 W
WIn neuroanatomy, a sulcus is a depression or groove in the cerebral cortex. It surrounds a gyrus, creating the characteristic folded appearance of the brain in humans and other mammals. The larger sulci are usually called fissures.
 W
WThe calcarine sulcus is an anatomical landmark located at the caudal end of the medial surface of the brain of humans and other primates. Its name comes from the Latin "calcar" meaning "spur". It is very deep, and known as a complete sulcus.
 W
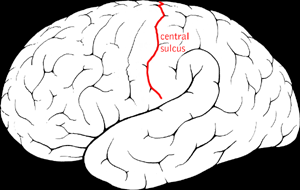
WThe central sulcus is a sulcus, or groove, in the cerebral cortex in the brains of vertebrates. Also called the central fissure, or the fissure of Rolando or the Rolandic fissure, after Luigi Rolando. It is sometimes confused with the longitudinal fissure.
 W
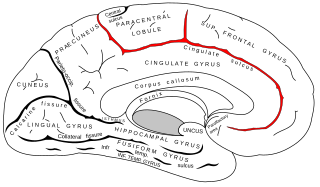
WThe cingulate sulcus is a sulcus on the cingulate cortex in the medial wall of the cerebral cortex. The frontal and parietal lobes are separated from the cingulate gyrus by the cingulate sulcus. It terminates as the marginal sulcus of the cingulate sulcus. It sends a ramus to separate the paracentral lobule from the frontal gyri, the paracentral sulcus.
 W
WThe collateral fissure is on the tentorial surface of the hemisphere and extends from near the occipital pole to within a short distance of the temporal pole.
 W
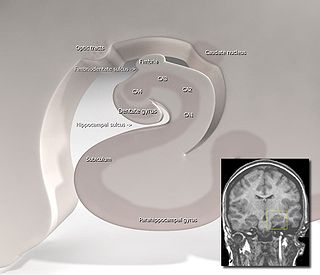
WThe hippocampal sulcus, also known as the hippocampal fissure, is a sulcus that separates the dentate gyrus from the subiculum and the CA1 field in the hippocampus.
 W
WThe inferior frontal sulcus is a sulcus between the middle frontal gyrus and the inferior frontal gyrus.
 W
WThe inferior surface of the temporal lobe is concave, and is continuous posteriorly with the tentorial surface of the occipital lobe. It is traversed by the inferior temporal sulcus, which extends from near the occipital pole behind, to within a short distance of the temporal pole in front, but is frequently subdivided by bridging gyri.
 W
WThe intraparietal sulcus (IPS) is located on the lateral surface of the parietal lobe, and consists of an oblique and a horizontal portion. The IPS contains a series of functionally distinct subregions that have been intensively investigated using both single cell neurophysiology in primates and human functional neuroimaging. Its principal functions are related to perceptual-motor coordination and visual attention, which allows for visually-guided pointing, grasping, and object manipulation that can produce a desired effect.
 W
WIn the occipital lobe, the lateral occipital sulcus, where present, divides the lateral, or middle occipital gyrus into a superior and an inferior part, which are then continuous in front with the parietal and temporal lobes. The anterior portion is often incomplete, but in some individuals it may encounter the superior temporal sulcus whilst the posterior portion originates from the middle of the curved lunate sulcus, or from a curved portion of the transverse occipital sulcus if absent.
 W
WThe lateral sulcus is one of the most prominent features of the human brain. The lateral sulcus is a deep fissure in each hemisphere that separates the frontal and parietal lobes from the temporal lobe. The insular cortex lies deep within the lateral sulcus.
 W
WIn brain anatomy, the lunate sulcus or simian sulcus also known as the sulcus lunatus is a fissure in the occipital lobe variably found in humans and more often larger when present in apes and monkeys. The lunate sulcus marks the transition between V1 and V2.
 W
WThe marginal sulcus may be considered the termination of the cingulate sulcus. It separates the paracentral lobule anteriorly and the precuneus posteriorly.
 W
WThe longitudinal fissure is the deep groove that separates the two cerebral hemispheres of the vertebrate brain. Lying within it is a continuation of the dura mater called the falx cerebri. The inner surfaces of the two hemispheres are convoluted by gyri and sulci just as is the outer surface of the brain.
 W
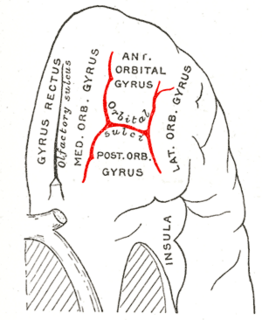
WThe inferior or orbital surface of the frontal lobe is concave, and rests on the orbital plate of the frontal bone. It is divided into four orbital gyri by a well-marked H-shaped orbital sulcus
 W
WThe paracentral sulcus is a sulcus of the brain. It forms the paracentral lobule's anterior border. It is part of the cingulate sulcus.
 W
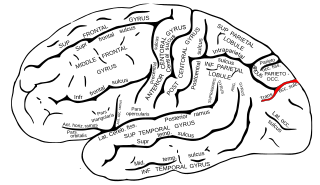
WThe parieto-occipital sulcus is a deep sulcus in the cerebral cortex that marks the boundary between the cuneus and precuneus, and also between the parietal and occipital lobes. Only a small part can be seen on the lateral surface of the hemisphere, its chief part being on the medial surface.
 W
WThe postcentral sulcus of the parietal lobe lies parallel to, and behind, the central sulcus in the human brain.
 W
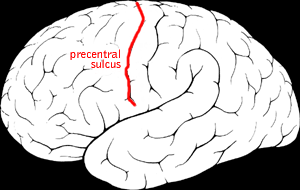
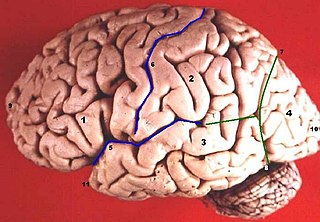
WThe precentral sulcus is a part of the human brain that lies parallel to, and in front of, the central sulcus.
 W
WAbout 5 centimetres (2.0 in) in front of the occipital pole of the human brain, on the infero-lateral border is an indentation or notch, named the preoccipital notch. It is considered a landmark because the occipital lobe is located just behind the line that connects that notch with the parietoccipital sulcus.
 W
WIn the human brain, the entorhinal cortex appears as a longitudinal elevation anterior to the parahippocampal gyrus, with a corresponding internal furrow, the external rhinal sulcus, separating it from the inferiolateral surface of the hemisphere close to the lamina terminalis. It is analogous to the collateral fissure found further caudally in the inferior part of the temporal lobe.
 W
WThe subparietal sulcus or suprasplenial sulcus is a sulcus, or crevice, on the medial surface of each cerebral hemisphere, above the splenium of the corpus callosum. It separates the precuneus from the posterior part of the cingulate gyrus. It is the posterior continuation of the cingulate sulcus. The cingulate sulcus actually "terminates" as the marginal sulcus of the cingulate sulcus. It extends posteriorly toward the calcarine sulcus.
 W
WThe superior frontal sulcus is a sulcus between the superior frontal gyrus and the middle frontal gyrus.
 W
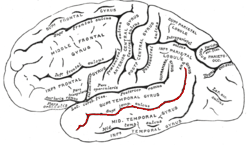
WThe superior temporal sulcus (STS) is the sulcus separating the superior temporal gyrus from the middle temporal gyrus in the temporal lobe of the brain. A sulcus is a deep groove that curves into the largest part of the brain, the cerebrum, and a gyrus is a ridge that curves outward of the cerebrum.
 W
WThe transverse occipital sulcus is a structure in the occipital lobe.