 W
WJoinery is a part of woodworking that involves joining together pieces of wood or lumber, to produce more complex items. Some wood joints employ fasteners, bindings, or adhesives, while others use only wood elements. The characteristics of wooden joints - strength, flexibility, toughness, appearance, etc. - derive from the properties of the materials involved and the purpose of the joint. Therefore, different joinery techniques are used to meet differing requirements. For example, the joinery used to construct a house can be different from that used to make puzzle toys, although some concepts overlap. In British English usage it is distinguished from carpentry which relates to structural timber work.
 W
WIn light frame construction, a birdsmouth joint or bird's beak cut is a woodworking joint that is generally used to connect a roof rafter to the top plate of a supporting wall. It is an indentation cut into the rafter which consists of a "seat cut" and a "heel cut" or "plumb cut", forming a shape resembling a bird's mouth. The indentation should not extend unsupported on the interior in order to maintain the structural integrity of the rafter because the unsupported section can split along the grain of the wood. The joint is generally fastened with nails by toenailing the rafter from the side into the top plate below.
 W
WA biscuit joiner or biscuit jointer is a woodworking tool used to join two pieces of wood together. A biscuit joiner uses a small circular saw blade to cut a crescent-shaped hole in the opposite edges of two pieces of wood or wood composite panels. An oval-shaped, highly dried and compressed wooden biscuit is covered with glue, or glue is applied in the slot. The biscuit is immediately placed in the slot, and the two boards are clamped together. The wet glue expands the biscuit, further improving the bond.
 W
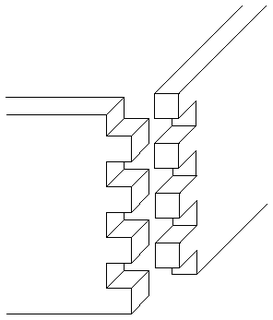
WA box joint, is a woodworking joint made by cutting a set of complementary, interlocking profiles in two pieces of wood, which are then joined (usually) at right angles, usually glued. The glued box joint has a high glued surface area resulting in a strong bond, on a similar principle to a finger joint. Box joints are used for corners of boxes or box-like constructions, hence the name. The joint does not have the same interlocking properties as a dovetail joint, but is much simpler to make, and can be mass-produced fairly easily.
 W
WA bridle joint is a woodworking joint, similar to a mortise and tenon, in that a tenon is cut on the end of one member and a mortise is cut into the other to accept it. The distinguishing feature is that the tenon and the mortise are cut to the full width of the tenon member.
 W
WA butt joint is a technique in which two pieces of material are joined by simply placing their ends together without any special shaping. The name 'butt joint' comes from the way the material is joined together. The butt joint is the simplest joint to make since it merely involves cutting the wood to the appropriate length and butting them together. It is also the weakest because unless some form of reinforcement is used it relies upon glue alone to hold it together. Because the orientation of the wood usually presents only one end to a long grain gluing surface, the resulting joint is inherently weak.
 W
WA butterfly joint, also called a bow tie, dovetail key, Dutchman joint, or Nakashima joint, is a type of joint or inlay used to hold two or more pieces of woods together. These types of joints are mainly used for aesthetics. But these types of joints can be used to reinforce cracks in pieces of wood, doors, picture frames, or drawers.
 W
WCoping or scribing is the woodworking technique of shaping the end of a moulding or frame component to neatly fit the contours of an abutting member. Joining tubular members in metalworking is also referred to as a cope, or sometimes a "fish mouth joint" or saddle joint.
 W
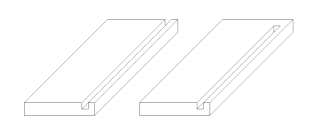
WA dado, housing (UK) or trench (Europe) is a slot or trench cut into the surface of a piece of machinable material, usually wood. When viewed in cross-section, a dado has three sides. A dado is cut across, or perpendicular to, the grain and is thus differentiated from a groove which is cut with, or parallel to the grain. Dados are often used to affix shelves to cabinetry carcasses. Similar to the dado, see rabbet (rebate).
 W
WThe Domino is a loose mortise and tenon joining tool manufactured by the German company Festool.
 W
W W
WA dovetail joint or simply dovetail is a joinery technique most commonly used in woodworking joinery (carpentry), including furniture, cabinets, log buildings, and traditional timber framing. Noted for its resistance to being pulled apart, the dovetail joint is commonly used to join the sides of a drawer to the front. A series of 'pins' cut to extend from the end of one board interlock with a series of 'tails' cut into the end of another board. The pins and tails have a trapezoidal shape. Once glued, a wooden dovetail joint requires no mechanical fasteners.
 W
WA dowel is a cylindrical rod, usually made from wood, plastic, or metal. In its original manufactured form, a dowel is called a dowel rod. Dowel rods are often cut into short lengths called dowel pins. Dowels are commonly used as structural reinforcements in cabinet making and in numerous other applications, including:Furniture shelf supports Moveable game pieces Hangers for items such as clothing, key rings, and tools Wheel axles in toys Detents in gymnastics grips Supports for tiered wedding cakes
 W
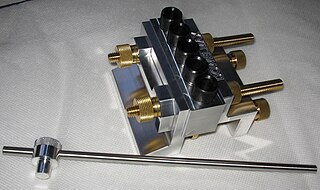
WThe Dowelmax is a loose tenon dowelling jig manufactured by the O.M.S. Tool company in Canada. The manufacturer claims that the small manufacturing tolerances of 0.026 millimetres (0.0010 in) for the aluminium, brass and steel components of the jig ensure accuracy and repeatability. The precision manufacturing adds to the unit's cost, which is higher than other dowelling jigs.
 W
WA face frame in cabinet making is the frame fixed to the front of a cabinet carcass which obscures the edges of the carcass and provides the fixing point for doors and other external hardware. A face frame provides strength to the front of a cabinet and is also considered a visual feature of particular styles of furniture.
 W
WA finger joint, also known as a comb joint, is a woodworking joint made by cutting a set of complementary, interlocking profiles in two pieces of wood, which are then glued. The cross-section of the joint resembles the interlocking of fingers between two hands, hence the name "finger joint". The sides of each profile increases the surface area for gluing, resulting in a strong bond, stronger than a butt joint but not very visually appealing. Finger joints are regularly confused with box joints, which are used for corners of boxes or box-like constructions.
 W
WIn joinery, a groove is a slot or trench cut into a member which runs parallel to the grain. A groove is thus differentiated from a dado, which runs across the grain.
 W
WA halved joint is a woodworking joint in which the two members are joined by removing material from each at the point of intersection so that they overlap. The halved joint is differentiated from the lap joint in that the members are joined on edge, rather than on flat.
 W
WA joiner is an artisan and tradesperson who builds things by joining pieces of wood, particularly lighter and more ornamental work than that done by a carpenter, including furniture and the "fittings" of a house, ship, etc. Joiners may work in a workshop, because the formation of various joints is made easier by the use of non-portable, powered machinery, or on job site. A joiner usually produces items such as interior and exterior doors, windows, stairs, tables, bookshelves, cabinets, furniture, etc. In shipbuilding a marine joiner may work with materials other than wood such as linoleum, fiberglass, hardware, and gaskets.
 W
WA lap joint or overlap joint is a joint in which the members overlap. Lap joints can be used to join wood, plastic, or metal. A lap joint can be used in woodworking for joining wood together.
 W
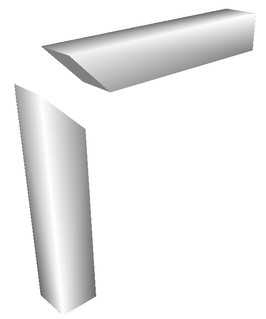
WA mitre joint is a joint made by cutting each of two parts to be joined, across the main surface, usually at a 45° angle, to form a corner, usually a 90° angle. It is called beveling when the angled cut is done on the side, although the resulting joint is still a mitre joint.
 W
WA mortise and tenon joint connects two pieces of wood or of material. Woodworkers around the world have used it for thousands of years to join pieces of wood, mainly when the adjoining pieces connect at right angles.
 W
WNuki is a Japanese style of carpentry joint connection. Nuki joints are common in Japanese and oriental carpentry, and comprise one of the simplest structural connectors. They are similar to mortise and tenon joints, and have been used traditionally in historic buildings, such as Shinto shrines and Buddhist temples, and also in modern domestic houses. The basic principle involves penetrating one element through another ; in Japan and other Asian countries this method is used to connect wooden posts and beams.
 W
WPocket-hole joinery, or pocket-screw joinery, involves drilling a hole at an angle — usually 15 degrees — into one work piece, and then joining it to a second work piece with a self-tapping screw.
 W
WA scarf joint is a method of joining two members end to end in woodworking or metalworking. The scarf joint is used when the material being joined is not available in the length required. It is an alternative to other joints such as the butt joint and the splice joint and is often favored over these in joinery because it yields a barely visible glue line.
 W
WA slab hut is a kind of dwelling or shed made from slabs of split or sawn timber. It was a common form of construction used by settlers in Australia and New Zealand during their nations' colonial periods.
 W
WStitch and glue is a simple boat building method which uses plywood panels stitched together, usually with copper wire, and glued together with epoxy resin. This type of construction can eliminate much of the need for frames or ribs. Plywood panels are cut to shape and stitched together to form an accurate hull shape without the need for forms or special tools. This technique is also called "tack and tape", or "stitch and tape". Seams are reinforced with fiberglass tape and thickened epoxy.
 W
WTongue and groove is a method of fitting similar objects together, edge to edge, used mainly with wood, in flooring, parquetry, panelling, and similar constructions. Tongue and groove joints allow two flat pieces to be joined strongly together to make a single flat surface. Before plywood became common, tongue and groove boards were also used for sheathing buildings and to construct concrete formwork.