 W
WA hallucination is a perception in the absence of external stimulus that has qualities of real perception. Hallucinations are vivid, substantial, and are perceived to be located in external objective space. They are distinguishable from several related phenomena, such as dreaming, which does not involve wakefulness; pseudohallucination, which does not mimic real perception, and is accurately perceived as unreal; illusion, which involves distorted or misinterpreted real perception; and imagery (imagination), which does not mimic real perception and is under voluntary control. Hallucinations also differ from "delusional perceptions", in which a correctly sensed and interpreted stimulus is given some additional significance.
 W
WAlice in Wonderland syndrome (AIWS), also known as Todd's syndrome or dysmetropsia, is a neuropsychological condition that causes a distortion of perception. People may experience distortions in visual perception of objects such as appearing smaller (micropsia) or larger (macropsia), or appearing to be closer (pelopsia) or farther (teleopsia) away than they actually are. Distortion may occur for other senses besides vision as well.
 W
WAn aura is a perceptual disturbance experienced by some with epilepsy or migraine.
 W
WFlying ointment is a hallucinogenic ointment said to have been used by witches in the practice of European witchcraft from at least as far back as the Early Modern period, when detailed recipes for such preparations were first recorded.
 W
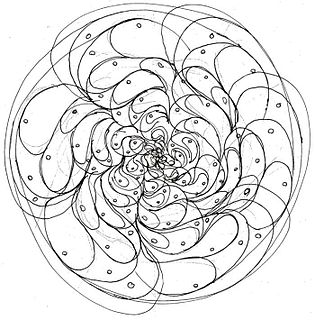
WA form constant is one of several geometric patterns which are recurringly observed during hypnagogia, hallucinations and altered states of consciousness.
 W
WSeveral species of fish are claimed to produce hallucinogenic effects when consumed. For example, Sarpa salpa, a species of sea bream, is commonly claimed to be hallucinogenic. These widely distributed coastal fish are normally found in the Mediterranean and around Spain, and along the west and south coasts of Africa. Occasionally they are found in British waters. They may induce hallucinogenic effects similar to LSD if eaten. However, based on the reports of exposure they are more likely to resemble hallucinogenic effects of deliriants than the effects of serotonergic psychedelics such as LSD. In 2006, two men who apparently ate the fish experienced hallucinations lasting for several days. The likelihood of hallucinations depends on the season. Sarpa salpa is known as "the fish that makes dreams" in Arabic.
 W
WThe Marian Apparitions of Ilača were reported sightings of miraculous events in Croatia in 1865. This was seven years after the Lourdes apparitions.Ilača became the most important Catholic pilgrimage site in the historical region of Syrmia. Initially, church authorities tried to prevent congregations from pilgrimage. Later, it was permitted by bishop Josip Juraj Strossmayer.
 W
WImaginary friends are a psychological and social phenomenon where a friendship or other interpersonal relationship takes place in the imagination rather than external physical reality. Although they may seem very real to their creators, children usually understand that their imaginary friends are not real. The first studies focusing on imaginary friends are believed to have been conducted during the 1890s. There is little information about the development and the appearance of imaginary friends in children. However, Klausen and Passman (2007) report that imaginary companions were originally described as being supernatural creatures and spirits that were thought to connect people with their past lives. Adults in early historic times had entities such as household gods and guardian angels, and muses that functioned as imaginary companions to provide comfort, guidance and inspiration for creative work. Eventually, the phenomenon of imaginary companions passed on to children. The era when children began having imaginary friends is unknown, but it is possible the phenomenon appeared in the mid–19th century when childhood was emphasized as an important time to play and imagine.
 W
WDesigner drugs are structural or functional analogues of controlled substances that are designed to mimic the pharmacological effects of the parent drug while avoiding detection or classification as illegal. Many of the older designer drugs are structural analogues of psychoactive tryptamines or phenethylamines but there are many other chemically unrelated new psychoactive substances that can be considered part of the designer drug group. Designer drugs can also include substances that are not psychoactive in effect, such as analogues of controlled anabolic steroids and other performance and image enhancing drugs (PIEDs), including nootropics, weight loss drugs and erectile dysfunction medications. The pharmaceutical activities of these compounds might not be predictable based strictly upon structural examination. Many of the substances have common effects while structurally different or different effects while structurally similar due to SAR paradox. As a result of no real official naming for some of these compounds, as well as regional naming, this can all lead to potentially hazardous mix ups for users. The following list is not exhaustive.
 W
WA list of plants that are used as psychoactive drugs. Some of them have been used entheogenically for millennia. The plants are listed according to the substances they contain.
 W
WThe Marian Apparitions at Lourdes were reported in 1858 by Bernadette Soubirous, a 14-year-old miller's daughter from the town of Lourdes in southern France.
 W
WAn out-of-body experience is a phenomenon in which a person perceives the world from a location outside their physical body. An OBE is a form of autoscopy, although this term is more commonly used to refer to the pathological condition of seeing a second self, or doppelgänger.
 W
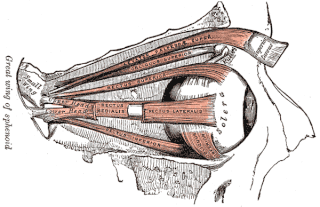
WThe phantom eye syndrome (PES) is a phantom pain in the eye and visual hallucinations after the removal of an eye.
 W
WA phantom limb is the sensation that an amputated or missing limb is still attached. Approximately 80 to 100% of individuals with an amputation experience phantom sensations in their amputated limb. However, only a small percentage will experience painful phantom limb sensation. These sensations are relatively common in amputees and usually resolve within two to three years without treatment. Research continues to explore the underlying mechanisms of phantom limb pain (PLP) and effective treatment options.
 W
WPhotopsia is the presence of perceived flashes of light in the field of vision.
 W
WPrivate revelation is, in Christian theology, a message from God which can come in a variety of types.
 W
WPsychedelia is an American documentary film from Hard Rain Films, that was initially released in 2015, and then re-released as a revised version in 2020. The film discusses the history of psychedelic drugs and their ability to produce mystical experiences. The therapeutic role of such drugs is considered, and controlled research studies conducted before the 1960s, are discussed. Several study participant users are interviewed. The film was a winner for best documentary film at the New Jersey International Film Festival, and was an official selection at the Southern Utah International Documentary Film Festival (DOCUTAH) and the Orlando Film Festival.
 W
WPsychedelics are a hallucinogenic class of psychoactive drug whose primary effect is to trigger non-ordinary states of consciousness via serotonin 2A receptor agonism. This causes specific psychological, visual and auditory changes, and often a substantially altered state of consciousness. "Classical" psychedelic drugs include mescaline, LSD, psilocybin, and DMT.
 W
WPsychotic depression, also known as depressive psychosis, is a major depressive episode that is accompanied by psychotic symptoms. It can occur in the context of bipolar disorder or major depressive disorder. It can be difficult to distinguish from schizoaffective disorder, a diagnosis that requires the presence of psychotic symptoms for at least two weeks without any mood symptoms present. Unipolar psychotic depression requires that the psychotic features occur only during episodes of major depression. Diagnosis using the DSM-5 involves meeting the criteria for a major depressive episode, along with the criteria for "mood-congruent or mood-incongruent psychotic features" specifier.
 W
WA shadow person is the perception of a patch of shadow as a living, humanoid figure, and, interpreted as the presence of a spirit or other entity by believers in the paranormal or supernatural.
 W
WTactile hallucination is the false perception of tactile sensory input that creates a hallucinatory sensation of physical contact with an imaginary object. It is caused by the faulty integration of the tactile sensory neural signals generated in the spinal cord and the thalamus and sent to the primary somatosensory cortex (SI) and secondary somatosensory cortex (SII). Tactile hallucinations are recurrent symptoms of neurological diseases such as schizophrenia, Parkinson's disease, Ekbom's syndrome and delerium tremens. Patients who experience phantom limb pains also experience a type of tactile hallucination. Tactile hallucinations are also caused by drugs such as cocaine and alcohol.
 W
WTheophany is the manifestation of a deity in an observable way.
 W
WA vision is something seen in a dream, trance, or religious ecstasy, especially a supernatural appearance that usually conveys a revelation. Visions generally have more clarity than dreams, but traditionally fewer psychological connotations. Visions are known to emerge from spiritual traditions and could provide a lens into human nature and reality. Prophecy is often associated with visions.
 W
WVisual snow, also known as visual static, is a condition in which people see white or black dots in parts or the whole of their visual fields. The condition is typically always present and can last years.