 W
WAcanthochirana is an extinct genus of prawn that existed during the upper Jurassic period. It was named by Strand in 1928, and contains five species, including Acanthochirana cordata. They are distinguished from the related genus Aeger by the presence of teeth on the rostrum, which are absent in Aeger.
 W
WAeger is a genus of fossil prawns. They first occur in the Middle Triassic, and died out at the end of the Late Cretaceous. A total of 20 species are known.
 W
WAeger elegans is a species of fossil prawn from the Solnhofen Plattenkalk.
 W
WAntrimpos is an extinct genus of crustacean which existed during the Triassic and Jurassic periods. It contains 15 species, including Antrimpos speciosus.
 W
WCancrinos is a genus of fossil crustacean closely allied with the slipper lobsters. One species is known, C. claviger from the Jurassic of southern Germany.
 W
WColeia is an extinct genus of decapods in the group Polychelida that lived from the Late Triassic to the Late Jurassic. It was described by Broderip in 1835, and the type species is C. antiqua. A new species, C. martinlutheri, which existed during the Sinemurian of what is now Germany, was described by Günter Schweigert and Werner Ernst in 2012.
 W
WCycleryon is an extinct genus of decapod crustaceans. The type species is Cycleryon propinquus.
 W
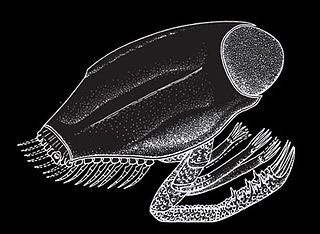
WDollocaris was a genus of Thylacocephalan that lived during the Jurassic period. Fossils have been found in France, specifically the La Voulte-sur-Rhône lagerstätte. It is known for its massively compound eyes, giving Dollocaris a rather characteristic appearance. One species is currently known, D. ingens.
 W
WDrobna deformis is an extinct species of prawn, the only species in the genus Drobna.
 W
WEryma is a genus of fossil lobster-like crustaceans, containing 44 species.
 W
WEryma mandelslohi is a species of decapod crustacean that lived in Europe in the Jurassic of England. Fossils of the species have been found in the Oxford Clay.
 W
WEryma modestiforme is a species of decapod crustacean that lived in Europe in the Jurassic.
 W
WErymidae is a family of decapod crustaceans known only from fossils. They survived for 100 million years, from the Permo-Triassic boundary to the Hauterivian. Eleven genera are recognised:Clytiella Glaessner, 1931 – 1 species Clytiopsis Bill, 1914 – 3 species Enoploclytia M’Coy, 1849 – 20 species Eryma Von Meyer, 1840 – 44 species Galicia Garassino & Krobicki, 2002 – 3 species Lissocardia Von Meyer, 1851 – 3 species Palaeastacus Bell, 1850 – 24 species Paraclytiopsis Oravec, 1962 – 1 species Protoclytiopsis Birshtein, 1958 – 1 species Pustulina Quenstedt, 1857 – 12 species Stenodactylina Beurlen, 1928 – 1 species
 W
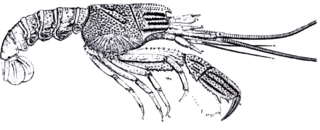
WEryon (animal), is an extinct genus of decapod crustaceans from the Late Jurassic of Germany. Its remains are known from the Solnhofen limestone. It reached a length of around 10 cm (3.9 in), and may have fed on particulate matter on the sea bed.
 W
WEryonidae is a family of fossil decapod crustaceans which lived from the Upper Triassic to the Lower Cretaceous. It contains four genera: An aggregation of three unidentified eryonids was reported in 2012 inside a Late Jurassic ammonoid of the species Harpoceras falciferum; they represent the earliest evidence of gregarious behaviour in decapods.Cycleryon Glaessner, 1965 Eryon A. G. Desmarest, 1817 Knebelia Van Straelen, 1922 Rosenfeldia Garassino, Teruzzi & Dalla Vecchia, 1996
 W
WGlyphea is a genus of fossil glypheoid crustaceans that lived from the Jurassic to the Eocene. It includes the following species:
 W
WIliella spinosa is an extinct species of kazacharthran branchiopod crustaceans from the Lower Jurassic of Kazakhstan. It had a unique carapace that was shaped like a spiny double-oval.
 W
WCyclida is an order of fossil arthropods that lived from the Carboniferous to the Cretaceous. Their classification is uncertain, but they are generally treated as a group of maxillopod crustaceans.
 W
WKazacharthra is an extinct order of branchiopod crustaceans that appear to be closely related to the living order Notostraca. Kazacharthrans lived in marshes and ponds in the Upper Triassic of Western China and Mongolia, and in Lower Jurassic Kazakhstan. It is presumed that the kazacharthrids lived much like their living relatives, in that they were opportunistic omnivores that fed on any available food source, from bacterial biofilms to detritus to smaller animals that could be overpowered.
 W
WKoelga is an extinct genus of prawn in the order Decapoda. It contains the species Koelga curvirostris and Koelga muensteri.
 W
WMecochirus is an extinct genus of lobster-like decapod crustaceans, containing 17 species.
 W
WMecochirus longimanatus is an extinct species of lobster-like decapod crustacean from the Jurassic of Europe.
 W
WOstenocaris is a Jurassic species of giant Thylacocephalan crustacean, sufficiently distinct from its relatives to be placed in its own family, Ostenocarididae. It is believed to be a bethonic animal and one of the most important necrophagus animals of its environment.