known as the candy cane hogfish or Pacific redstriped hogfish, is a species of wrasse native to the Pacific Ocean from Sulawesi to the Line Islands. It can be found in groups at depths from 20 to 75 m. This species can reach 8.7 cm (3.4 in) in standard length. Juveniles are white and black. Adults are white with four broad red stripes, suffused with black on caudal peduncle and caudal fin. It can be found in the aquarium trade.
 W
WEntomocorus radiosus is a species of driftwood catfish endemic to Brazil where it is found in the Rio Paraguay in the Pantanal region of Mato Grosso. It is the smallest known member of its genus growing to a length of 5.3 cm. It can be distinguished from its congeners because its anal fin base is longer and has more branched anal fin rays. E. radiosus is a zooplanktivore which also eats insects; this species predominantly consumes microcrustaceans, but also fed on insects.
 W
WEricandersonia sagamia is a species of eelpout, a deepwater fish in the family Zoarcidae. The genus and species were newly described in 2006. It was found in Sagami Bay, Japan, at depths of between 880 and 930 m.
 W
WEtmopterus burgessi, sometimes known as the broad-snout lanternshark, is a lanternshark of the family Etmopteridae in the order Squaliformes. It is found only around Taiwan.
 W
WGastromyzon viriosus is a species of ray-finned fish in the genus Gastromyzon.
 W
WThe Kapala stingaree is a species of stingray in the family Urolophidae, endemic to inshore waters off southeastern Queensland and New South Wales. It is commonly found on and around rocky reefs at a depth of 10–130 m (33–427 ft). Reaching 51 cm (20 in) in length, the Kapala stingaree has a rounded, diamond-shaped pectoral fin disc and a slender tail, which ends in a leaf-shaped caudal fin and bears lateral skin folds and a small dorsal fin in front of the stinging spine. It has a distinctive bell-shaped curtain of skin between its nostrils. This species is greenish above, with a highly variable pattern of dark markings usually found outside and between the eyes, and over the back and tail.
 W
WThe Natal shyshark, eastern shyshark or happy chappie is a species of catshark, belonging to the family Scyliorhinidae. It was once regarded as the "Natal" form of the puffadder shyshark. This shark is endemic to a small area off South Africa from the Western Cape to KwaZulu-Natal. It is found close to the coast, from the surf zone to a depth of 30 m (98 ft), and has benthic habits. Reaching 50 cm (20 in) in length, the Natal shyshark is similar to the puffadder shyshark in appearance but has a stockier body, less flattened head, a compressed caudal peduncle, and a different color pattern. Rare and under threat from habitat degradation and commercial fishing, it has been assessed as Vulnerable by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
 W
WThe Onaç spring minnow is a species of cyprinid fish. It is found in the Onaç drainage in Anatolia in Turkey.
 W
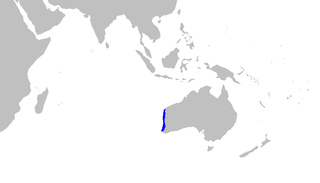
WOrectolobus hutchinsi, the western wobbegong, is a species of carpet shark in the family Orectolobidae. The western wobbegong shark is a moderate sized marine shark found off the coast of Western Australia. Its scientific name is Orectolobus hutchinsi, and it was first identified in 1983 by Dr. Barry Hutchins, but was only recently classified, described, and published in 2006. O. hutchinsi is found on the shallow continental shelf in Western Australia from Coral Bay to Groper Bluff. This species is distinct from other wobbegong sharks because the western wobbegong shark has a yellowish brown upper body and darker brown saddles on their backs. Unlike other wobbegong sharks from the same area, the western wobbegong shark doesn’t have white rings or blotches on their backs.
 W
WPaedocypris progenetica is a tiny species of cyprinid fish endemic to the Indonesian islands of Sumatra and Bintan where it is found in peat swamps and blackwater streams.
 W
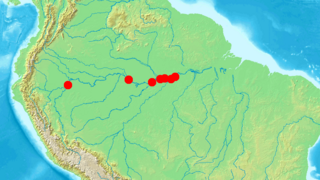
WPariosternarchus amazonensis is a little-known species of weakly electric knifefish in the family Apteronotidae, and the only member of its genus. It is found in the main channel of the Amazon River in Brazil and Peru, likely near the bottom in deep, fast-moving water. This species is characterized by a wide head with a flat bottom, and very large sensory canals along the lower jaw. Like several other knifefishes found in deep river channels, it has reduced eyes, scales, and body pigmentation.
 W
WPtychochromis insolitus, also known as the Mangarahara cichlid or joba mena, is a species of cichlid endemic to certain river systems in northern Madagascar. This critically endangered fish is threatened by habitat loss and competition from introduced species; after the last-known female was killed during a breeding attempt, its conservation received significant international attention as London Zoo launched a media campaign to identify any remaining individuals. A remnant population was discovered by aquaculture entrepreneur Guy Tam Hyock in 2013, and breeding programs in Madagascar and at Toronto Zoo have resulted in thousands of successful hatchlings.
 W
WSpiniphryne duhameli is a species of dreamer known from the central Pacific Ocean. The females of this species grow to a length of 11.7 centimetres (4.6 in) SL. The esca contains a pair of short, slender filaments at the tip, a small, simple appendage without distal filaments on the back, and three pairs of long, slender filaments on the sides. S. duhameli also has more dental teeth than S. gladisfenae.
 W
WSqualius valentinus, commonly known as the Valencia chub and the Levantine bagra, is a species of freshwater fish in the carp family Cyprinidae. It was first isolated from the Turia River in Valencia, hence its name. It is considered endangered. This species is differentiated from its cogeneratesa by having eight branched rays in its dorsal fin; eight branched rays in its anal fin; two rows of pharyngeal teeth on both sides possessing 2 and 5 teeth ; a wide caudal peduncle; its number of gill rakers; the number of scales in its lateral line; the number of scale rows above the latter; by possessing three scale rows below it; by having thirty-nine vertebrae ; showing large 4th and 5th infraorbital bones; a maxilla with a very distinctlt marked anterior process; exhibiting a frontal bone expanded at the middle; a wide neurocranium bone; the lower branch of the pharyngeal bone being robust; a large and narrow urohyal; as well as genetic differences (allozymes).
 W
WSynodontis grandiops is a species of upside-down catfish endemic to the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Burundi, and Tanzania, where it is only known from Lake Tanganyika. It was first described by Jeremy John Wright and Lawrence M. Page in 2006, from specimens collected at multiple points along the shore of Lake Tanganyika. The species name is a Latinized combination of the Latin "grandi", meaning large or big, and the Greek "ops", meaning eye, a reference to the relatively large eyes of this fish.
 W
WTiktaalik is a monospecific genus of extinct sarcopterygian from the Late Devonian Period, about 375 Mya, having many features akin to those of tetrapods.