 W
WThe acuminate horseshoe bat is a species of bat in the family Rhinolophidae. It is found in Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, the Philippines, and Thailand. It lives in forests and urban areas.
 W
WAnderson's squirrel is a species of rodent in the family Sciuridae. It is found in forests in China and Myanmar. It is threatened by habitat loss.
 W
WThe arcuate horseshoe bat is a species of bat in the family Rhinolophidae. It is found in Indonesia, Malaysia, Papua New Guinea, and the Philippines.
 W
WThe black-fronted duiker is a small antelope found in central and west-central Africa.
 W
WThe black-shanked douc is an endangered species of douc found mostly in the forests of eastern Cambodia, with some smaller populations in Vietnam. This species is unique among the doucs in having a largely greyish-blue face. No global population estimate exists, although the Wildlife Conservation Society report an estimated 23,000 individuals present in Cambodia's Keo Seima Wildlife Sanctuary. Prior to the discovery of the significance of this population, the largest populations were believed to be in adjacent Vietnam, where the largest known population is around 500-600 individuals. They are primarily arboreal and their diet consists on leaves, of which they obtain most of their water.
 W
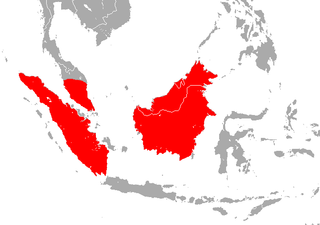
WThe Borneo roundleaf bat or Bornean leaf-nosed bat is a species of bat in the family Hipposideridae. It is found in Borneo, Sumatra and Peninsular Malaysia. Hipposideros sabanus is a synonym of this species.
 W
WThe cave nectar bat, dawn bat, common dawn bat, common nectar bat or lesser dawn bat is a species of megabat within the genus Eonycteris. The scientific name of the species was first published by Dobson in 1871.
 W
WThe Chinese shrew mole is a species of mammal in the family Talpidae. It is endemic to China, Sichuan Province. Its natural habitat is temperate forests.
 W
WThe Chinese water myotis is a species of vesper bat. It is native to eastern India, Vietnam and China where it is found in forest habitats. It is believed to roost in caves and hollow trees.
 W
WThe crowned sifaka is a sifaka endemic to western Madagascar. It is of comparable size to the Golden-crowned sifaka and up to a meter in length, of which 47-57 centimeters are tail. The species is an arboreal vertical climber and leaper whose diet consists of leaves, fruits and flowers. It is threatened by habitat destruction and currently classified as critically endangered by the IUCN.
 W
WThe greater bamboo lemur, also known as the broad-nosed bamboo lemur and the broad-nosed gentle lemur, is the largest bamboo lemur, at over five pounds or nearly 2.5 kilograms. It has greyish brown fur and white ear tufts, and has a head-body length of around one and a half feet, or forty to fifty centimeters. They have relatively long tails and long back legs for leaping vertically amongst the trees of their forest habitat. It feeds almost exclusively on the bamboo species of Cathariostachys madagascariensis, preferring the shoots but also eating the pith and leaves. It is unknown how their metabolism deals with the cyanide found in the shoots. The typical daily dose would be enough to kill humans. Greater bamboo lemurs occasionally consume fungi, flowers, and fruit. Its main food source is bamboo and it is the main reason why it has become critically endangered. Areas with high density of bamboo have major human disturbances, where humans cut or illegally cut down bamboo. Its only confirmed predators are the fossa and the bushpigs, but raptors are also suspected. Its current range is restricted to southeastern Madagascar, although fossils indicate its former range extended across bigger areas of the island, including as far north as Ankarana. Some notable parts of the current range are the Ranomafana and Andringitra National Parks.
 W
WThe hairy-faced bat is a species of vesper bat.
 W
WHector's beaked whale, is a small mesoplodont living in the Southern Hemisphere. This whale is named after Sir James Hector, a founder of the colonial museum in Wellington, New Zealand. The species has rarely been seen in the wild.
 W
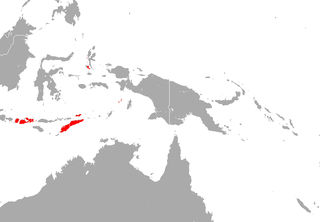
WThe insular horseshoe bat is a species of bat in the family Rhinolophidae. It is endemic to Indonesia.
 W
WThe large Mindanao roundleaf bat is a species of bat in the family Hipposideridae endemic to the Philippines.
 W
WThe lesser ricefield rat is a rodent in the family Muridae. The species was first described by Robert Swinhoe in 1871. It is found in China, Laos, Taiwan, Thailand, and Vietnam.
 W
WThe mandarin vole is a species of vole found in central China as well as the southern and central Korean Peninsula. An adult mandarin vole is typically of about 115 millimeters in length, in addition to about 28 mm of tail. It is smaller and darker in color than the reed vole, Microtus fortis.
 W
WMilne-Edwards's sifaka, or Milne-Edwards's simpona, is a large arboreal, diurnal lemur endemic to the eastern coastal rainforest of Madagascar. Milne-Edwards's sifaka is characterized by a black body with a light-colored "saddle" on the lower part of its back. It is closely related to the diademed sifaka, and was until recently considered a subspecies of it. Like all sifakas, it is a primate in the family Indriidae.
 W
WThe Moupin pika, also known as Ribetischer Pika, Moupin-Pika, Pika del Tibet, and Manipuri pika, is a species of mammal in the pika family, Ochotonidae. It has many subspecies, some of which may be distinct species. Its summer pelage is dark russet-brown with some light spots on the dorsal side, and ochraceous buff tinged on the belly. In winter it is lighter, with buff to dull brown dorsal pelage. A generalist herbivore, it is found in the mountains of the eastern Tibetan Plateau in China, Bhutan, India (Sikkim), and northern Myanmar. Both the International Union for Conservation of Nature Red List of Endangered Species and the Red List of China's Vertebrates classify it as a species of least concern; although one subspecies may be endangered.
 W
WMyotis fimbriatus is a species of vesper bat in the family Vespertilionidae. It is found only in China. It's also called the fringed long-footed myotis. The fringed long-footed myotis is described as having short, thick, brown fur with pale whitish fur ventrally. A captured female was measured with ears that were 14.4 mm long, a forearm 42.2 mm long, and a weight of 9.9 grams. Myotis fimbriatus is listed as being of least concern by the IUCN as of 2008. In 2000, Myotis fimbriatus was listed as being "lower risk/near threatened".
 W
WMyotis nipalensis commonly known as Nepal myotis is a vesper bat of genus Myotis.
 W
WThe northern Chinese boar is a subspecies of wild boar native to China and Vietnam. The subspecies was described by Alphonse Milne-Edwards in 1871. It also occurs in Sichuan. It is likely to be the ancestor of domestic pigs.
 W
WThe rufous trident bat, Persian trident bat, or triple nose-leaf bat is a species of bat in the genus Triaenops. It occurs in southwestern Pakistan, southern Iran, the United Arab Emirates, Oman, and Yemen. In the last country, it occurs together with the much smaller Triaenops parvus. Populations from Madagascar and mainland Africa have also been assigned to T. persicus, but are referable to the species Triaenops menamena and Triaenops afer, respectively. Madagascar populations have also been referred to as Triaenops rufus, but this name is a synonym of T. persicus.
 W
WThe silky sifaka is a large lemur characterized by long, silky, white fur. It has a very restricted range in northeastern Madagascar, where it is known locally as the simpona. It is one of the rarest mammals on Earth, and is listed by the International Union for Conservation of Nature as one of the world's 25 most critically endangered primates. The silky sifaka is one of nine sifaka species, and one of four former subspecies of diademed sifaka (P. diadema). Studies in 2004 and 2007 compared external proportions, genetics, and craniodental anatomy supporting full species status, which has generally been accepted.
 W
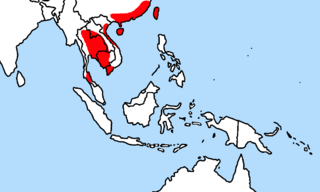
WStoliczka's trident bat is a species of bat in the family Hipposideridae. It is found in China, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Thailand, and Vietnam.