 W
WThyroid disease is a medical condition that affects the function of the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland is located at the front of the neck and produces thyroid hormones that travel through the blood to help regulate many other organs, meaning that it is an endocrine organ. These hormones normally act in the body to regulate energy use, infant development, and childhood development.
 W
WColloid nodules, also known as adenomatous nodules or colloid nodular goiter are benign, noncancerous enlargement of thyroid tissue. Although they may grow large, and there may be more than one, they are not malignant and they will not spread beyond the thyroid gland. Colloid nodules are the most common kind of thyroid nodule.
 W
WCongenital hypothyroidism (CH) is thyroid hormone deficiency present at birth. If untreated for several months after birth, severe congenital hypothyroidism can lead to growth failure and permanent intellectual disability. Infants born with congenital hypothyroidism may show no effects, or may display mild effects that often go unrecognized as a problem. Significant deficiency may cause excessive sleeping, reduced interest in nursing, poor muscle tone, low or hoarse cry, infrequent bowel movements, significant jaundice, and low body temperature.
 W
WCongenital iodine deficiency syndrome is a medical condition present at birth marked by impaired physical and mental development, due to insufficient thyroid hormone (hypothyroidism) often caused by insufficient dietary iodine during pregnancy. It is one cause of underactive thyroid function at birth, called congenital hypothyroidism, and also referred to as cretinism.
 W
WDe Quervain's thyroiditis, also known as subacute granulomatous thyroiditis or giant cell thyroiditis, is a member of the group of thyroiditis conditions known as resolving thyroiditis. People of all ages and genders may be affected.
 W
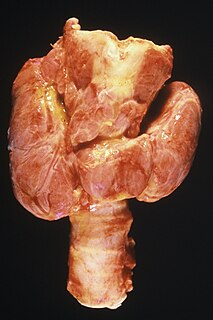
WA goitre, or goiter, is a swelling in the neck resulting from an enlarged thyroid gland. A goitre can be associated with a thyroid that is not functioning properly.
 W
WGraves disease, also known as toxic diffuse goiter, is an autoimmune disease that affects the thyroid. It frequently results in and is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism. It also often results in an enlarged thyroid. Signs and symptoms of hyperthyroidism may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, poor tolerance of heat, diarrhea and unintentional weight loss. Other symptoms may include thickening of the skin on the shins, known as pretibial myxedema, and eye bulging, a condition caused by Graves ophthalmopathy. About 25 to 80% of people with the condition develop eye problems.
 W
WGraves ophthalmopathy, also known as thyroid eye disease (TED), is an autoimmune inflammatory disorder of the orbit and periorbital tissues, characterized by upper eyelid retraction, lid lag, swelling, redness (erythema), conjunctivitis, and bulging eyes (exophthalmos). It occurs most commonly in individuals with Graves' disease, and less commonly in individuals with Hashimoto's thyroiditis, or in those who are euthyroid.
 W
WHashimoto's thyroiditis, also known as chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis and Hashimoto's disease, is an autoimmune disease in which the thyroid gland is gradually destroyed. Early on, symptoms may not be noticed. Over time, the thyroid may enlarge, forming a painless goiter. Some people eventually develop hypothyroidism with accompanying weight gain, fatigue, constipation, depression, hair loss, and general pains. After many years the thyroid typically shrinks in size. Potential complications include thyroid lymphoma.
 W
WHyperthyroidism is the condition that occurs due to excessive production of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland. Thyrotoxicosis is the condition that occurs due to excessive thyroid hormone of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidism. Some, however, use the terms interchangeably. Signs and symptoms vary between people and may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, heat intolerance, diarrhea, enlargement of the thyroid, hand tremor, and weight loss. Symptoms are typically less severe in the elderly and during pregnancy. An uncommon complication is thyroid storm in which an event such as an infection results in worsening symptoms such as confusion and a high temperature and often results in death. The opposite is hypothyroidism, when the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone.
 W
WHyperthyroxinemia is a thyroid disease where the serum levels of thyroxine are higher than expected.
 W
WHypothyroidism, also called underactive thyroid or low thyroid, is a disorder of the endocrine system in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone. It can cause a number of symptoms, such as poor ability to tolerate cold, a feeling of tiredness, constipation, slow heart rate, depression, and weight gain. Occasionally there may be swelling of the front part of the neck due to goiter. Untreated cases of hypothyroidism during pregnancy can lead to delays in growth and intellectual development in the baby or congenital iodine deficiency syndrome.
 W
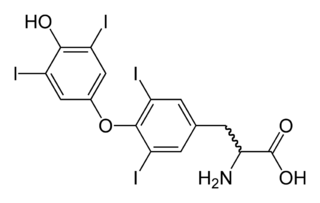
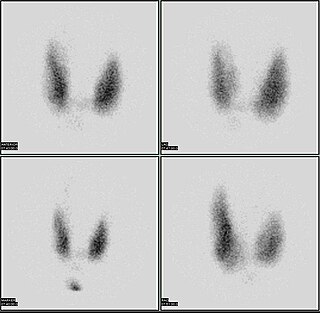
WThe radioactive iodine uptake test is a type of scan used in the diagnosis of thyroid problems, particularly hyperthyroidism. It is entirely different from radioactive iodine therapy, which uses much higher doses to destroy cancerous cells. The RAIU test is also used as a follow up to RAI therapy to verify that no thyroid cells survived, which could still be cancerous.
 W
WThe Sign of Hertoghe or Queen Anne's sign is a thinning or loss of the outer third of the eyebrows, and is a classical sign of hypothyroidism or dermatitis atopica, but it can also be detected in lepromatous leprosy. The sign is named after the Belgian Internist Eugene Ludovic Christian Hertoghe, who was a native of Antwerp, and was the first pioneer in thyroid function research.
 W
WSubacute thyroiditis is a form of thyroiditis that can be a cause of both thyrotoxicosis and hypothyroidism. It is uncommon and can affect individuals of both sexes, occurring three times as often in women than in men. and people of all ages. The most common form, subacute granulomatous, or de Quervain's, thyroiditis manifests as a sudden and painful enlargement of the thyroid gland accompanied with fever, malaise and muscle aches. Indirect evidence has implicated viral infection in the etiology of subacute thyroiditis. This evidence is limited to preceding upper respiratory tract infection, elevated viral antibody levels, and both seasonal and geographical clustering of cases. There may be a genetic predisposition.
 W
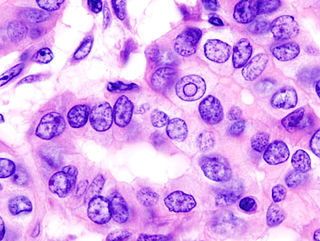
WThyroid cancer is cancer that develops from the tissues of the thyroid gland. It is a disease in which cells grow abnormally and have the potential to spread to other parts of the body. Symptoms can include swelling or a lump in the neck. Cancer can also occur in the thyroid after spread from other locations, in which case it is not classified as thyroid cancer.
 W
WThyroid dyshormonogenesis is a rare condition due to genetic defects in the synthesis of thyroid hormones.
 W
WThyroid hormone resistance describes a rare syndrome in which the thyroid hormone levels are elevated but the thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) level is not suppressed, or not completely suppressed as would be expected. The first report of the condition appeared in 1967. Essentially this is decreased end organ responsiveness to thyroid hormones. A new term "impaired sensitivity to thyroid hormone" has been suggested in March 2014 by Refetoff et al.
 W
WThyroid neoplasm is a neoplasm or tumor of the thyroid. It can be a benign tumor such as thyroid adenoma, or it can be a malignant neoplasm, such as papillary, follicular, medullary or anaplastic thyroid cancer. Most patients are 25 to 65 years of age when first diagnosed; women are more affected than men. The estimated number of new cases of thyroid cancer in the United States in 2010 is 44,670 compared to only 1,690 deaths. Of all thyroid nodules discovered, only about 5 percent are cancerous, and under 3 percent of those result in fatalities.
 W
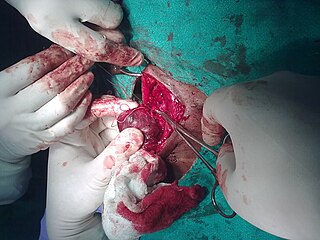
WThyroid nodules are nodules which commonly arise within an otherwise normal thyroid gland. They may be hyperplastic or tumorous, but only a small percentage of thyroid tumors are malignant. Small, asymptomatic nodules are common, and often go unnoticed. Nodules that grow larger or produce symptoms may eventually need medical care. A goitre may have one nodule – uninodular, multiple nodules – multinodular, or be diffuse.
 W
WA thyroidectomy is an operation that involves the surgical removal of all or part of the thyroid gland. General, endocrine or head and neck surgeons often perform a thyroidectomy when a patient has thyroid cancer or some other condition of the thyroid gland or goiter. Other indications for surgery include cosmetic, or symptomatic obstruction. Thyroidectomy is a common surgical procedure that has several potential complications or sequelae including: temporary or permanent change in voice, temporary or permanently low calcium, need for lifelong thyroid hormone replacement, bleeding, infection, and the remote possibility of airway obstruction due to bilateral vocal cord paralysis. Complications are uncommon when the procedure is performed by an experienced surgeon.
 W
WThyroiditis is the inflammation of the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland is located on the front of the neck below the laryngeal prominence, and makes hormones that control metabolism.
 W
WThyrotoxic periodic paralysis (TPP) is a condition featuring attacks of muscle weakness in the presence of hyperthyroidism. Hypokalemia is usually present during attacks. The condition may be life-threatening if weakness of the breathing muscles leads to respiratory failure, or if the low potassium levels lead to cardiac arrhythmias. If untreated, it is typically recurrent in nature.
 W
WThe winter-over syndrome is a condition that occurs in individuals who "winter-over" throughout the Antarctic winter, which can last seven to eight months. It has been observed in inhabitants of research stations in Antarctica, as well as in polar bases such as Thule, Alert and Eureka. It consists of a variety of behavioral and medical disturbances, including irritability, depression, insomnia, absentmindedness, aggressive behavior, and irritable bowel syndrome.