 W
WThe Archaeopsyllini form a flea tribe in the family Pulicidae.
 W
WCeratophyllidae is a family of fleas. Its members are parasites of mainly rodents and birds. It contains two subfamilies, one containing over 40 genera, and the other just three.
 W
WCeratophyllus is a widespread genus of fleas found in temperate climates. Some of its members include the chicken flea, Ceratophyllus gallinae, and the poultry flea, Ceratophyllus niger.
 W
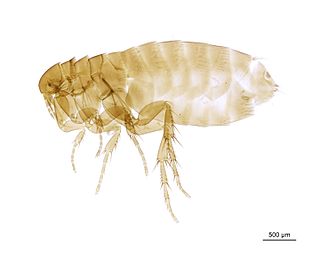
WCeratophyllus borealis , also known as the boreal flea, is an ectoparasite of birds. It is a black species found on ground-nesting birds such as pipits, wheatears and wagtails.
 W
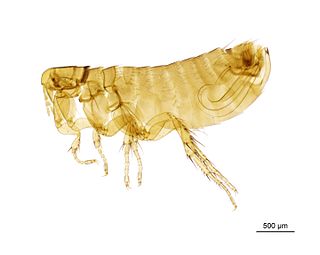
WCeratophyllus chasteli is a species of flea in the family Ceratophyllidae. It was described by Beaucournu, Monnat and Launay in 1982.
 W
WCeratophyllus columbae is a species of flea in the family Ceratophyllidae. It was described by Gervais in 1844.
 W
WCeratophyllus farreni is a species of flea in the family Ceratophyllidae. It was described by Rothschild in 1905.
 W
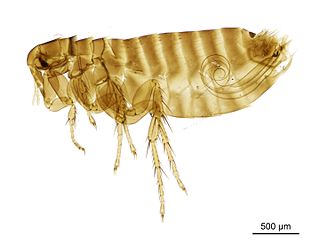
WCeratophyllus fionnus is a species of flea in the family Ceratophyllidae. It was described by Usher in 1968.
 W
WCeratophyllus fringillae is a species of flea in the family Ceratophyllidae. It was described by Francis Walker in 1856.
 W
WThe duck flea, Ceratophyllus garei, is a species of flea in the family Ceratophyllidae. It was described by Rothschild in 1902.
 W
WCeratophyllus hirundinis is a species of flea in the family Ceratophyllidae. It was described by John Curtis in 1826.
 W
WCeratophyllus rossittensis is a species of flea in the family Ceratophyllidae. It was described by Dampf in 1913.
 W
WCeratophyllus rusticus is a species of flea in the family Ceratophyllidae. It was described by Wagner in 1903.
 W
WCeratophyllus styx is a species of flea in the family Ceratophyllidae. It was described by Rothschild in 1900.
 W
WCtenocephalides is a flea genus in the tribe Archaeopsyllini which includes the cat flea, Ctenocephalides felis and the dog flea, C canis. Species and subspecies in the genus infest a wide variety of hosts, including sheep and goats, wild carnivores, hares, hyraxes, ground squirrels and hedgehogs.
 W
WEchidnophaga is a genus of fleas. It includes species which are found in Africa, parts of Asia, southern Europe, and Australia. Fleas in this genus remain attached to their host in a single location for long periods of time, causing swelling and ulceration of tissue. To remain attach for long periods they use specialized mouthparts, which, compared to other fleas, are relatively much longer.
 W
WEchidnophaga gallinacea, commonly known as the hen flea, stickfast flea and sticktight flea, occurs on a wide range of bird and mammal hosts. If uncontrolled it causes anaemia, loss of condition, severe skin irritation and sometimes death.
 W
WThe goblin flea is a critically endangered insect endemic to the Australian state of Victoria. It is host specific, and lives only with the co-endangered Leadbeater's possum. Although it has been suggested as a good candidate species for conservation, there is presently no work directed towards its conservation. The key threat factor driving the decline of the Leadbeater's possum, and by extension the co-endangered goblin flea, is logging in the Mountain Ash forests of the Victorian central highlands. To avoid extinction, a number of conservation steps will need to be taken including amalgamating the goblin flea into the captive breeding program for its host at Healesville Sanctuary
 W
WHectopsyllidae is a small family of fleas, containing only the chigoe flea Tunga penetrans and the genus Hectopsylla. They were formerly known as Tungidae, and by authorities that demote the Pulicoidea to family rank they are treated as subfamily Hectopsyllinae. Only 2 genera with some handfuls of species are placed here nowadays, making further subdivision of the family unnecessary.
 W
WLeptopsyllidae is a family of fleas in the order Siphonaptera. There are at least 30 genera and 250 described species in Leptopsyllidae.
 W
WThe moorhen flea is a flea originating from South America. It is now a globally widespread. It is a large flea, easily identified because the male has two heavy horn-like spines on one of the genital flaps, and the female has a deep "bite" on the seventh sternite.
 W
WThe New Zealand bat flea is a threatened species of flea endemic to New Zealand. The species was first described in 1946 from samples collected near Masterton in 1915, and from chocolate wattled bats on Pelorus Island.
 W
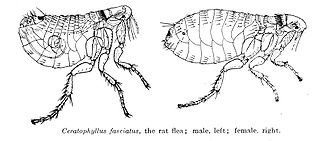
WNosopsyllus fasciatus, the northern rat flea, is a species of flea found on domestic rats and house mice. Northern rat fleas are external parasites, living by hematophagy off the blood of rodents. It is the most widely spread of its genus, having originated in Europe, but has been transported to temperate regions all over the world.
 W
WPulex is a genus of fleas. It comprises seven species. One is the human flea, and five of the others are confined to the Nearctic and Neotropical realms.
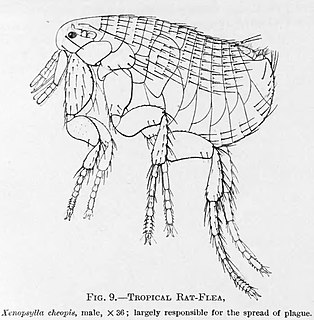 W
WThe Pulicidae are a flea family in the order Siphonaptera. Currently, this family has 181 species in 27 genera. Of these, 16 are known from North America.
 W
WXenopsylla is a flea genus in the family Pulicidae.
 W
WXenopsylla brasiliensis is a species of flea found on rats. It is a vector of bubonic plague, and is found in South America, Africa, and India.
 W
WThe Xenopsyllini form a flea tribe in the family Pulicidae.