 W
WCoronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The first case was identified in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. It has since spread worldwide, leading to an ongoing pandemic.
 W
WThe Access to COVID-19 Tools Accelerator, or the Global Collaboration to Accelerate the Development, Production and Equitable Access to New COVID-19 diagnostics, therapeutics and vaccines, is a G20 initiative announced by pro-tem Chair Mohammed al-Jadaan on 24 April 2020. A call to action was published simultaneously by the World Health Organization (WHO) on 24 April.
 W
WBradykinin is a peptide that promotes inflammation. It causes arterioles to dilate (enlarge) via the release of prostacyclin, nitric oxide, and endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor and makes veins constrict, via prostaglandin F2, thereby leading to leakage into capillary beds, due to the increased pressure in the capillaries. Bradykinin is a physiologically and pharmacologically active peptide of the kinin group of proteins, consisting of nine amino acids.
 W
WIn the psychology of human behavior, denialism is a person's choice to deny reality as a way to avoid a psychologically uncomfortable truth. Denialism is an essentially irrational action that withholds the validation of a historical experience or event, when a person refuses to accept an empirically verifiable reality.
 W
WCovid-Organics (CVO) is an Artemisia-based Ayurvedic drink that Andry Rajoelina, president of Madagascar, claims can prevent and cure Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). The Ayurvedic drink is produced from a species under the Artemisia genus from which artemisinin is extracted for malaria treatment.
 W
WDexamethasone is a corticosteroid medication used to treat rheumatic problems, a number of skin diseases, severe allergies, asthma, chronic obstructive lung disease, croup, brain swelling, eye pain following eye surgery, and along with antibiotics in tuberculosis. In adrenocortical insufficiency, it may be used in combination with a mineralocorticoid medication such as fludrocortisone. In preterm labor, it may be used to improve outcomes in the baby. It may be given by mouth, as an injection into a muscle, as an injection into a vein, as a topical cream or ointment for the skin or as a topical ophthalmic solution to the eye. The effects of dexamethasone are frequently seen within a day and last for about three days.
 W
WCOVID‑19 drug development is the research process to develop preventative therapeutic prescription drugs that would alleviate the severity of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‑19). From early 2020 through 2021, several hundred drug companies, biotechnology firms, university research groups, and health organizations were developing over 600 potential therapies for COVID‑19 disease in various stages of preclinical or clinical research, with 391 therapeutic candidates in clinical trials, as of January 2021.
 W
WDrug repositioning is the re-purposing of an approved drug for the treatment of a different disease or medical condition than that for which it was originally developed. This is one line of scientific research which is being pursued to develop safe and effective COVID-19 treatments. Other research directions include the development of a COVID-19 vaccine and convalescent plasma transfusion.
 W
WPandemic fatigue is the state of being worn out by recommended precautions and restrictions relating to a pandemic, often due to the length of the restrictions and lack of activities for one to engage in, resulting in boredom, depression, and other issues, thereby leading one to abandoning these precautions and risk catching the disease. Pandemic fatigue can be responsible for an increased number of cases.
 W
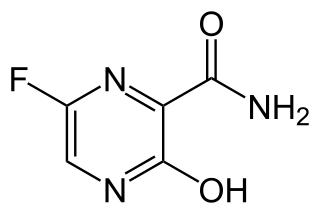
WFavipiravir, sold under the brand name Avigan among others, is an antiviral medication used to treat influenza in Japan. It is also being studied to treat a number of other viral infections. Like the experimental antiviral drugs T-1105 and T-1106, it is a pyrazinecarboxamide derivative.
 W
WThe glossary of the COVID-19 pandemic is a list of definitions of terms relating to the COVID-19 pandemic. The pandemic has created and popularized many terms relating to disease and videoconferencing.
 W
WInvestigations into the origin of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) include several ongoing missions and efforts by governments, international organisations, and others.
 W
WLong COVID, also known as chronic COVID syndrome (CCS) and long-haul COVID, is the condition characterised by long-term sequelae—persisting after the typical convalescence period—of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Persistent symptoms include fatigue, headaches, shortness of breath, anosmia, muscle weakness, low fever and cognitive dysfunction.
 W
WMultisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C), or paediatric inflammatory multisystem syndrome, is a rare systemic illness involving persistent fever and extreme inflammation following exposure to SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for COVID-19. It can rapidly lead to medical emergencies such as insufficient blood flow around the body. Failure of one or more organs can occur. A warning sign is unexplained persistent fever with severe symptoms following exposure to COVID-19. Prompt referral to paediatric specialists is essential, and families need to seek urgent medical assistance. Most affected children will need intensive care.
 W
WNir Eyal is a bioethicist and Henry Rutgers Professor of Bioethics and Director of the Center for Population–Level Bioethics at Rutgers University in New Jersey. Formerly he was a bioethicist in the Department of Global Health and Population of the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health and the Department of Global Health and Social Medicine of the Harvard Medical School. He has long worked closely with Harvard bioethicist Daniel Wikler. Eyal's current visibility concerns his role in studying the ethics of human challenge trials in HIV, malaria, and coronavirus vaccine development. He has also written on 'bystander risks' during pandemics and infectious diseases and contract tracing during ebola.
 W
WPPE Needed is a Dutch "grassroots" initiative to address the global shortage of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) among frontliners. The platform is founded by Dunya Ressang, brothers Omar Kbiri, and Rachid Kbiri. They are a free-to-use global PPE initiative that, according to their website, seeks “to create an overview of the global PPE shortage during the Covid-19 Crisis and to locally enable matching of supply and shortages of PPE during this crisis.”
 W
WThe effect of COVID-19 infection on pregnancy is not completely known because of the lack of reliable data. If there is increased risk to pregnant women and fetuses, so far it has not been readily detectable.
 W
WSpeed and scale are key to mitigation of COVID-19, due to the fat-tailed nature of pandemic risk and the exponential growth of COVID-19 infections. For mitigation to be effective, (a) chains of transmission must be broken as quickly as possible through screening and containment, (b) health care must be available to provide for the needs of those infected, and (c) contingencies must be in place to allow for effective rollout of (a) and (b).
 W
WThe term "silent hypoxia" refers to hypoxia that does not coincide with shortness of breath. It is known to be a complication of coronavirus disease 2019. It is speculated that this condition is caused by SARS-CoV-2 affecting the blood flow of the lungs' airways, in addition to the blood vessels within the lungs, which must match in order to allow proper airflow, but not affecting them enough to cause shortness of breath. It is also speculated that silent hypoxia may be caused by the formation of small blood clots within the lungs. It has been shown that the breathing rates of patients with COVID-19 gradually increase, which in turn leads to silent hypoxia. It has also been shown that COVID-19 patients experience lesser levels of shortness of breath after exercise than non-COVID-19 patients. The condition is also known to be caused by walking pneumonia and altitude sickness.
 W
WDue to the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, people can sometimes be labelled, stereotyped, discriminated against, treated separately, or experience loss of status because of real or perceived links with the disease. As a result of such treatment, those who have or are perceived to have the disease, as well as their caregivers, family, friends, and communities, may be subjected to social stigma.
 W
WThe Solidarity trial for treatments is a multinational Phase III-IV clinical trial organized by the World Health Organization (WHO) and partners to compare four untested treatments for hospitalized people with severe COVID-19 illness. The trial was announced 18 March 2020, and as of 1 July, nearly 5,500 patients in 21 countries had been recruited to participate in the trial.
 W
WCOVID-19 surveillance involves monitoring the spread of the coronavirus disease in order to establish the patterns of disease progression. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends active surveillance, with focus of case finding, testing and contact tracing in all transmission scenarios. COVID-19 surveillance is expected to monitor epidemiological trends, rapidly detect new cases, and based on this information, provide epidemiological information to conduct risk assessment and guide disease preparedness.
 W
WCOVID-19 testing involves analyzing samples to assess the current or past presence of SARS-CoV-2. The two main branches detect either the presence of the virus or of antibodies produced in response to infection. Tests for viral presence are used to diagnose individual cases and to allow public health authorities to trace and contain outbreaks. Antibody tests instead show whether someone once had the disease. They are less useful for diagnosing current infections because antibodies may not develop for weeks after infection. It is used to assess disease prevalence, which aids the estimation of the infection fatality rate.
 W
WCoronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) spreads from person to person mainly through the respiratory route after an infected person coughs, sneezes, sings, talks or breathes. A new infection occurs when virus-containing particles exhaled by an infected person, either respiratory droplets or aerosols, get into the mouth, nose, or eyes of other people who are in close contact with the infected person. During human-to-human transmission, an average 1000 infectious SARS-CoV-2 virions are thought to initiate a new infection.
 W
WThere are many fake or unproven medical products and methods that claim to diagnose, prevent or cure COVID-19. Fake medicines sold for COVID-19 may not contain the ingredients they claim to contain, and may even contain harmful ingredients. In March 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) released a statement recommending against taking any medicines in an attempt to treat or cure COVID-19, although research on potential treatment was underway, including the Solidarity trial spearheaded by WHO. The WHO requested member countries to immediately notify them if any fake medicines or other falsified products were discovered. There are also many claims that existing products help against COVID-19; these spread through rumours online rather than conventional advertising.
 W
WBioNTech SE is a German biotechnology company based in Mainz that develops and manufactures active immunotherapies for patient-specific approaches to the treatment of diseases. It develops pharmaceutical candidates based on messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) for use as individualized cancer immunotherapies, as vaccines against infectious diseases and as protein replacement therapies for rare diseases, and also engineered cell therapy, novel antibodies and small molecule immunomodulators as treatment options for cancer.
 W
WHazard controls for COVID-19 in workplaces are the application of occupational safety and health methodologies for hazard controls to the prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). The proper hazard controls in the workplace depend on the worksite and job task, based on an occupational risk assessment of sources of exposure, disease severity in the community, and risk factors of individual workers who may be vulnerable to contracting COVID-19.