 W
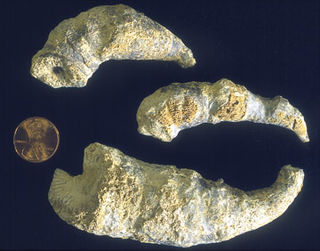
WAviculopecten is an extinct genus of bivalve mollusc that lived from the Early Devonian to the Late Triassic in Asia, Australia, Europe, North America, and South America.
 W
WCaninia is an extinct genus of rugose coral. Its fossils occur worldwide from the Devonian to the Permian periods.
 W
WCephalerpeton is an extinct genus of "protorothyridid" eureptile known from the Late Carboniferous of Illinois.
 W
WThe Climatiiformes is an order of extinct fish belonging to the class Acanthodii. Like most other "spiny sharks", the Climatiiformes had sharp spines. These animals were often fairly small in size and lived from the Late Silurian to the Early Carboniferous period. The type genus is Climatius. The order used to be subdivided into the suborders Climatiida and Diplacanthida, but subsequently Diplacanthida has been elevated to a separate order, the Diplacanthiformes. The Diplacanthiformes take their name from Diplacanthus, first described by Agassiz in 1843.
 W
WEuconcordia is an extinct genus of Late Carboniferous captorhinid known from Greenwood County, Kansas of the United States.
 W
WGerarus is an extinct genus of Archaeorthopteran insect, and is one of the most abundant genera of Carboniferous insects. They had a wingspan of up to 10 centimetres (4 in), and an inflated thorax armed with sharp spines up to 1 millimetre (0.04 in) long.
 W
WGyracanthides is an extinct genus of large acanthodian fish. They are mainly known for their long pectoral spine.
 W
WGyracanthus is an extinct genus of acanthodian.
 W
WHylonomus is an extinct genus of reptile that lived 312 million years ago during the Late Carboniferous period. It is the earliest unquestionable reptile. The only species is the type species Hylonomus lyelli.
 W
WJeletzkya douglassae is a fossil coleoid from the early Pennsylvanian Mazon Creek lagerstätten and represents the earliest known crown-group squid. Non-mineralized anatomy is preserved and comprises ten hooked tentacles and a radula.
 W
WLithostrotion is a genus of rugose coral which is commonly found as a fossil within Carboniferous Limestone. Lithostrotion is a member of the family Lithostrotionidae. The genus Lithostrotion, a common and readily recognised group of fossils, became extinct by the end of the Palaeozoic era.
 W
WMazothairos is an extinct genus of very large insect from the Carboniferous period. It was a member of the order Palaeodictyoptera. Although it is only known from very fragmentary remains it is estimated to have had a wingspan of about 56 centimeters (22 in), making it one of the largest-known insects, only being rivaled in size by the largest members of the order Meganisoptera, such as Meganeura and Meganeuropsis.
 W
WThe Palaeodictyopteroidea or Paleodictyopterida are an extinct superorder of Palaeozoic beaked insects, characterised by unique mouthparts consisting of 5 stylets. They represent the first important terrestrial herbivores, and the first major group of herbivorous insects. They appear during the Middle Carboniferous and continue through to the Late Permian. This large and diverse group includes 50% of all known Paleozoic insects. Palaeodictyopteroidea nymphs possessed movable wing pads and appear to have been able to perform simple flapping flight.
 W
WPaleothyris was a small, agile, anapsid romeriidan reptile which lived in the Middle Pennsylvanian epoch in Nova Scotia. Paleothyris had sharp teeth and large eyes, meaning that it was likely a nocturnal hunter. It was about a foot long. It probably fed on insects and other smaller animals found on the floor of its forest home. Paleothyris was an early sauropsid, yet it still had some features that were more primitive, more labyrinthodont-like than reptile-like, especially its skull, which lacked fenestrae, holes found in the skulls of most modern reptiles and mammals.
 W
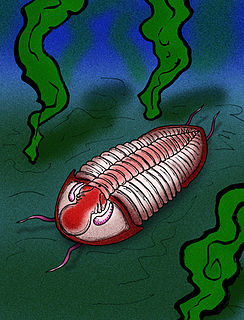
WPhillipsiidae is a family of proetid trilobites, the various genera of which comprise some of the last of the trilobites, with a range that extended from the Kinderhookian epoch of the Lower Mississippian, to the end of Changhsingian age at Permian-Triassic extinction event in the latest Permian period.
 W
WProtophasma is an extinct genus of Protorthopteran insect from the Carboniferous of France.
 W
WRecumbirostra is a clade of tetrapods which lived during the Carboniferous and Permian periods. It includes the families Pantylidae, Gymnarthridae, Ostodolepidae, Rhynchonkidae and Brachystelechidae, with additional families such as Microbrachidae and Molgophidae being included by some authors. Recumbirostra was erected as a clade in 2007 to include many of the taxa traditionally grouped in "Microsauria", which has since been shown to be a paraphyletic or polyphyletic grouping. Like other "microsaurs", the recumbirostrans have traditionally been considered to be members of the subclass Lepospondyli; however, phylogenetic analyses conducted by Pardo, Szostakiwskyj and Anderson (2015) and Pardo et al. (2017) recovered them as early-branching sauropsid amniotes instead.
 W
WSphenacanthus is an extinct genus of a chondrichtyan xenacanthiform that belongs to the Sphenacanthidae family and lived from the Late Devonian, through Carboniferous until the Late Permian period in Scotland, Spain, Russia and Brazil. It lived 359 million years ago, and probably it was one of the first member of the elasmobranchians, the lineage that leads to the modern sharks. Sphenacanthus probably hunts small fishes and, unlike their modern-day relatives, its inhabited fresh water lagoons. Sphenacanthus had seven fins, two in the upper part and five in the underside, and it have a heterodont dentition and mandibles relatively long and deeper. Sphenacanthus serrulatus is still only known from incomplete neurocranial remains and associated dermal material. These suggest that it was a relatively large shark, probably well over one meter in length when fully grown. Its body form was probably similar to that of other phalacanthous sharks.
 W
WSpilapterida is an extinct family of palaeodictyopterans. It is regarded as one of the most species-rich of its order.
 W
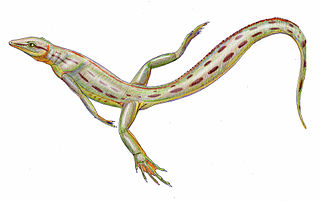
WSpinoaequalis is an extinct genus of diapsid reptile.
 W
WStrepsodus is a genus of rhizodont lobe-finned fish that lived during the Carboniferous period. Fossils have been found in North America and Australia.
 W
WTabulata, commonly known as tabulate corals, are an order of extinct forms of coral. They are almost always colonial, forming colonies of individual hexagonal cells known as corallites defined by a skeleton of calcite, similar in appearance to a honeycomb. Adjacent cells are joined by small pores. Their distinguishing feature is their well-developed horizontal internal partitions (tabulae) within each cell, but reduced or absent vertical internal partitions. They are usually smaller than rugose corals, but vary considerably in shape, from flat to conical to spherical.
 W
WTerebratulidae is a family of brachiopods with a fossil record dating back to the Late Devonian. It is subdivided into 11 subfamilies.
 W
WThamnoporella is an extinct genus of tabulate corals.
 W
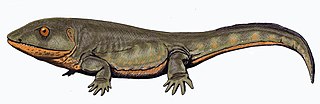
WWhatcheeriidae is an extinct family of tetrapods which lived in the Mississippian sub-period, a subdivision of the Carboniferous period. It contains the genera Pederpes, Whatcheeria, and possibly Ossinodus. Fossils of a possible whatcheeriid have been found from the Red Hill locality of Pennsylvania. If these remains are from a whatcheeriid, they extend the range of the family into the Late Devonian and suggest that advanced tetrapods may have lived alongside primitive tetrapod ancestors like Hynerpeton and Densignathus. They also imply that a very long ghost lineage of whatcheeriids lived through Romer's gap, a period during the Early Carboniferous conspicuously lacking in tetrapod remains.
 W
WXenacanthida is an order of prehistoric sharks that appeared during the Lower Carboniferous period. The order includes the families Xenacanthidae, Diplodoselachidae, and Orthacanthidae. The most notable members of the group are the genera Xenacanthus and Orthacanthus. Some Xenacanthida may have grown to lengths of 5 m (16 ft). Most forms had large serrated spines extending backwards from the neck. Xenacanthus had characteristic teeth. Most xenacanths died out at the end of the Permian in the Permian Mass Extinction, with only a few forms surviving into the Triassic period. They were native to freshwater, marginal marine and shallow marine habitats.
 W
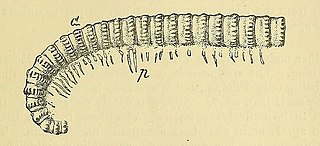
WXyloiulus is an extinct genus of millipede that lived during the Late Carboniferous which grew up to 2.25 inches (5.7 cm) in length. Fossils of the animal have been found in North America and Europe. The fossils are typically found in Sigillarian stumps.