 W
WAcamptonectes is a genus of ophthalmosaurid ichthyosaur, a type of dolphin-like marine reptile, that lived during the Early Cretaceous, around 130 million years ago. The first specimen, a partial adult skeleton, was discovered in Speeton, England, in 1958. However, it was not described until 2012 by Valentin Fischer and colleagues, who recognised additional specimens belonging to the genus from Cremlingen, Germany and other localities in England. The genus contains the single species A. densus; the generic name means "rigid swimmer", and the specific name means "compact" or "tightly packed".
 W
WAcamptonectes is a genus of ophthalmosaurid ichthyosaur, a type of dolphin-like marine reptile, that lived during the Early Cretaceous, around 130 million years ago. The first specimen, a partial adult skeleton, was discovered in Speeton, England, in 1958. However, it was not described until 2012 by Valentin Fischer and colleagues, who recognised additional specimens belonging to the genus from Cremlingen, Germany and other localities in England. The genus contains the single species A. densus; the generic name means "rigid swimmer", and the specific name means "compact" or "tightly packed".
 W
WAegirosaurus is an extinct genus of platypterygiine ophthalmosaurid ichthyosaurs known from the late Jurassic and early Cretaceous of Europe. It was originally named as a species of Ichthyosaurus.
 W
WArthropterygius is a widespread genus of ophthalmosaurid ichthyosaur which existed in Canada, Norway, Russia, and Argentina from the late Jurassic period to the earliest Cretaceous.
 W
WCetarthrosaurus is an extinct genus of ichthyosaur known from the eastern United Kingdom. It was collected from the Cambridge Greensand Formation, dating to late Albian or early Cenomanian stage, of the Early Cretaceous-Late Cretaceous boundary. Cetarthrosaurus was first named by Harry G. Seeley in 1873 and the type species is Cetarthrosaurus walkeri.
 W
WContectopalatus was a primitive ichthyosaur, an extinct fish-like marine reptile from the Middle Triassic of Germany. It was originally named Ichthyosaurus atavus, and later Mixosaurus atavus. It was recognised as a valid genus by Maisch and Matzke in 1998, though other authorities argue that it is synonymous with Mixosaurus. It was 5 metres long.
 W
WCryopterygius is an extinct genus of ophthalmosaurid ichthyosaur known from the uppermost Jurassic of Central Spitsbergen, Norway. The type species, Cryopterygius kristiansenae , is known from a single, but largely complete specimen from the Slottsmøya Member of the Agardhfjellet Formation. With a total length of 5.0–5.5 metres (16.4–18.0 ft), it is a large ichthyosaur. A second species, C. kielanae, was found in the Kcynia Formation from the Late Jurassic of Poland. It is smaller than the type species, with a length of 3.5–4 metres (11–13 ft).
 W
WEurhinosaurus is an extinct genus of ichthyosaur from the Early Jurassic (Toarcian), ranging between 183 and 175 million years. Fossils of the aquatic reptile have been found in Western Europe. They used to live in the deep, open sea area. Eurhinosaurus was a large genus of ichthyosaurs. An adult individual could reach over 6 metres (20 ft).
 W
WExcalibosaurus is a monotypic genus of marine prehistoric reptiles (ichthyosaurs) that lived during the Sinemurian stage of the Early Jurassic period in what is now England. It is characterized by the extreme elongation of the rostrum, with the lower jaw about three-fourths of the length of the upper jaw, giving the animal a swordfish-like look. The only known species is Excalibosaurus costini.
 W
WIchthyosauridae is an extinct family of thunnosaur ichthyosaurs from the latest Triassic and Early Jurassic of Europe, and possibly also from the middle Early Cretaceous of Iraq. Named by Charles Lucien Bonaparte, in 1841, it is usually thought to contain a single genus, Ichthyosaurus, which is known from several species from the Early Jurassic. In 2013, Fischer et al. named and described Malawania anachronus from the middle Early Cretaceous of Iraq. It was found to share several synapomorphies with the type species of this family, Ichthyosaurus communis, and a large phylogenetic analysis recovered these species as sister taxa. Despite its geologically younger age, M. anachronus was also assigned to Ichthyosauridae.
 W
WIchthyosaurus is a genus of ichthyosaurs from the late Triassic and early Jurassic of Europe and Asia (Indonesia). It is among the best known ichthyosaur genera, as it is the type genus of the order Ichthyosauria.
 W
WAcamptonectes is a genus of ophthalmosaurid ichthyosaur, a type of dolphin-like marine reptile, that lived during the Early Cretaceous, around 130 million years ago. The first specimen, a partial adult skeleton, was discovered in Speeton, England, in 1958. However, it was not described until 2012 by Valentin Fischer and colleagues, who recognised additional specimens belonging to the genus from Cremlingen, Germany and other localities in England. The genus contains the single species A. densus; the generic name means "rigid swimmer", and the specific name means "compact" or "tightly packed".
 W
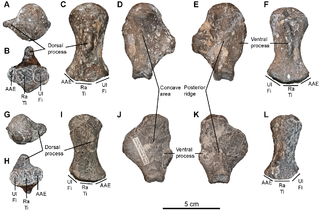
WKeilhauia is a genus of ophthalmosaurid ichthyosaur, a type of dolphin-like, large-eyed marine reptile, from the Early Cretaceous shallow marine Slottsmøya Member of the Agardhfjellet Formation in Svalbard, Norway. The genus contains a single species, K. nui, known from a single specimen discovered in 2010 and described by Delsett et al. in 2017. In life, Keilhauia probably measured approximately 4 metres (13 ft) in length; it can be distinguished by other ophthalmosaurids by the wide top end of its ilium and the relatively short ischiopubis compared to the femur. Although it was placed in a basal position within the Ophthalmosauridae by phylogenetic analysis, this placement is probably incorrect.
 W
WMacropterygius is a genus of ichthyosaurs known from the Late Jurassic of England. Though many specimens have been referred to this genus from all over Europe, the type specimen of the only recognized species, M. trigonus, consists of just a single vertebra. Because this cannot be used to distinguish ichthyosaurs from one another, the genus and species are currently considered nomena dubia.
 W
WOphthalmosaurus is an ichthyosaur of the Middle Jurassic period, named for its extremely large eyes. It had a graceful 6 m (19.5 ft) long dolphin-shaped body, and its almost toothless jaw was well adapted for catching squid. Major fossil finds of this genus have been recorded in Europe and North and South America.
 W
WNannopterygius is a genus of ophthalmosaurid ichthyosaur that lived in the Middle Jurassic to the Early Cretaceous . Fossils have been found in Europe, where there was a shallow and warm sea covering much of Europe at this time. It therefore lived in shallow seas, probably around coral reefs, rather than in the open ocean. The first specimen was found in the Kimmeridgian Kimmeridge Clay Formation of Kimmeridge Bay, Dorset, UK and described by Hulke in 1871, who named it Ichthyosaurus enthekiodon. This referred to its teeth being 'sheathed' in cementum and less likely to fall out than those of other ichthyosaurs. A year earlier, Hulke had described some remains from the same horizon and locality that he thought were ichthyosaurian, naming them Enthekiodon. These are now lost, but Hulke considered them sufficiently similar to demote the name to species level. In 1922, Huene separated this species into the new genus Nannopterygius, named for the small fore- and hindpaddles. The first fossil is the most complete, but is flattened. All subsequent fossils are fragmentary. In 2020, several more species, including N. borealis, and the species once contained in the genera Paraophthalmosaurus and Yasykovia were named based on remains found in Norway and Russia.
 W
WNannopterygius is a genus of ophthalmosaurid ichthyosaur that lived in the Middle Jurassic to the Early Cretaceous . Fossils have been found in Europe, where there was a shallow and warm sea covering much of Europe at this time. It therefore lived in shallow seas, probably around coral reefs, rather than in the open ocean. The first specimen was found in the Kimmeridgian Kimmeridge Clay Formation of Kimmeridge Bay, Dorset, UK and described by Hulke in 1871, who named it Ichthyosaurus enthekiodon. This referred to its teeth being 'sheathed' in cementum and less likely to fall out than those of other ichthyosaurs. A year earlier, Hulke had described some remains from the same horizon and locality that he thought were ichthyosaurian, naming them Enthekiodon. These are now lost, but Hulke considered them sufficiently similar to demote the name to species level. In 1922, Huene separated this species into the new genus Nannopterygius, named for the small fore- and hindpaddles. The first fossil is the most complete, but is flattened. All subsequent fossils are fragmentary. In 2020, several more species, including N. borealis, and the species once contained in the genera Paraophthalmosaurus and Yasykovia were named based on remains found in Norway and Russia.
 W
WParvipelvia is an extinct clade of euichthyosaur ichthyosaurs that existed from the Late Triassic to the early Late Cretaceous of Asia, Australia, Europe, North America and South America. Named by Ryosuke Motani, in 1999, it contains the basal taxa like Macgowania and Hudsonelpidia. Maisch and Matzke (2000) found in their analysis seven synapomorphies that support Parvipelvia. They also found 10 synapomorphies that support the existence of post-Triassic clade of ichthyosaurs, for which the name Neoichthyosauria was found to be available.
 W
WProtoichthyosaurus is a genus of ichthyosaur from the early Jurassic of southern England. Two species are known, P. prostaxalis—the type species, named by Appleby in 1979—and P. applebyi. A third species, P. prosostealis, was named by Appleby, but it was removed from the genus in 2017 due to its similarity to Ichthyosaurus. The genus Protoichthyosaurus was synonymized with Ichthyosaurus by Maisch and Hungerbuhler in 1997, and again by Maisch and Matzke in 2000. However, it was found to be distinct in 2017 by Dean Lomax and colleagues, who separated it from Ichthyosaurus on account of differences in the arrangement and shape of the carpal ossifications, as well as the absence of the fifth digit. The species most likely lived during the Hettangian stage, but may have lived as early as the Rhaetian and as late as the Sinemurian.
 W
WStenopterygius is an extinct genus of thunnosaur ichthyosaur known from Europe. This genus of ichthyosaur grew to a maximum length of 4 meters.
 W
WTemnodontosaurus is an extinct genus of ichthyosaurs from the Early Jurassic, ranging between 200 and 175 million years ago, and known from Europe and Chile. They lived in the deeper areas of the open ocean. University of Bristol paleontologist Jeremy Martin described the genus Temnodontosaurus as “one of the most ecologically disparate genera of ichthyosaurs”.
 W
WTemnodontosaurus eurycephalus is an extinct species of marine reptile. It is thought to have been a nektonic carnivore. Its name comes from the Greek ευρύς, for "wide" and κεφαλή for "head". It possibly belongs to a new genus.
 W
WThunnosauria is an extinct clade of parvipelvian ichthyosaurs from the Early Jurassic to the early Late Cretaceous of Asia, Australia, Europe, North America, and South America. Named by Ryosuke Motani in 1999, it contains the basal taxa Ichthyosaurus and Stenopterygius and the family Ophthalmosauridae. In thunnosaurs, the fore fin is at least twice as long as the hind fin.
 W
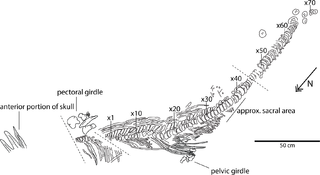
WWahlisaurus is an extinct genus of leptonectid ichthyosaur. The holotype was found in the Scunthorpe Mudstone in Nottinghamshire in 1951 and described for the first time only in 2016 by Dean Lomax. The type species is Wahlisaurus massare.