 W
WAgalma is a genus of siphonophores in the family Agalmatidae. Siphonophores are colonial hydrozoans that feed on zooplankton.
 W
WAgalma elegans is a species of siphonophores in the family Agalmatidae. It has been found in a wide variety of locations, including between the Reloncavi Fjord and the Boca del Guafo Passage, in the Chiloe Inland Sea (CIS), Chile.
 W
WAgalmatidae, or Agalmidae, is a family of siphonophores.
 W
WAmyostaurida is a suborder of jellyfishes. It contains two families.
 W
WApolemia is a genus of siphonophores. It is the only genus in the monotypic family Apolemiidae.
 W
WBathyphysa is a genus of siphonophores with 3 species in it.
 W
WBivalvulida is an order of myxosporean parasites which contains a number of species which cause economically significant losses to aquaculture and fisheries, such as Myxobolus cerebralis and Ceratomyxa shasta. The Myxosporean stages of members of the bivalvulida are characterised by their two spore valves, which meet in a "suture line" which encircles the spore. They usually contain two polar capsules, but species have been reported which contain either one or four.
 W
WCallogorgia is a genus of soft corals in the family Primnoidae.
 W
WCavernularia is a genus of marine cnidarians in the family Veretillidae.
 W
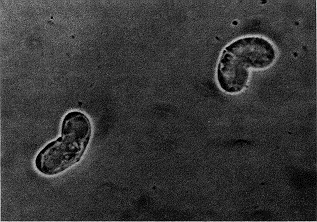
WCeratomyxidae is a family of myxozoans.
 W
WClavulariidae is a family of soft corals in the suborder Stolonifera. Colonies in this family consist of separate retractable polyps growing from a horizontal, encrusting stolon or basal membrane. The tissues are stiffened by sclerites.
 W
WCryptolaria is a genus of hydrozoans in the family Zygophylacidae.
 W
WEudendriidae is a taxonomic family of hydroids (Hydrozoa). The family contains around 85 species.
 W
WEudendrium is a large genus of hydroids (Hydrozoa), one of two in the family Eudendriidae. These animals are marine cnidarias in the family Eudendriidae.
 W
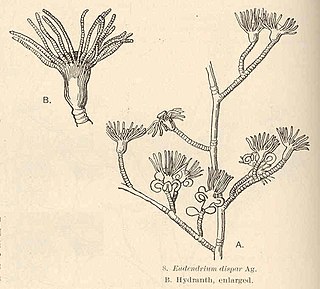
WEudendrium dispar is a marine species of cnidaria, a hydroid (Hydrozoa) in the family Eudendriidae.
 W
WForskalia is a genus of siphonophores. It is the only genus in the monotypic family Forskaliidae.
 W
WThe gastrovascular cavity is the primary organ of digestion and circulation in two major animal phyla: the Cnidaria and Platyhelminthes (flatworms). The cavity may be extensively branched into a system of canals. In cnidarians, the gastrovascular system is also known as the coelenteron, and is commonly known as a "blind gut" or "blind sac", since food enters and waste exits through the same orifice.
 W
WGeryonia is a monotypic genus of hydrozoans in the family Geryoniidae. It is represented by the species Geryonia proboscidalis which occurs in the Mediterranean and subtropical seas. In the Mediterranean the species is more numerous and the polyps are larger than in other parts of the world. The diameter of a polyp can be up to 80 mm, while in Florida and the Bahamas it is rare to find specimens of more than 50 mm in diameter.
 W
WHaliclystus stejnegeri is a species of stalked jellyfish in the family Haliclystidae.
 W
WMarrus is a genus of siphonophores. Species include:Marrus antarcticus Totton, 1954 Marrus claudanielis Dunn, Pugh & Haddock, 2005 Marrus orthocanna Kramp, 1942 Marrus orthocannoides Totton, 1954
 W
WMetridium dianthus is a species of sea anemone in the family Metridiidae. It is found in the northern Atlantic Ocean and in the northeast Pacific Ocean. There is also a record from South Africa, possible resulting from an introduction.
 W
WMonobrachium is a genus of hydroids. These marine cnidarians form the only genus of the monotypic family Monobrachiidae.
 W
WMyostaurida is a suborder of jellyfishes. It contains four families.
 W
WMyxobolidae is a family of myxosporean parasites which typically infect freshwater fishes, and includes the economically significant species, Myxobolus cerebralis. They have been shown to have a complex life cycle, involving an alternate stage in an invertebrate, typically an annelid or polychaete worm.
 W
WMyxobolus is a genus of myxozoa that includes important parasites of fish like Myxobolus cerebralis. The genus is polyphyletic, with members scattered throughout the myxozoa. Some stages of Myxobolus species were previously thought to be different organisms entirely, but are now united in this group.
 W
WMyxobolus spinacurvatura is a species of Myxozoa in the family Myxobolidae, that inhabits the Mediterranean Sea.
 W
WPrimnoidae is a family of soft corals.
 W
WStaurozoa is a class of Medusozoa, jellyfishes and hydrozoans. It has one extant order: Stauromedusae. A fossil group called Conulariida has been proposed as a second order, although this is highly speculative. The extinct order is largely unknown and described as a possibly cnidarian clade of marine life with shell-like structures, the Conulariida. Staurozoans are small animals that live in marine environments, usually attached to seaweeds, rocks, or gravel. They have a large antitropical distribution, a majority found in boreal or polar, near-shore, and shallow waters. Few staurozoans are found in warmer tropical and subtropical water environments of the Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific Ocean basins, but most are known from the Northern Hemisphere. Over the years their number of species has increased, thus right now it is said to have an estimated 50 species.
 W
WVeretillidae is a family of sea pens.