 W
WA hunting deity is a god or goddess in mythology associated with the hunting of animals and the skills and equipment involved. They are a common feature of polytheistic religions.
 W
WAntinous or Antinoös was a Greek youth from Bithynia and a favourite beloved of the Roman emperor Hadrian. After his premature death before his twentieth birthday, Antinous was deified on Hadrian's orders, being worshipped in both the Greek East and Latin West, sometimes as a god (theos) and sometimes merely as a hero.
 W
WIn Gallo-Roman religion, Cernunnos was a deity depicted with antlers, seated cross-legged, and is associated with stags, horned serpents, dogs, bulls, and rats. He is usually holding or wearing a torc and has been seen holding a bag of coins and a cornucopia. Believed to have originally been a Celtic deity, over 50 examples have been found from this time believed to be associated with him, concentrating in the north-eastern region of what was called Gaul by the ancient Romans. Cernunnos is also associated with the Wiccan Horned God in the modern religious tradition of Wicca.
 W
WHeracles Kynagidas was the patron god of hunting in the Macedonian Kingdom, to whom hunting trophies were dedicated. The epithet was also attributed to "Artemis Kynago" Κυναγὼ, in its female form.
 W
WThe Horned God is one of the two primary deities found in Wicca and some related forms of Neopaganism. The term Horned God itself predates Wicca, and is an early 20th-century syncretic term for a horned or antlered anthropomorphic god partly based on historical horned deities.
 W
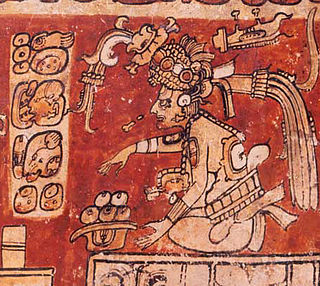
WItzamna is, in Maya mythology, an upper god and creator deity thought to reside in the sky. Itzamna is one of the most important gods in the Classic and Postclassic Maya pantheon. Although little is known about him, scattered references are present in early-colonial Spanish reports (relaciones) and dictionaries. Twentieth-century Lacandon lore includes tales about a creator god who may be a late successor to him. In the pre-Spanish period, Itzamna was often depicted in books and in ceramic scenes derived from them. Before the names of the Maya deities were deciphered, Itzamna was known as "god D", and is still sometimes referred to as "god D" by archeologists.
 W
WKumugwe is a figure in the mythology of Pacific Northwest peoples. Known as "Copper-Maker", he is the god of the undersea world revered by the Kwakwaka'wakw and Nuxalk indigenous nations. He has a house under the sea filled with riches and his name means "wealthy one". He is sometimes identified as one and the same as Qaniqilak, the spirit of the summer fishing season, and is then regarded as the adversary of Tseiqami otherwise known as Thunderbird, the guiding spirit of the Winter Hamatsa Dance season.
 W
WThe Master of Animals, Lord of Animals, or Mistress of the Animals is a motif in ancient art showing a human between and grasping two confronted animals. The motif is very widespread in the art of the Ancient Near East and Egypt. The figure may be female or male, it may be a column or a symbol, the animals may be realistic or fantastical, and the human figure may have animal elements such as horns, an animal upper body, an animal lower body, legs, or cloven feet. Although what the motif represented to the cultures that created the works probably varies greatly, unless shown with specific divine attributes, when male the figure is typically described as a hero by interpreters. The motif is so widespread and visually effective that many depictions probably were conceived as decoration with only a vague meaning attached to them. The Master of Animals is the "favorite motif of Achaemenian official seals", but the figures in these cases should be understood as the king.
 W
WMixcoatl, or Camaztle [kaˈmaʃt͡ɬe] from camaz "deer sandal" and atle "without", or Camaxtli, was the god of the hunt and identified with the Milky Way, the stars, and the heavens in several Mesoamerican cultures. He was the patron deity of the Otomi, the Chichimecs, and several groups that claimed descent from the Chichimecs. Under the name of Camaxtli, Mixcoatl was worshipped as the central deity of Huejotzingo and Tlaxcala.
 W
WMoccus is a Celtic god who is identified with Mercury. He is the boar- or swine-god of the continental Celtic tribe of Lingones. Moccus was invoked as the protector of boar hunters and warriors. Boar meat was sacred among the ancient Celts, and features in accounts of feasts in Irish mythology. The Lingones, whose tribal center was at modern-day Langres, were a Gaulish tribe located in the area of the rivers Seine and Marne in what is now northeastern France. They were neighbors to the Celto-Germanic tribe of Treveri. Another tribe known as Lingones was located near the mouth of the Po River in northeastern Italy, and were known for agriculture, weaving and metalworking.
 W
WMoreya or Moriya is a Japanese god who appears in various myths and legends of the Suwa region in Nagano Prefecture. The most famous of such stories is that of his battle against Takeminakata, the god of the Grand Shrine of Suwa.
 W
WNinurta (Sumerian: 𒀭𒊩𒌆𒅁: DNIN.URTA, "Lord [of] Urta" meaning of this name not known), also known as Ninĝirsu (Sumerian: 𒀭𒊩𒌆𒄈𒋢: DNIN.ĜIR2.SU, meaning “Lord [of] Girsu”), is an ancient Mesopotamian god associated with farming, healing, hunting, law, scribes, and war who was first worshipped in early Sumer. In the earliest records, he is a god of agriculture and healing, who cures humans of sicknesses and releases them from the power of demons. In later times, as Mesopotamia grew more militarized, he became a warrior deity, though he retained many of his earlier agricultural attributes. He was regarded as the son of the chief god Enlil and his main cult center in Sumer was the Eshumesha temple in Nippur. Ninĝirsu was honored by King Gudea of Lagash (ruled 2144–2124 BC), who rebuilt Ninĝirsu's temple in Lagash.
 W
W*Nodens or *Nodons is a Celtic healing god worshipped in Ancient Britain. Although no physical depiction of him has survived, votive plaques found in a shrine at Lydney Park (Gloucester) indicate his connection with dogs, a beast associated with healing symbolism in antiquity. The deity is known is only one other location, in Cockersand Moss (Lancashire). He was equated on most inscriptions with the Roman god Mars and likened to Silvanus. His name is cognate with that of later Celtic mythological figures, such as the Irish Nuada and the Welsh Nudd.
 W
WOdin is a widely revered god in Germanic mythology. Norse mythology, the source of most surviving information about him, associates him with wisdom, healing, death, royalty, the gallows, knowledge, war, battle, victory, sorcery, poetry, frenzy, and the runic alphabet, and depicts him as the husband of the goddess Frigg. In wider Germanic mythology and paganism, the god was known in Old English as Wōden, in Old Saxon as Wōdan, in Old Dutch as Wuodan, and in Old High German as Wuotan, all ultimately stemming from the Proto-Germanic theonym *Wōđanaz, meaning 'lord of frenzy', or 'leader of the possessed'.
 W
WOgun or Ogoun is a spirit that appears in several African religions. He attempted to seize the throne after the demise of Obatala who reigned twice, before and after Oduduwa, but was ousted by Obamakin and sent on an exile - an event which serves as the core of the Olojo Festival. Ogun was a warrior and a powerful spirit of metal work, as well as of rum and rum-making. He is also known as the "god of Iron", and is present in Yoruba religion, Haitian Vodou, and West African Vodun.
 W
WOkó, also known in Brazil as Ocô, is an Orisha. In Nigeria and the Benin Republic, he is a strong hunter & farming deity as well as a fighter against sorcery. He is associated with the annual new harvest of the white African yam. Among the deities, he is considered a close friend of Oosa Ogiyan and Shango, as well as at one time husband of Oya and Yemoja. Bees are considered the messengers of Oko.
 W
WOshosi is an Orisha of the Yoruba religion in West Africa and subsequently in Brazil.
 W
WRevanta or Raivata is a minor Hindu deity. According to the Rig-Veda, Revanta is the youngest son of the sun-god Surya, and his wife Saranyu. Revanta is chief of the Guhyakas, semi-divine and demonic class entities – like the Yakshas – who are believed to live as forest dwellers in the Himalayas. Images and sculptures of Revanta often show him as a huntsman on a horse, with a bow and arrow.
 W
WRudra is a Rigvedic deity associated with wind or storm, Vayu and the hunt. One translation of the name is 'the roarer'. In the Rigveda, Rudra is praised as the 'mightiest of the mighty'. Rudra means "who eradicates problems from their roots". Depending upon the periodic situation, Rudra can mean 'the most severe roarer/howler' (could be a hurricane or tempest) or 'the most frightening one'. This name appears in the Shiva Sahasranama, and R. K. Śarmā notes that it is used as a name of Shiva often in later languages. The Shri Rudram hymn from the Yajurveda is dedicated to Rudra and is important in the Saivism sect. In Prathama anuvaka of Namakam, Sri Rudram the 'mightiest of the mighty' Rudra, is revered as Sadasiva and Mahadeva. Sadashiva, is the Supreme Being Lord Paramashiva in the Mantra marga Siddhanta sect of Shaivism. Also, the name siva is used plenty of times in the same Anuvaka for invoking Rudra.
 W
WRuntiya was the Luwian god of the hunt, who had a close connection with deer. He was among the most important gods of the Luwians.
 W
WTakeminakata (タケミナカタ), also known as Minakatatomi or Takeminakatatomi, is a kami in Japanese mythology. Also known as Suwa Myōjin (諏訪明神) or Suwa Daimyōjin (諏訪大明神) after Suwa Grand Shrine in Nagano Prefecture in which he is enshrined alongside his consort Yasakatome, Takeminakata is historically worshiped as a god of wind, water and agriculture, as well as a patron of hunting and warfare, in which capacity he enjoyed a particularly fervent cult from various samurai clans during the medieval period such as the Hōjō or the Takeda. Takeminakata was also held to be the mythical ancestor of certain families who once served at the shrine as priests, foremost among them being the Suwa clan, the high priests of the Upper Shrine of Suwa who were also revered as living vessels of the god.
 W
WIn Norse mythology, Ullr is a god associated with archery. Although literary attestations of Ullr are sparse, evidence including relatively ancient place-name evidence from Scandinavia suggests that he was a major god in earlier Germanic paganism. Proto-Germanic *wulþuz ('glory') appears to have been an important concept of which his name is a reflex. The word appears as owlþu- on the 3rd-century Thorsberg chape.