 W
WAchilles tendon rupture is when the Achilles tendon, at the back of the ankle, breaks. Symptoms include the sudden onset of sharp pain in the heel. A snapping sound may be heard as the tendon breaks and walking becomes difficult.
 W
WAn ALPSA lesion is an injury at the front of the shoulder associated with shoulder dislocation.
 W
WAn anterior cruciate ligament injury occurs when the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is either stretched, partially torn, or completely torn. The most common injury is a complete tear. Symptoms include pain, a popping sound during injury, instability of the knee, and joint swelling. Swelling generally appears within a couple of hours. In approximately 50% of cases, other structures of the knee such as surrounding ligaments, cartilage, or meniscus are damaged.
 W
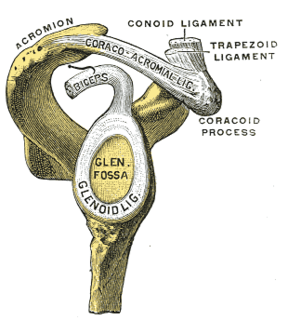
WA Bankart lesion is an injury of the anterior (inferior) glenoid labrum of the shoulder due to anterior shoulder dislocation. When this happens, a pocket at the front of the glenoid forms that allows the humeral head to dislocate into it. It is an indication for surgery and often accompanied by a Hill-Sachs lesion, damage to the posterior humeral head.
 W
WA biceps tendon rupture is a complete or partial rupture of a tendon of the biceps brachii muscle. It can affect the distal tendon, or either/both of the proximal tendons, attached to the long and short head of the muscle, respectively.
 W
WCuboid syndrome or cuboid subluxation describes a condition that results from subtle injury to the calcaneocuboid joint and ligaments in the vicinity of the cuboid bone, one of seven tarsal bones of the human foot.
 W
WA dislocated shoulder is when the head of the humerus is out of the shoulder joint. Symptoms include shoulder pain and instability. Complications may include a Bankart lesion, Hill-Sachs lesion, rotator cuff tear, or injury to the axillary nerve.
 W
WDislocations occur when two bones that originally met at the joint detach. Dislocations should not be confused with Subluxation. Subluxation is when the joint is still partially attached to the bone.
 W
WA hip dislocation is a disruption of the joint between the femur and pelvis. Specifically it is when the ball–shaped head of the femur comes out of the cup–shaped acetabulum of the pelvis. Symptoms typically include pain and an inability to move the hip. Complications may include avascular necrosis of the hip, injury to the sciatic nerve, or arthritis.
 W
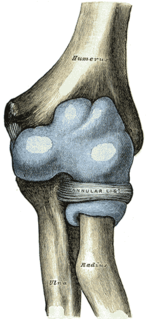
WA joint dislocation, also called luxation, occurs when there is an abnormal separation in the joint, where two or more bones meet. A partial dislocation is referred to as a subluxation. Dislocations are often caused by sudden trauma on the joint like an impact or fall. A joint dislocation can cause damage to the surrounding ligaments, tendons, muscles, and nerves. Dislocations can occur in any joint major or minor. The most common joint dislocation is a shoulder dislocation.
 W
WA knee dislocation is a knee injury in which there is a complete disruption of the joint between the tibia and the femur. Symptoms include knee pain and instability of the knee. Complications may include injury to an artery around the knee, most commonly the artery behind the knee, or compartment syndrome.
 W
WA metatarsophalangeal joint sprain is an injury to the connective tissue between the foot and one of the toes. When the big toe is involved, it is known as "turf toe".
 W
WA patellar dislocation is a knee injury in which the patella (kneecap) slips out of its normal position. Often the knee is partly bent, painful and swollen. The patella is also often felt and seen out of place. Complications may include a patella fracture or arthritis.
 W
WPatellar tendon rupture is a tear of the tendon that connects the knee cap (patella) to the tibia. Often there is sudden onset of pain and walking is difficult. In a complete rupture the ability to extend that knee is decreased. A pop may be felt when it occurs.
 W
WPerthes lesion is a variant of Bankart lesion, presenting as an anterior glenohumeral injury that occurs when the scapular periosteum remains intact but is stripped medially and the anterior labrum is avulsed from the glenoid but remains partially attached to the scapula by intact periosteum.
 W
WA pulled elbow, also known as a radial head subluxation, is when the ligament that wraps around the radial head slips off. Often a child will hold their arm against their body with the elbow slightly bent. They will not move the arm as this results in pain. Touching the arm, without moving the elbow, is usually not painful.
 W
WStraining of the hamstring, also known as a pulled hamstring, is defined as an excessive stretch or tear of muscle fibers and related tissues. Hamstring injuries are common in athletes participating in many sports. Track and field athletes are particularly at risk, as hamstring injuries have been estimated to make up 29% of all injuries in sprinters.
 W
WA quadriceps tendon rupture is a tear of the tendon that runs from the quadriceps muscle to the top of the knee cap.
 W
WA separated shoulder, also known as acromioclavicular joint injury, is a common injury to the acromioclavicular joint. The AC joint is located at the outer end of the clavicle where it attaches to the acromion of the scapula. Symptoms include non-radiating pain which may make it difficult to move the shoulder. The presence of swelling or bruising and a deformity in the shoulder is also common depending on how severe the dislocation is.
 W
WA shin splint, also known as medial tibial stress syndrome, is pain along the inside edge of the shinbone (tibia) due to inflammation of tissue in the area. Generally this is between the middle of the lower leg to the ankle. The pain may be dull or sharp and is generally brought on by exercise. It generally resolves during periods of rest. Complications may include stress fractures.
 W
WA SLAP tear or SLAP lesion is an injury to the glenoid labrum. SLAP is an acronym for "superior labral tear from anterior to posterior".
 W
WA sprain, also known as a torn ligament, is the stretching or tearing of ligaments within a joint, often caused by trauma abruptly forcing the joint beyond its functional range of motion. Ligaments are tough, inelastic fibers made of collagen that connect two or more bones to a joint and are important for joint stability and proprioception, which is the body's sense of limb position and movement. The majority of sprains are mild, causing minor swelling and bruising that can be resolved with conservative treatment. However, severe sprains involve complete tears, ruptures, or fractures, often leading to joint instability, severe pain, and decreased functional ability. These sprains require surgical fixation, prolonged immobilization, and physical therapy. Sprains can occur at any joint but most commonly occur in the ankle, knee, or wrist. An equivalent injury to a muscle or tendon is known as a strain.
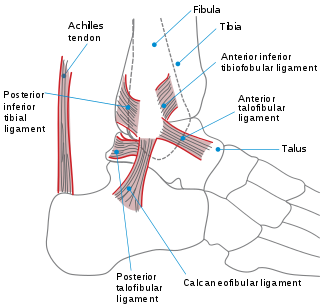 W
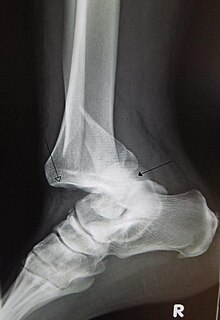
WA sprained ankle, also known as a twisted ankle, or rolled ankle is an injury where sprain occurs on one or more ligaments of the ankle.
 W
WA strain is an acute or chronic soft tissue injury that occurs to a muscle, tendon, or both. The equivalent injury to a ligament is a sprain.
 W
WA tear of a meniscus is a rupturing of one or more of the fibrocartilage strips in the knee called menisci. When doctors and patients refer to "torn cartilage" in the knee, they actually may be referring to an injury to a meniscus at the top of one of the tibiae. Menisci can be torn during innocuous activities such as walking or squatting. They can also be torn by traumatic force encountered in sports or other forms of physical exertion. The traumatic action is most often a twisting movement at the knee while the leg is bent. In older adults, the meniscus can be damaged following prolonged 'wear and tear'. Especially acute injuries can lead to displaced tears which can cause mechanical symptoms such as clicking, catching, or locking during motion of the joint. The joint will be in pain when in use, but when there is no load, the pain goes away.
 W
WGamekeeper's thumb is a type of injury to the ulnar collateral ligament (UCL) of the thumb. The UCL may be merely stretched, or it may be torn from its insertion site into the proximal phalanx of the thumb; in approximately 90% of cases part of the bone is actually avulsed from the joint. This condition is commonly observed among gamekeepers and Scottish fowl hunters, as well as athletes. It also occurs among people who sustain a fall onto an outstretched hand while holding a rod, frequently skiers grasping ski poles.
 W
WThe unhappy triad, also known as a blown knee among other names, is an injury to the anterior cruciate ligament, medial collateral ligament, and meniscus. Analysis during the 1990s indicated that this 'classic' O'Donoghue triad is actually an unusual clinical entity among athletes with knee injuries. Some authors mistakenly believe that in this type of injury, "combined anterior cruciate and medial collateral ligament disruptions that were incurred during athletic endeavors" always present with concomitant medial meniscus injury. However, the 1990 analysis showed that lateral meniscus tears are more common than medial meniscus tears in conjunction with sprains of the ACL.
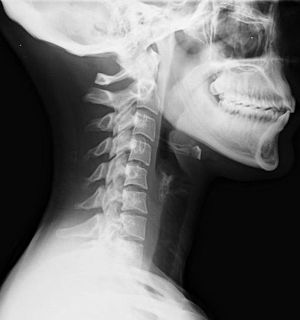 W
WWhiplash is a non-medical term describing a range of injuries to the neck caused by or related to a sudden distortion of the neck associated with extension, although the exact injury mechanisms remain unknown. The term "whiplash" is a colloquialism. "Cervical acceleration–deceleration" (CAD) describes the mechanism of the injury, while the term "whiplash associated disorders" (WAD) describes the injury sequelae and symptoms.