 W
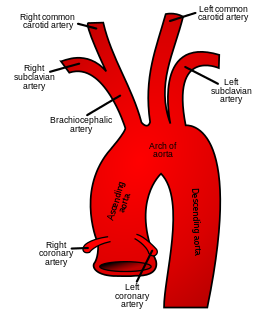
WThe aorta is the main and largest artery in the human body, originating from the left ventricle of the heart and extending down to the abdomen, where it splits into two smaller arteries. The aorta distributes oxygenated blood to all parts of the body through the systemic circulation.
 W
WThe aortic arch, arch of the aorta, or transverse aortic arch is the part of the aorta between the ascending and descending aorta. The arch travels backward, so that it ultimately runs to the left of the trachea.
 W
WThe ascending aorta (AAo) is a portion of the aorta commencing at the upper part of the base of the left ventricle, on a level with the lower border of the third costal cartilage behind the left half of the sternum.
 W
WThe atrial branches of right coronary artery derive from the right coronary artery and provide part of the blood supply to the right atrium and left atrium.
 W
WThe atrioventricular nodal branch is a cardiac artery that is crucial because it feeds the atrioventricular node, necessary for the excitation and contraction of the ventricles. Most frequently it arises as a distal branch from the right coronary artery near the crux of the heart. In some people, the atrioventricular node instead receives blood from the circumflex branch of the left coronary artery, otherwise known as the left circumflex coronary artery or LCX. Very rarely, in approximately 2% of people, the vascular supply to the atrioventricular node arises from both the right coronary artery and the left circumflex branch.
 W
WThe brachiocephalic artery is an artery of the mediastinum that supplies blood to the right arm and the head and neck.
 W
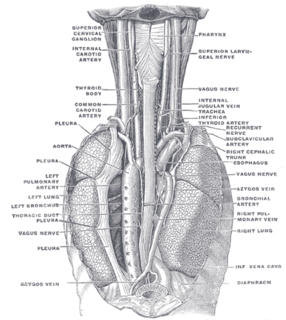
WIn human anatomy, the bronchial arteries supply the lungs with nutrition and oxygenated blood. Although there is much variation, there are usually two bronchial arteries that run to the left lung, and one to the right lung.
 W
WThe "LCX", or left circumflex artery is an artery of the heart.
 W
WIn anatomy, the left and right common carotid arteries (carotids) are arteries that supply the head and neck with oxygenated blood; they divide in the neck to form the external and internal carotid arteries.
 W
WThe costocervical trunk arises from the upper and back part of the second part of subclavian artery, behind the scalenus anterior on the right side, and medial to that muscle on the left side.
 W
WThe deep cervical artery is an artery of the neck.
 W
WThe descending aorta is part of the aorta, the largest artery in the body. The descending aorta begins at the aortic arch and runs down through the chest and abdomen. The descending aorta anatomically consists of two portions or segments, the thoracic and the abdominal aorta, in correspondence with the two great cavities of the trunk in which it is situated. Within the abdomen, the descending aorta branches into the two common iliac arteries which serve the pelvis and eventually legs.
 W
WThe intercostal arteries are a group of arteries that supply the area between the ribs ("costae"), called the intercostal space. The highest intercostal artery is an artery in the human body that usually gives rise to the first and second posterior intercostal arteries, which supply blood to their corresponding intercostal space. It usually arises from the costocervical trunk, which is a branch of the subclavian artery. Some anatomists may contend that there is no supreme intercostal artery, only a supreme intercostal vein.
 W
WIn human anatomy, the internal thoracic artery (ITA), previously commonly known as the internal mammary artery, is an artery that supplies the anterior chest wall and the breasts. It is a paired artery, with one running along each side of the sternum, to continue after its bifurcation as the superior epigastric and musculophrenic arteries.
 W
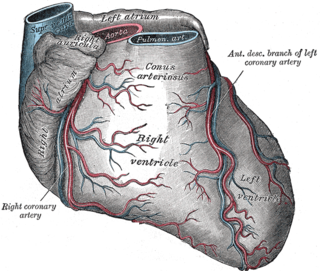
WThe left anterior descending artery is a branch of the left coronary artery. Blockage of this artery is often called the widow-maker infarction due to a high death risk.
 W
WThe left coronary artery is an artery that arises from the aorta above the left cusp of the aortic valve and feeds blood to the left side of the heart. It is also known as the left main coronary artery and the left main stem coronary artery. It is one of the coronary arteries.
 W
WThe left marginal artery is a branch of the circumflex artery, originating at the left atrioventricular sulcus, traveling along the left margin of heart towards the apex of the heart.
 W
WThe pericardiacophrenic artery is a long slender branch of the internal thoracic artery. It accompanies the phrenic nerve, between the pleura and pericardium, to the diaphragm, to which it is distributed. It anastomoses with the musculophrenic and superior phrenic arteries.
 W
WIn the coronary circulation, the posterior interventricular artery, most often called the posterior descending artery (PDA), is an artery running in the posterior interventricular sulcus to the apex of the heart where it meets with the anterior interventricular artery or also known as Left Anterior Descending artery. It supplies the posterior third of the interventricular septum. The remaining anterior two-thirds is supplied by the anterior interventricular artery which is a septal branch of the left anterior descending artery, which is a branch of left coronary artery.
 W
WA pulmonary artery is an artery in the pulmonary circulation that carries deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs. The largest pulmonary artery is the main pulmonary artery or pulmonary trunk from the heart, and the smallest ones are the arterioles, which lead to the capillaries that surround the pulmonary alveoli.
 W
WIn the blood supply of the heart, the right coronary artery (RCA) is an artery originating above the right cusp of the aortic valve, at the right aortic sinus in the heart. It travels down the right coronary sulcus, towards the crux of the heart. It branches into the posterior descending artery and the right marginal artery. Although rare, several anomalous courses of the right coronary artery have been described including origin from the left aortic sinus.
 W
WThe right marginal branch of right coronary artery is a large marginal branch which follows the acute margin of the heart and supplies blood to both surfaces of the right ventricle.
 W
WThe sinoatrial nodal artery is an artery of the heart which supplies the sinoatrial node, the natural pacemaker center of the heart, and arises from the right coronary artery in around 60% of people. In about 40% of cases, the sinoatrial artery is a branch of the left circumflex coronary artery. In less than 1% of humans, the artery has an anomalous origin directly from the coronary sinus, descending aorta, or distal right coronary artery.
 W
WIn human anatomy, the subclavian arteries are paired major arteries of the upper thorax, below the clavicle. They receive blood from the aortic arch. The left subclavian artery supplies blood to the left arm and the right subclavian artery supplies blood to the right arm, with some branches supplying the head and thorax. On the left side of the body, the subclavian comes directly off the aortic arch, while on the right side it arises from the relatively short brachiocephalic artery when it bifurcates into the subclavian and the right common carotid artery.
 W
WIn human anatomy, superior epigastric artery refers to a blood vessel that carries oxygenated blood and arises from the internal thoracic artery. It anastomoses with the inferior epigastric artery at the umbilicus and supplies the anterior part of the abdominal wall and some of the diaphragm.
 W
WThe descending thoracic aorta is a part of the aorta located in the thorax. It is the third and last part of the thoracic aorta and is a continuation of the aortic arch. It is located within the posterior mediastinal cavity. The descending thoracic aorta begins at the lower border of the fourth thoracic vertebra and ends in front of the lower border of the twelfth thoracic vertebra, at the aortic hiatus in the diaphragm where it becomes the abdominal aorta.